[LeetCode] Gray Code 格雷碼
The gray code is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit.
Given a non-negative integer n representing the total number of bits in the code, print the sequence of gray code. A gray code sequence must begin with 0.
For example, given n = 2, return [0,1,3,2]. Its gray code sequence is:
00 - 0 01 - 1 11 - 3 10 - 2
Note:
For a given n, a gray code sequence is not uniquely defined.
For example, [0,2,3,1] is also a valid gray code sequence according to the above definition.
For now, the judge is able to judge based on one instance of gray code sequence. Sorry about that.
這道題是關於
Int Grey Code Binary0 000 000 1 001 001 2 011 010 3 010 011 4 110 100 5 111 101 6 101 110 7 100 111
其實這道題還有多種解法。首先來看一種最簡單的,是用到格雷碼和二進位制數之間的相互轉化,可參見我之前的部落格 Convertion of grey code and binary 格雷碼和二進位制數之間的轉換 ,明白了轉換方法後,這道題完全沒有難度,程式碼如下:
解法一:
// Binary to grey code class Solution { public: vector<int> grayCode(int n) { vector<int> res; for (int i = 0; i < pow(2,n); ++i) { res.push_back((i >> 1) ^ i); } return res; } };
然後我們來看看其他的解法,參考維基百科上關於格雷碼的性質,有一條是說鏡面排列的,n位元的格雷碼可以從n-1位元的格雷碼以上下鏡射後加上新位元的方式快速的得到,如下圖所示一般。
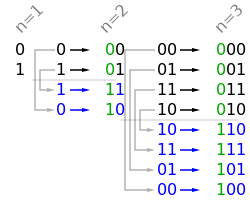
有了這條性質,我們很容易的寫出程式碼如下:
解法二:
// Mirror arrangement class Solution { public: vector<int> grayCode(int n) { vector<int> res{0}; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int size = res.size(); for (int j = size - 1; j >= 0; --j) { res.push_back(res[j] | (1 << i)); } } return res; } };
維基百科上還有一條格雷碼的性質是直接排列,以二進位制為0值的格雷碼為第零項,第一項改變最右邊的位元,第二項改變右起第一個為1的位元的左邊位元,第三、四項方法同第一、二項,如此反覆,即可排列出n個位元的格雷碼。根據這條性質也可以寫出程式碼,不過相比前面的略微複雜,程式碼如下:
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 1
0 1 0
1 1 0
1 1 1
1 0 1
1 0 0
解法三:
// Direct arrangement class Solution { public: vector<int> grayCode(int n) { vector<int> res{0}; int len = pow(2, n); for (int i = 1; i < len; ++i) { int pre = res.back(); if (i % 2 == 1) { pre = (pre & (len - 2)) | ((~pre) & 1); } else { int cnt = 1, t = pre; while ((t & 1) != 1) { ++cnt; t >>= 1; } if ((pre & (1 << cnt)) == 0) pre |= (1 << cnt); else pre &= ~(1 << cnt); } res.push_back(pre); } return res; } };
上面三種解法都需要事先了解格雷碼及其性質,假如我們之前並沒有接觸過格雷碼,那麼我們其實也可以用比較笨的方法來找出結果,比如下面這種方法用到了一個set來儲存已經產生的結果,我們從0開始,遍歷其二進位制每一位,對其取反,然後看其是否在set中出現過,如果沒有,我們將其加入set和結果res中,然後再對這個數的每一位進行遍歷,以此類推就可以找出所有的格雷碼了,參見程式碼如下:
解法四:
class Solution { public: vector<int> grayCode(int n) { vector<int> res; unordered_set<int> s; helper(n, s, 0, res); return res; } void helper(int n, unordered_set<int>& s, int out, vector<int>& res) { if (!s.count(out)) { s.insert(out); res.push_back(out); } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int t = out; if ((t & (1 << i)) == 0) t |= (1 << i); else t &= ~(1 << i); if (s.count(t)) continue; helper(n, s, t, res); break; } } };
既然遞迴方法可以實現,那麼就有對應的迭代的寫法,當然需要用stack來輔助,參見程式碼如下:
解法五:
class Solution { public: vector<int> grayCode(int n) { vector<int> res{0}; unordered_set<int> s; stack<int> st; st.push(0); s.insert(0); while (!st.empty()) { int t = st.top(); st.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int k = t; if ((k & (1 << i)) == 0) k |= (1 << i); else k &= ~(1 << i); if (s.count(k)) continue; s.insert(k); st.push(k); res.push_back(k); break; } } return res; } };
參考資料:
