Sping 原始碼深度解析——容器的功能擴充套件 【學習筆記】
我為什麼 看的不夠遠,因為高度不夠!
學習和整理總結Spring容器的功能擴充套件,本文為學習筆記,其中有一些內容是自己的思考總結!
一、兩種Spring中bean載入的方式
第一種
# 第一種使用 BeanFactory 以及它預設的實現類 XmlBeanFactory
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("beanFactoryTest.xml"));
# 注:XmlBeanFactory這種方式已經在最新的Spring5中已經被標記為@Deprecated!第二種
# 第二種使用 ApplicationContext 以及它的實現類 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext 都是用於載入Bean的,對比之下 ApplicationContext 包含了BeanFactory 所有的功能,並提供了更多的擴充套件。
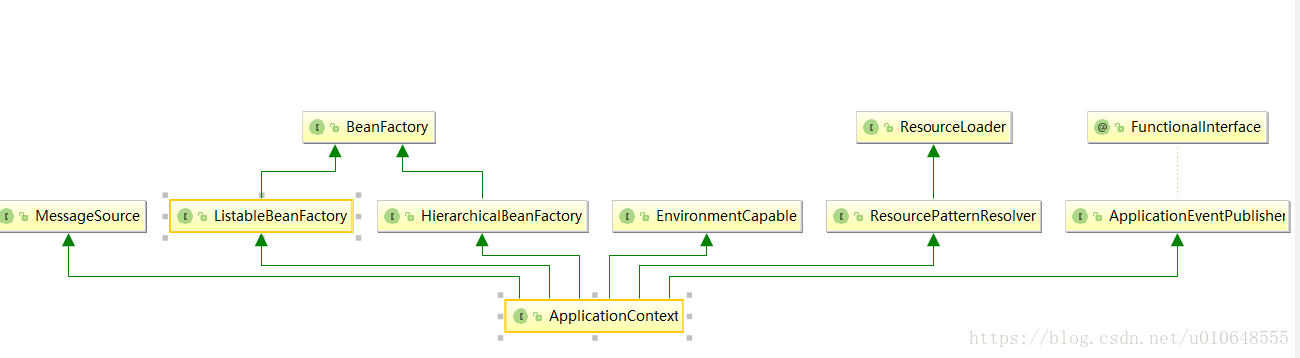
下面是ApplicationContext的類圖:
從類圖上看, ApplicationContext是BeanFactory 的子類!子類繼承了父類所有的功能,並在父類的基礎上添加了一些功能,在大多數時候,ApplicationContext
二、從 new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“beanFactoryTest.xml”)開啟原始碼之旅
1、建構函式
/**
* Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, loading the definitions
* from the given XML file and automatically refreshing the context.
* 建立一個新的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,載入定義
* 從給定的XML檔案中自動重新整理上下文。
* @param 2 具體的setConfigLocations 和 refresh
2.1 設定配置路徑
/**
* Set the config locations for this application context.
* 設定此應用程式上下文的配置位置。
* <p>If not set, the implementation may use a default as appropriate.
* 如果沒有設定,實現可以適當地使用預設值。
*/
public void setConfigLocations(@Nullable String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
// 解析給定路徑
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
此函式主要是用於解析給定的路徑陣列,如果路徑中包含特殊字元,如${bar},那麼resolvePath會搜尋匹配的系統變數並替換。
2.2 擴充套件功能
設定完路徑後,就可以根據路徑做配置檔案的解析以及各種功能的實現了。refresh中包含了ApplicationContext中提供的全部功能。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
// `startupShutdownMonitor` 同步監視器用於“重新整理”和“銷燬”。
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 準備重新整理的上下文環境
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 初始話beanFactory,並及逆行XML檔案讀取
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 對BeanFactory 進行各種功能填充
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 子類覆蓋方法的額外處理,預設實現為空
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 啟用各種BeanFactory處理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 註冊攔截Bean的建立的處理器,這裡只是註冊,真正呼叫是在getBean時候
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 為上下問初始化message源,既不同語言的訊息體,國際化處理
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化應用訊息廣播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 留給子類初始化其他的Bean,預設實現為空
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 在所有註冊的Bean中查詢Listener bean,註冊到訊息廣播器中
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 初始化剩下的單例項,非惰性的
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 最後一步,完成重新整理過程,通知生命週期處理器initLifecycleProcessor重新整理過程,同時發出
// ContextRefreshedEvent通知別人
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
// 銷燬已經建立的單例,以避免懸空資源。
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
//重置Spring核心中的常見內省快取,因為我們
//可能再也不需要單例bean的元資料了…
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}上面這一段程式碼,真的是值得學習,每個功能抽離出一個單獨的方法實現,思路清晰,讓看程式碼的人也神清氣爽! 很多時候在開發專案中,一個業務功能的實現成百上千行,看著就頭痛。
下面對refresh()中的過程進行簡單概括:
- 初始化的準備工作,例如對系統屬性或者環境變數進行準備及驗證。
- 初始化
BeanFactory,並對XML檔案讀取。 - 對
BeanFactory進行各種功能填充。如@Qualifier和@Autowired這兩個註解正是在這一步驟增加的支援。 - 子類覆蓋方法做的額外處理。(這就是Spring強大的地方,除了功能強大,可擴充套件性也很強大。)
- 啟用各種
BeanFactory處理器。 - 註冊攔截bean建立的bean處理器
- 為上下文初始化message源
- 初始化應用訊息廣播器
- 留著子類初始化其他的bean
- 在所有註冊的bean中查詢listener bean
- 初始化剩下的單例項
- 完成重新整理過程。
2.2.1 環境準備 prepareRefresh()
初始化的準備工作,例如對系統屬性或者環境變數進行準備及驗證。
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// startupDate 當此上下文啟動時的 系統時間(以毫秒為單位)
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
// closed 標誌,指示此上下文是否已經關閉
this.closed.set(false);
// active 標誌,指示此上下文當前是否活動。
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Refreshing " + this);
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment
// 在上下文環境中初始化任何佔位符屬性源,預設實現為空,留給子類覆蓋(實現個性化的需求)
initPropertySources();
// 驗證需要的屬性檔案是否都已經放入環境中
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
//允許收集早期應用程式事件,
//一旦有了廣播機,就可以釋出……
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
準備這個上下文重新整理,設定它的啟動日期和主動標誌,以及執行任何屬性源的初始化。
2.2.2 載入BeanFactory的 obtainFreshBeanFactory()
obtainFreshBeanFactory 方法代表獲取 BeanFactory !上面類圖也可以看出ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子類,經歷過這個方法後,ApplicationContext 就擁有了 BeanFactory全部功能。
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
// 初始化BeanFactory並進行XML的讀取,並將得到的BeanFactory記錄到當前的實體屬性中
refreshBeanFactory();
// 返回當前實體的BeanFactory屬性
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
//# 核心方法為 refreshBeanFactory()
//# AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.refreshBeanFactory()
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// 建立了 DefaultListableBeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
// 為了序列號指定ID,
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
// 定製BeanFactory,設定相關屬性
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 初始化 DocumentReader ,並進行XML檔案讀取及解析
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
簡述上述過程:
1. 建立 DefaultListableBeanFactory,這個是BeanFactory的子類,它提供了XmlBeanDefinitionReader 型別的reader屬性,也就是說 DefaultListableBeanFactory 是容器的基礎。
2. 指定序列號ID。
3. 定製BeanFactory。
4. 載入BeanDefinition。
5. 使用全域性變數記錄BeanFactory類的例項。
1、 定製BeanFactory,customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory)
從這裡開始對BeanFactory的擴充套件,在基本容器的基礎上,增加了是否允許覆蓋,是否允許擴充套件的設定。並提供了註解 @Qualifier 和 @Autowired的支援。
protected void customizeBeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 如果屬性 allowBeanDefinitionOverriding 不為空,設定給 beanFactory 物件相應屬性。
// 此屬性含義:是否允許覆蓋同名稱的不同定義的物件
if (this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding != null) {
beanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
// 如果屬性 allowBeanDefinitionOverriding 不為空,設定給 beanFactory 物件相應屬性。
// 此屬性含義:是否允許bean之間存在迴圈依賴
if (this.allowCircularReferences != null) {
beanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
}
}
這裡允許覆蓋和允許依賴的設定只是判斷了是否為空,其中setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()和 setAllowCircularReferences() 預設為 true! 子類可以通過覆蓋方法修改預設值:
如下:
public class MyClassPathXmlApplicationContext extends ClassPathXmlApplicationContext {
@Override
protected void customizeBeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(false);
super.setAllowCircularReferences(false);
super.customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
}2、載入BeanDefintion ,loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory)
/**
* Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
* 載入 bean的定義 通過 XmlBeanDefinitionReader
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #initBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
*/
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
// 為指定的BeanFactory 建立 一個 XmlBeanDefinitionReader
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
// 對 beanDefinitionReader 進行 環境變數設定
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
// 對 beanDefinitionReader 進行設定,可以覆蓋
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
// 通過指定的 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 載入 bean定義
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
// 載入bean的定義
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}載入beanDefinition的核心就是建立一個XmlBeanDefinitionReader 然後對配置檔案的載入以及註冊。
2.2.3 對BeanFactory 進行各種功能填充 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)
在進入prepareBeanFactory前,Spring已經完成了對配置的解析,ApplicationContext的擴充套件從這裡也真正的展開了。
/**
* Configure the factory's standard context characteristics,
* such as the context's ClassLoader and post-processors.
* 配置工廠的標準上下文特性,例如上下文的類載入器和後處理器。
* @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to configure
*/
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
// 設定 beanFactory 的 ClassLoader 為當前 context 的ClassLoader。
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
// 設定 beanFactory 的 表示式語言處理器
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
// 為beanFacotry 增加一個預設的 PropertyEditor,主要是對bean的屬性等設定管理的一個工具
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
// 使用上下文回撥配置bean工廠。增加了 BeanPostProcessor
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
// 設定 了幾個 忽略自動裝配的介面
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
// 在普通工廠中,BeanFactory介面未註冊為可解析型別。
// MessageSource註冊(用於自動連線)為bean。
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
// 註冊早期後處理器,以檢測內部bean作為應用程式監聽器。
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
// 檢測一個LoadTimeWeaver並準備編織,如果找到的話。增加對 AspectJ的支援
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
// 為型別匹配設定臨時類載入器。
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
// 添的預設系統環境bean。
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}綜合上面的程式碼,上面的函式主要進行了幾個方面的擴充套件:
- 增加了SPEL語言的支援。支援 #{…}方式呼叫相關屬性。
- 增加了對屬性編輯器的支援。
- 設定了一些內建類資訊的注入。
- 設定了依賴功能可以忽略的介面。
- 註冊一些固定依賴的屬性。
- 增加了 AspectJ的支援。
- 新增預設系統環境bean。如屬性註冊和單例項模式註冊。
1.增加SPEL語言的支援
SPEL:Spring 表示式語法,Spring Expression Language。能夠在執行時候構建複雜表示式、存取物件屬性,物件方法呼叫等。Spel是單獨的模組,依賴Spring的core,解析過程是在Spring的expression包內。
簡單舉例:
<bean id="testSpel" value="org.xxx.xxx" />
<bean>
<property name="csdn" value="#{testSpel}">
</bean>
相當於:
<bean id="testSpel" value="org.xxx.xxx" />
<bean>
<property name="csdn" ref="testSpel">
</bean>
2.增加對屬性編輯器
通過原始碼的檢視,這裡面無非就是註冊一些常用的屬性編輯器,並且能夠自定義一些屬性編輯器。
演示程式碼:
public class UserManager {
private Date dateValue;
public Date getDateValue() {
return dateValue;
}
public void setDateValue(Date dateValue) {
this.dateValue = dateValue;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserManager{" + "dateValue=" + dateValue + '}';
}
}
<bean id="userManager" class="org.learn.beans.customerPropertyEditor.UserManager">
<property name="dateValue">
<value>2018-08-01</value>
</property>
</bean>
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beanFactoryTest.xml");
UserManager userManager = (UserManager) context.getBean("userManager");
System.out.println(userManager);
}
// 報錯
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.ConversionNotSupportedException: Failed to convert property value of type 'java.lang.String' to required type 'java.util.Date' for property 'dateValue';
nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: Cannot convert value of type
'java.lang.String' to required type 'java.util.Date' for property 'dateValue': no matching editors or conversion strategy found
解決方法1:
// 繼承 PropertyEditorSupport ,重寫 setAsText方法
public class DatePropertyEditor extends PropertyEditorSupport {
private String format = "yyyy-MM-dd";
public void setFormat(String format) {
this.format = format;
}
@Override
public void setAsText(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
System.out.println("text : " + text);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(format);
try {
Date d = sdf.parse(text);
this.setValue(d);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.CustomEditorConfigurer">
<property name="customEditors">
<map>
<entry key="java.util.Date"
value="org.learn.beans.customerPropertyEditor.DatePropertyEditor" />
</map>
</property>
</bean>
// 注意:上面這個是SPring 4之後的配置,Spring4之前配置如下,不同版本使用不同配置,否則允許會報錯!
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.CustomEditorConfigurer">
<property name="customEditors">
<map>
<entry key="java.util.Date">
<bean class="org.learn.beans.customerPropertyEditor.DatePropertyEditor">
<property name="format" value="yyyy-MM-dd"/>
</bean>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
解決方法2:
實現Spring自帶的屬性編輯器 CustomerDateEditor
public class MyDatePropertyEditorRegistrar implements PropertyEditorRegistrar {
public void registerCustomEditors(PropertyEditorRegistry registry) {
registry.registerCustomEditor(Date.class,
new CustomDateEditor(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"),true));
}
}
//配置
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.CustomEditorConfigurer">
<property name="propertyEditorRegistrars">
<list>
<bean class="org.learn.beans.customerPropertyEditor.MyDatePropertyEditorRegistrar"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>3.新增 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 處理器
這一步主要的目的是註冊一個 BeanPostProcessor,真正的邏輯還在 new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor中。
class ApplicationContextAwareProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor 。在例項化Bean的時候,也就是Spring啟用bean的 init-method的前後,會有BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization 和 postProcessAfterInitialization方法。
所以在 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 處理器中我們也關注這兩個方法。
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
AccessControlContext acc = null;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null &&
(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)) {
acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext();
}
if (acc != null) {
// 使用了Aware介面的bean在被初始化後,可以獲得一些對應的資源。
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return null;
}, acc);
}
else {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
}
return bean;
}
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
/**
* 這個方法沒有做什麼邏輯處理
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}4.設定忽略依賴
因為在上面postProcess操作中,實現了Awar介面的bean已經不是普通的bean了,如ResourceLoaderAware等,那麼需要在SPring做bean的依賴注入的時候忽略它們。
5.註冊依賴
2.2.4 對BeanFactory 的後處理
BeanFactory作為Spring中容器功能的基礎,用於存放所有已經載入的bean,為了保證程式的高可擴充套件性,Spring針對BeanFactory做了大量的擴充套件,如PostProcessor等。
2.2.5 啟用註冊的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
下面是Spring 5 中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor原始碼,函式式介面
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* 在標準初始化之後修改應用程式上下文的內部bean工廠。
* 將載入所有bean定義,但尚未例項化任何bean。 這允許覆蓋或新增屬性,甚至是初始化bean。
*
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
BeanFactoryPostProcessor和 BeanPostProcessor可以對bean的定義(配置元資料)進行處理,也就是說,Spring Ioc 容器允許 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 在容器實際 例項化任何 其他的bean 之前 讀取配置元資料,並有可能修改它。
需要強調的一點,就是如果你想改變實際bean的例項,那麼你最好是用 BeanPostProcessor ! 因為 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的作用域範圍是容器級的,只和你所使用的容器相關。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor不會對另一個容器的bean進行後置處理。即使這兩個容器都是在同一個層次上,Spring中存在對於BeanFactoryPostProcessor的典型應用。比如 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.
(1) BeanFactoryPostProcessor的典型應用PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
在spring配置的xml中,如配置datasource的時候可能會配置如下:
<property name="driverClassName" value="${DBCP.DataSource.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${DBCP.DataSource.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${DBCP.DataSource.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${DBCP.DataSource.dbpassword}" />這個配置裡面使用了變數引用:${DBCP.DataSource.url}等,這就是spring分散配置,可以在另外的配置檔案中為${DBCP.DataSource.url}等指定值。比如我在db.properties中指定:
DBCP.DataSource.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.DriverSpring 框架是怎麼知道存在這樣的配置檔案呢?
這就要靠 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 這個類的bean。
<bean id="dbProperties"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location">
<value>classpath:db.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>BeanFacotryPostProcessor介面間接繼承了BeanFacotryPostProcessor介面,這是一個特別的介面,當Spring載入任何實現了這個介面的bean的配置時,都會在bean工廠載入所有bean的配置之後執行postProcessBeanFactroy方法。
在BeanFacotryPostProcessor類中,實現了postProcessBeanFactory方法。如下:
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
try {
// 合併屬性
Properties mergedProps = mergeProperties();
// Convert the merged properties, if necessary.
// 如果需要,轉換合併的屬性
convertProperties(mergedProps);
// Let the subclass process the properties.
// 讓子類處理屬性。空實現
processProperties(beanFactory, mergedProps);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
}
通過 mergeProperties 、 convertProperties 、 processProperties 這三個方法,分別得到配置,將得到的配置轉換為合適的型別,最後將配置內容告訴 BeanFactory。
(2) 使用自定義的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
實現該介面,可以在spring的bean建立之前,修改bean的定義屬性。也就是說,Spring允許BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器例項化任何其它bean之前讀取配置元資料,並可以根據需要進行修改,例如可以把bean的scope從singleton改為prototype,也可以把property的值給修改掉。可以同時配置多個BeanFactoryPostProcessor,並通過設定’order’屬性來控制各個BeanFactoryPostProcessor的執行次序。
注意:BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在spring容器載入了bean的定義檔案之後,在bean例項化之前執行的。介面方法的入參是ConfigurrableListableBeanFactory,使用該引數,可以獲取到相關bean的定義資訊。
// 測試的類
public class MyTestBean {
private String name;
private String desc;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyTestBean{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", desc='" + desc + '\'' + '}';
}
}
// 自定義實現 postProcessBeanFactory
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor{
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("呼叫MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory");
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("myTestBean");
System.out.println("屬性值============" + bd.getPropertyValues().toString());
MutablePropertyValues pv = bd.getPropertyValues();
if (pv.contains("desc")) {
pv.addPropertyValue("desc", "best!");
}
}
}
// xml配置
<bean id="myTestBean" class="org.learn.beans.MyTestBean">
<property name="name" value="spring"/>
<property name="desc" value="good"/>
</bean>
<bean id="myBeanFactoryPostProcessor" class="org.learn.beans.customerPropertyEditor.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor" />
// 執行結果
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beanFactoryTest.xml");
MyTestBean testBean = (MyTestBean) context.getBean("myTestBean");
System.out.println(testBean);
呼叫MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory
屬性值============PropertyValues: length=2; bean property 'name'; bean property 'desc'
MyTestBean{name='spring', desc='best!'}
2.2.6 註冊的BeanPostProcessor
Spring中大部分功能都是通過後處理器的方式進行擴充套件的,這是Spring框架的一個特性。這裡探索一個BeanPostProcessor的註冊,真正的呼叫是在bean例項化階段進行的。在Spring的BeanFactory中並沒有自動註冊後處理器,所以在呼叫的時候沒有註冊是不能使用的。
對比分析總結 BeanFactoryPostProcessor和 BeanPostProcessor:
BeanFactoryPostProcessor在bean例項化之前執行,之後例項化bean(呼叫建構函式,並呼叫set方法注入屬性值),然後在呼叫BeanPostProcessor的兩個初始化方法前後!
2.2.7 初始化訊息資源- initMessageSource();
Spring國際化的相關功能,讀取並將自定義的資原始檔配置記錄到容器中,在獲取資原始檔的時候直接使用。
2.2.8 初始化ApplicationEventMulticaster - initApplicationEventMulticaster
在講解Spring的事件傳播之前,先了解一下事件監聽的簡單用法。
1.定義監聽事件
public class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private String msg;
/**
* Create a new ApplicationEvent.
* @param source the object on which the event initially occurred (never {@code null})
*/
public MyEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
public MyEvent(Object source, String msg) {
super(source);
this.msg = msg;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}2.定義監聽器
public class MyListener implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
event.show();
}
}3.配置監聽器
<bean id="myListener" class="org.learn.beans.event.MyListener"/>4.測試
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beanFactoryTest.xml");
MyEvent event = new MyEvent("hello", "world");
context.publishEvent(event);當程式執行Spring會將發出的Event事件轉給我們自定義的Listener進行處理。這裡其實是用了 設計模式中 觀察者模式。
2.2.9註冊監聽器 registerListeners();
在所有註冊的Bean中查詢Listener bean,註冊到訊息廣播器中。
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
// 首先註冊靜態指定的監聽器。
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
// 擁有了一個多播器,釋出早期應用程式事件……
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}2.2.10 初始化非延遲載入單例 - finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
完成了BeanFactory的初始化工作,其中包括ConversionService的設定,配置凍結以及非延遲載入的bean的初始化工作。
/**
* Finish the initialization of this context's bean factory,
* initializing all remaining singleton beans.
* 完成此上下文的bean工廠的初始化,
* 初始化所有剩餘的單例bean
*/
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
// 初始化此上下文的轉換服務。
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
be