CSS 樣式書寫規範(推薦)+CSS佈局例項(詳解)
CSS 樣式書寫規範(推薦)
編碼設定
採用 UTF-8 編碼,在 CSS 程式碼頭部使用:
@charset "utf-8";
注意,必須要定義在 CSS 檔案所有字元的前面(包括編碼註釋),@charset 才會生效。
例如,下面的例子都會使得 @charset 失效:
/* 字元編碼 */
@charset "utf-8";
html,
body {
height: 100%;
}
@charset "utf-8";
名稱空間規範
•佈局:以 g 為名稱空間,例如:.g-wrap 、.g-header、.g-content。
•狀態:以 s 為名稱空間,表示動態的、具有互動性質的狀態,例如:.s-current、s-selected。
•工具:以 u 為名稱空間,表示不耦合業務邏輯的、可複用的的工具,例如:u-clearfix、u-ellipsis。
•元件:以 m 為名稱空間,表示可複用、移植的元件模組,例如:m-slider、m-dropMenu。
•鉤子:以 j 為名稱空間,表示特定給 JavaScript 呼叫的類名,例如:j-request、j-open。
名稱空間思想
沒有選擇 BEM 這種命名過於嚴苛及樣式名過長過醜的規則,採取了一種比較折中的方案。
不建議使用下劃線 _ 進行連線
•節省操作,輸入的時候少按一個 shift 鍵
•能良好區分 JavaScript 變數命名
字元小寫
定義的選擇器名,屬性及屬性值的書寫皆為小寫。
選擇器
當一個規則包含多個選擇器時,每個選擇器獨佔一行。
、+、~、> 選擇器的兩邊各保留一個空格。
.g-header > .g-header-des,
.g-content ~ .g-footer {
}命名短且語義化良好
對於選擇器的命名,儘量簡潔且具有語義化,不應該出現 g-abc 這種語義模糊的命名。
規則宣告塊
•當規則宣告塊中有多個樣式宣告時,每條樣式獨佔一行。
•在規則宣告塊的左大括號 { 前加一個空格。
•在樣式屬性的冒號 : 後面加上一個空格,前面不加空格。
•在每條樣式後面都以分號 ; 結尾。
•規則宣告塊的右大括號 } 獨佔一行。
•每個規則宣告間用空行分隔。
•所有最外層引號使用單引號 ‘ 。
•當一個屬性有多個屬性值時,以逗號 , 分隔屬性值,每個逗號後新增一個空格,當單個屬性值過長時,每個屬性值獨佔一行。
完整示例如下:
.g-footer,
.g-header {
position: relative;
}
.g-content {
background:
linear-gradient(135deg, deeppink 25%, transparent 25%) -50px 0,
linear-gradient(225deg, deeppink 25%, transparent 25%) -50px 0,
linear-gradient(315deg, deeppink 25%, transparent 25%),
linear-gradient(45deg, deeppink 25%, transparent 25%);
}
.g-content::before {
content: '';
}
數值與單位
•當屬性值或顏色引數為 0 – 1 之間的數時,省略小數點前的 0 。color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.5)color: rgba(255, 255, 255, .5);
•當長度值為 0 時省略單位。margin: 0px automargin: 0 auto
•十六進位制的顏色屬性值使用小寫和儘量簡寫。color: #ffcc00color: #fc0
樣式屬性順序
單個樣式規則下的屬性在書寫時,應按功能進行分組,並以 Positioning Model > Box Model > Typographic > Visual 的順序書寫,提高程式碼的可讀性。
•如果包含 content 屬性,應放在最前面;
•Positioning Model 佈局方式、位置,相關屬性包括:position / top / right / bottom / left / z-index / display / float / …
•Box Model 盒模型,相關屬性包括:width / height / padding / margin / border / overflow / …
•Typographic 文字排版,相關屬性包括:font / line-height / text-align / word-wrap / …
•Visual 視覺外觀,相關屬性包括:color / background / list-style / transform / animation / transition / …
Positioning 處在第一位,因為他可以使一個元素脫離正常文字流,並且覆蓋盒模型相關的樣式。盒模型緊跟其後,因為他決定了一個元件的大小和位置。其他屬性只在元件內部起作用或者不會對前面兩種情況的結果產生影響,所以他們排在後面。
合理使用使用引號
在某些樣式中,會出現一些含有空格的關鍵字或者中文關鍵字。
font-family 內使用引號
當字型名字中間有空格,中文名字型及 Unicode 字元編碼表示的中文字型,為了保證相容性,都建議在字型兩端新增單引號或者雙引號:
body {
font-family: 'Microsoft YaHei', '黑體-簡', '\5b8b\4f53';
}
background-image 的 url 內使用引號
如果路徑裡面有空格,舊版 IE 是無法識別的,會導致路徑失效,建議不管是否存在空格,都新增上單引號或者雙引號:
div {
background-image: url('...');
}
避免使用 !important
除去某些極特殊的情況,儘量不要不要使用 !important。
!important 的存在會給後期維護以及多人協作帶來噩夢般的影響。
當存在樣式覆蓋層疊時,如果你發現新定義的一個樣式無法覆蓋一箇舊的樣式,只有加上 !important 才能生效時,是因為你新定義的選擇器的優先順序不夠舊樣式選擇器的優先順序高。所以,合理的書寫新樣式選擇器,是完全可以規避一些看似需要使用 !important 的情況的。
程式碼註釋
單行註釋
星號與內容之間必須保留一個空格。
/* 表格隔行變色 */
多行註釋
星號要一列對齊,星號與內容之間必須保留一個空格。
/** * Sometimes you need to include optional context for the entire component. Do that up here if it's important enough. */
規則宣告塊內註釋
使用 // 註釋,// 後面加上一個空格,註釋獨立一行。
.g-footer { border: 0; // .... }CSS佈局例項(詳解)
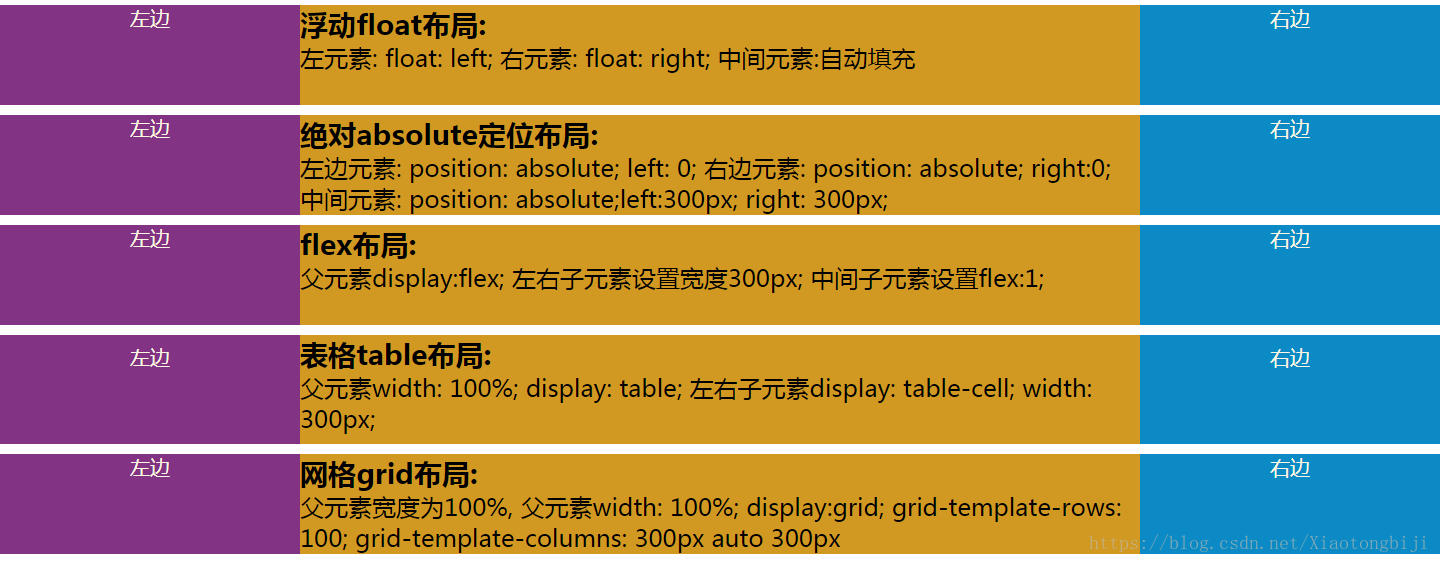
一、css佈局實現左中右佈局的5種方式
本文介紹了詳解css佈局實現左中右佈局的5種方式,分享給大家,具體如下:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
html *{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
article{
height: 100px;
}
section{
margin-top: 10px;
}
.left{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #823384;
text-align: center;
font-size: 20px;
color: #fdf6e3;
}
.center{
height: 100px;
background-color: #d29922;
}
.right{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0c8ac5;
text-align: center;
font-size: 20px;
color: #fdf6e3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--浮動佈局-->
<!--左浮動, 右浮動, 中間自動填充-->
<section class="layout float">
<style>
.float article div{
}
.float article .left{
float: left;
}
.float article .right{
float: right;
}
.float article .center{
}
</style>
<article class="left-right-center">
<div class="left">左邊</div>
<div class="right">右邊</div>
<div class="center"><h1>
浮動float佈局:
</h1> 左元素: float: left; 右元素: float: right; 中間元素:自動填充</div>
</article>
</section>
<!--絕對定位-->
<section class="layout absolute">
<style>
article{
position: relative;
}
.absolute .left-center-right div{
position: absolute;
}
.absolute .left-center-right .left{
left: 0;
}
.absolute .left-center-right .center{
left: 300px;
right: 300px;
}
.absolute .left-center-right .right{
right: 0;
}
</style>
<article class="left-center-right">
<div class="left">左邊</div>
<div class="center"><h1>
絕對absolute定位佈局:
</h1> 左邊元素: position: absolute; left: 0;
右邊元素: position: absolute; right:0; 中間元素: position: absolute;left:300px; right: 300px;
</div>
<div class="right">右邊</div>
</article>
</section>
<!--flex佈局-->
<section class="layout flexbox">
<style>
.flexbox .left-center-right{
display: flex;
}
.flexbox .left-center-right .left{
}
.flexbox .left-center-right .center{
flex:1;
}
.flexbox .left-center-right .right{
}
</style>
<article class="left-center-right">
<div class="left">左邊</div>
<div class="center"><h1>
flex佈局:
</h1> 父元素display:flex; 左右子元素設定寬度300px; 中間子元素設定flex:1;</div>
<div class="right">右邊</div>
</article>
</section>
<!--表格佈局-->
<section class="table-box layout">
<style>
.table-box .left-center-right{
width: 100%;
display: table;
}
.table-box .left-center-right>div{
display: table-cell;
}
.table-box .left-center-right .left{
}
.table-box .left-center-right .center{
}
.table-box .left-center-right .right {
}
</style>
<article class="left-center-right">
<div class="left">左邊</div>
<div class="center"><h1>
表格table佈局:
</h1> 父元素width: 100%; display: table;
左右子元素display: table-cell; width: 300px; </div>
<div class="right">右邊</div>
</article>
</section>
<!--網格佈局-->
<section class="grid layout">
<style>
.grid article{
display: grid;
width: 100%;
grid-template-rows: 100px;
grid-template-columns: 300px auto 300px;
}
</style>
<article class="left-center-right">
<div class="left">左邊</div>
<div class="center"><h1>
網格grid佈局:
</h1> 父元素寬度為100%,
父元素width: 100%; display:grid; grid-template-rows: 100; grid-template-columns: 300px auto 300px</div>
<div class="right">右邊</div>
</article>
</section>
</body>
</html>
二、CSS雙飛翼佈局的兩種方式實現示例
雙飛翼佈局,就是兩端固定寬高,中間自適應的三欄佈局:
方式一:通過flex彈性佈局來實現
<body>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</div>
</body>*{ //先簡單粗暴的解決一下瀏覽器的預設樣式
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
border: 0;
box-sizing:border-box; //使用border-box,盒模型好計算,媽媽再也不用擔心我算不清塊寬高了
}
.wrap{
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
display: flex; //使用彈性佈局
flex-flow:row nowrap; //以沿主軸方向行顯示,不換行,從而來顯示3個塊
justify-content:space-around; //這一個加和不叫其實也沒事,加上去的意思就是兩端對齊
}
[class^='div']{ // 給所有的div都加上高和邊框樣式,方便觀看,不然都縮成一條線了
height: 400px;
border: 1px solid #f00;
}
.div1,.div3{ //給兩端的div固定的寬
width: 200px;
background-color: #ccc;
flex-shrink: 1; //預設是1,所以不用寫也沒事,寫出來是表達這個意思
}
.div2{
background-color: #0f0;
flex-grow:1; //這個比較重要,作用是讓第二個塊的寬度撐滿剩餘的空間
}
三、三種絕對定位元素的水平垂直居中的方法
1.css實現居中
缺點:需要提前知道元素的寬度和高度。
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
position: absolute;
left: 50%; top: 50%;
border:1px solid #000;
background:red;
margin-top: -200px; /* 高度的一半 */
margin-left: -300px; /* 寬度的一半 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
</div>
</body>
</html>2、css3實現水平垂直居中
注意:無論元素的尺寸是多少,都可以居中。不過IE8以上才相容這種寫法,移動端可忽略。
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
border:1px solid #000;
background:red;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%); /* 50%為自身尺寸的一半 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
</div>
</body>
</html>3、margin:auto實現居中
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
border:1px solid #000;
background:red;
margin: auto; /* 有了這個就自動居中了 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
</div>
</body>
</html>四、兩種左側固定,右側自適應的方法
第一種方法:
<!DOCTYPE>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.one {
position: absolute;
height: 200px;
width: 300px;
background-color: blue;
}
.two {
height: 200px;
margin-left: 300px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="one"></div>
<div class="two">第一種方法</div>
</body>
</html>
第二種方法:
<!DOCTYPE>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.one {
float:left;
height: 200px;
width: 300px;
background-color: blue;
}
.two {
overflow: auto;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="one"></div>
<div class="two">第二種方法</div>
</body>
</html>
五、響應式佈局
響應式佈局在面對不同解析度裝置靈活性強,在平時的網頁設計中基本上都要用到響應式佈局設計,它給我們提供了良好的使用者瀏覽頁面,能帶給我們更好的客戶體驗,下面給大家分享下我做的一個簡單的響應式的佈局:
不同的頁面會適用不同大小瀏覽器頁面,它會隨著解析度的變化而變化。程式碼展示如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
2.<html>
3.<head>
4.<meta charset="utf-8" />
5.<title></title>
6.<style>
7. p{
8. font-size: 12px;
9. }
10. header{
11. width: 100%;
12. }
13. header img{
14. width: 100%;
15. }
16. @media (min-width: 1300px) and (max-width:1400px) {
17. #left{
18. float: left;
19. width: 30%;
20. margin: 0px 50px;
21. }
22. #left #logo-bg{
23. margin: 10% 10%;
24. width: 80%;
25. position: relative;
26. }
27. #left #logo{
28. float: left;
29. width: 12%;
30. position: absolute;
31. left: 13%;
32. top: 230px;
33. }
34. #left p{
35. margin-bottom: -20px;
36. }
37. #left p,h4{
38. text-align: center;
39. color: red;
40. }
41. #right{
42. float: left;
43. width: 60%;
44. margin: 15% 0px;
45. }
46. #right h2{
47. text-align: center;
48. }
49. #right fieldset{
50. text-align: center;
51. border-left: none;
52. border-right: none;
53. border-bottom: none;
54. }
55. #right fieldset legend{
56. padding: 0px 20px;
57. }
58. #fen{
59. width: 100%;
60. -webkit-column-count: 6;
61. -moz-column-count: 6;
62. -o-column-count: 6;
63. -ms-column-count: 6;
64. column-count: 6;
65. -webkit-column-gap: 1em;
66. -moz-column-gap: 1em;
67. -o-column-gap: 1em;
68. -ms-column-gap: 1em;
69. column-gap: 1em;
70. }
71. #fen img{
72. width: 100%;
73. border-radius: 10px 10px 10px 10px;
74. }
75. #fen p,h4{
76. text-align: center;
77. color: red;
78. }
79. #fen p{
80. margin-bottom: -20px;
81. }
82. #di p{
83. text-align: center;
84. }
85. #di p span{
86. color: red;
87. }
88. }
89. @media (min-width: 1000px) and (max-width:1300px){
90. #left{
91. float: left;
92. width: 30%;
93. margin: 0px 50px;
94. }
95. #left #logo-bg{
96. margin: 10% 10%;
97. width: 80%;
98. position: relative;
99. }
100. #left #logo{
101. width: 12%;
102. position: absolute;
103. left: 14%;
104. top: 190px;
105. }
106. #left p{
107. margin-bottom: -20px;
108. }
109. #left p,h4{
110. text-align: center;
111. color: red;
112. }
113. #right{
114. float: left;
115. width: 60%;
116. margin: 15% 0px;
117. }
118. #right h2{
119. text-align: center;
120. }
121. #right fieldset{
122. text-align: center;
123. border-left: none;
124. border-right: none;
125. border-bottom: none;
126. }
127. #right fieldset legend{
128. padding: 0px 20px;
129. }
130. #fen{
131. width: 100%;
132. -webkit-column-count: 3;
133. -moz-column-count: 3;
134. -o-column-count: 3;
135. -ms-column-count: 3;
136. column-count: 3;
137. -webkit-column-gap: 1em;
138. -moz-column-gap: 1em;
139. -o-column-gap: 1em;
140. -ms-column-gap: 1em;
141. column-gap: 1em;
142. }
143. #fen img{
144. width: 100%;
145. border-radius: 10px 10px 10px 10px;
146. }
147. #fen p,h4{
148. text-align: center;
149. color: red;
150. }
151. #fen p{
152. margin-bottom: -20px;
153. }
154. #di p{
155. text-align: center;
156. }
157. #di p span{
158. color: red;
159. }
160. }
161.</style>
162.</head>
163.<body>
164. <header>
165. <img src="img/rag.png" />
166. </header>
167. <aside id="left">
168. <img src="img/logo-bg.png" id="logo-bg"/>
169. <img src="img/logo.png" id="logo" />
170. <hr />
171. <p>THE</p>
172. <h4>WEBLOCUE</h4>
173. <hr />
174. <p>THE</p>
175. <h4>WEBLOCUE</h4>
176. <hr />
177. <p>THE</p>
178. <h4>WEBLOCUE</h4>
179. <hr />
180. </aside>
181. <article id="right">
182. <h2>“Give me problems, give me work.”</h2>
183. <p>In the year 1878 I took dogree of Doctor of Medicline of the Unibertive of the London and problems to Netbody to go through the course,In the year 1878 I took dogree of Doctor of Medicline of the Unibertive of the London and problems to Netbody to go through the course,In the year 1878 I took dogree of Doctor of Medicline of the Unibertive of the London and problems to Netbody to go through the course.</p>
184. <p>In the year 1878 I took dogree of Doctor of Medicline of the Unibertive of the London and problems to Netbody to go through the course,In the year 1878 I took dogree of Doctor of Medicline of the Unibertive of the London and problems to Netbody to go through the course,In the year 1878 I took dogree of Doctor of Medicline of the Unibertive of the London and problems to Netbody to go through the course.</p>
185. <fieldset><legend>victors</legend></fieldset>
186. <div id="fen">
187. <img src="img/1.jpg" />
188. <p>SETCOME</p>
189. <h4>HOLEMES</h4>
190. <img src="img/2.jpg" />
191. <p>SETCOME</p>
192. <h4>HOLEMES</h4>
193. <img src="img/3.jpg" />
194. <p>SETCOME</p>
195. <h4>HOLEMES</h4>
196. <img src="img/4.jpg" />
197. <p>SETCOME</p>
198. <h4>HOLEMES</h4>
199. <img src="img/5.jpg" />
200. <p>SETCOME</p>
201. <h4>HOLEMES</h4>
202. <img src="img/6.jpg" />
203. <p>SETCOME</p>
204. <h4>HOLEMES</h4>
205. </div>
206. <fieldset><legend>*</legend></fieldset>
207. <div id="di">
208. <p>In the year 1878 I took <span>Suing table</span> dogree of Doctor</p>
209. <p>What the year 2016 I took dogree <span>Ruing roid</span> of Doctor</p>
210. </div>
211. </article>
212.</body>
213.</html>
六、CSS固定寬度的三列布局運用例項解析
這很基礎,我們直接看程式碼便能明白:
<div id="wrapper">
<div id="header">header</div>
<div id="body" class="cls">
<div id="aside">
<div class="inner">
aside
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
</div>
</div>
<div id="content" class="cls">
<div id="main">
<div class="inner">
main
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
</div>
</div>
<div id="content-aside">
<div class="inner">
content-aside
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div id="footer">footer</div>
</div>
#header{ width: 980px; height: 90px; margin: 0 auto; background: #f60;}
#body{ width: 980px; margin: 0 auto;}
#aside{ float: left; width: 240px; background: #ccc;}
#content{ margin-left: 240px;}
#main{ float: left; width: 540px; background: pink;}
#content-aside{ float: left; width: 200px; background: orange; }
#footer{ width: 980px; height: 90px; margin: 0 auto; background: #08f;}
例項:實現三列圖片等寬等間距佈局
每個圖片塊左浮動,寬25%,左外邊距2.5%:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale= ,maximum-scale= ,user-scalable=0">
<title>三列圖片等寬佈局</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
img {
display: block;
width: 25%;
margin: 5% 0 0 5%;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<img src=" images/photo1.jpg" /><img src=" images/photo1.jpg" /><img src=" images/photo1.jpg" />
<img src=" images/photo1.jpg" /><img src=" images/photo1.jpg" /><img src=" images/photo1.jpg" />
<img src=" images/photo1.jpg" /><img src=" images/photo1.jpg" /><img src=" images/photo1.jpg" />
</div>
</body>
</html> width: 25%; 表示父級元素寬度的30%.
height: 30%; 如果沒有設定父級元素的具體高度,那麼這個height是沒有效果的.
百分比佈局也可以看做是一種響應式佈局.
簡單實用的 百分比佈局 還是很適合手機WAP頁面佈局的:
min-width:320px;
max-width:980px;
width:100%;
overflow-x: hidden;
margin: 0 auto;
最小寬度320px,最大寬度980px,在320px和980px之間自動適應寬度,看起來還行.
在<img>標籤裡只用設定width屬性百分比值,比如width="40%",不用設定height屬性,這樣圖片能夠自行按原比例縮放.
容器裡面的塊,同樣可以用百分比佈局,比如左邊的60%,右邊的40%.