[LeetCode] Max Points on a Line 共線點個數
Given n points on a 2D plane, find the maximum number of points that lie on the same straight line.
這道題給了我們一堆二維點,然後讓我們求最大的共線點的個數,根據初中數學我們知道,兩點確定一條直線,而且可以寫成y = ax + b的形式,所有共線的點都滿足這個公式。所以這些給定點兩兩之間都可以算一個斜率,每個斜率代表一條直線,對每一條直線,帶入所有的點看是否共線並計算個數,這是整體的思路。但是還有兩點特殊情況需要考慮,二是當兩個點重合時,無法確定一條直線,但這也是共線的情況,需要特殊處理。二是斜率不存在的情況,由於兩個點(x1, y1)和(x2, y2)的斜率k表示為(y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1),那麼當x1 = x2時斜率不存在,這種共線情況需要特殊處理。我們需要用到雜湊表來記錄斜率和共線點個數之間的對映,其中第一種重合點的情況我們假定其斜率為INT_MIN,第二種情況我們假定其斜率為INT_MAX,這樣都可以用map映射了。我們還需要頂一個變數duplicate來記錄重合點的個數,最後只需和雜湊表中的數字相加即為共線點的總數,這種方法現在已經無法通過OJ了,貼出來權當紀念。程式碼如下:
C++ 解法一:
// Failed on case: [[0,0],[94911151,94911150],[94911152,94911151]] class Solution { public: int maxPoints(vector<Point>& points) { int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) { unordered_map<float, int> m; int duplicate = 1; for (int j = i + 1; j < points.size(); ++j) { if (points[i].x == points[j].x && points[i].y == points[j].y) { ++duplicate; } else if (points[i].x == points[j].x) { ++m[INT_MAX]; } else{ float slope = (float)(points[j].y - points[i].y) / (points[j].x - points[i].x); ++m[slope]; } } res = max(res, duplicate); for (auto it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); ++it) { res = max(res, it->second + duplicate); } } return res; } };
Java 解法一:
// Failed on case: [[0,0],[94911151,94911150],[94911152,94911151]] public class Solution { public int maxPoints(Point[] points) { int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < points.length; ++i) { int duplicate = 1, vertical = 0; Map<Double, Integer> m = new HashMap<>(); for (int j = i + 1; j < points.length; ++j) { if (points[i].x == points[j].x && points[i].y == points[j].y) { ++duplicate; } else if (points[i].x == points[j].x) { m.put(Double.MAX_VALUE, m.getOrDefault(Double.MAX_VALUE, 0) + 1); } else if (points[i].y == points[j].y) { m.put(0.0, m.getOrDefault(0.0, 0) + 1); } else { double slope = (double)(points[j].y - points[i].y) / (points[j].x - points[i].x); m.put(slope, m.getOrDefault(slope, 0) + 1); } } res = Math.max(res, duplicate); for (Map.Entry<Double, Integer> e : m.entrySet()) { res = Math.max(res, e.getValue() + duplicate); } } return res; } }
由於通過斜率來判斷共線需要用到除法,而用double表示的雙精度小數在有的系統裡不一定準確,為了更加精確無誤的計算共線,我們應當避免除法,從而避免無線不迴圈小數的出現,那麼怎麼辦呢,我們把除數和被除數都儲存下來,不做除法,但是我們要讓這兩數分別除以它們的最大公約數,這樣例如8和4,4和2,2和1,這三組商相同的數就都會存到一個對映裡面,同樣也能實現我們的目標,而求GCD的函式如果用遞迴來寫那麼一行就搞定了,叼不叼,這個方法能很好的避免除法的出現,算是犧牲了空間來保證精度吧,參見程式碼如下:
C++ 解法二:
class Solution { public: int maxPoints(vector<Point>& points) { int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) { map<pair<int, int>, int> m; int duplicate = 1; for (int j = i + 1; j < points.size(); ++j) { if (points[i].x == points[j].x && points[i].y == points[j].y) { ++duplicate; continue; } int dx = points[j].x - points[i].x; int dy = points[j].y - points[i].y; int d = gcd(dx, dy); ++m[{dx / d, dy / d}]; } res = max(res, duplicate); for (auto it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); ++it) { res = max(res, it->second + duplicate); } } return res; } int gcd(int a, int b) { return (b == 0) ? a : gcd(b, a % b); } };
Java 解法二:
public class Solution { public int maxPoints(Point[] points) { int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < points.length; ++i) { Map<Map<Integer, Integer>, Integer> m = new HashMap<>(); int duplicate = 1; for (int j = i + 1; j < points.length; ++j) { if (points[i].x == points[j].x && points[i].y == points[j].y) { ++duplicate; continue; } int dx = points[j].x - points[i].x; int dy = points[j].y - points[i].y; int d = gcd(dx, dy); Map<Integer, Integer> t = new HashMap<>(); t.put(dx / d, dy / d); m.put(t, m.getOrDefault(t, 0) + 1); } res = Math.max(res, duplicate); for (Map.Entry<Map<Integer, Integer>, Integer> e : m.entrySet()) { res = Math.max(res, e.getValue() + duplicate); } } return res; } public int gcd(int a, int b) { return (b == 0) ? a : gcd(b, a % b); } }
令我驚奇的是,這道題的OJ居然容忍brute force的方法通過,那麼我感覺下面這種O(n3)的解法之所以能通過OJ,可能還有一個原因就是用了比較高效的判斷三點共線的方法。一般來說判斷三點共線有三種方法,斜率法,周長法,面積法(請參見這個帖子)。而其中通過判斷叉積為零的面積法是墜好的。比如說有三個點A(x1, y1)、B(x2, y2)、C(x3, y3),那麼判斷三點共線就是判斷下面這個等式是否成立:
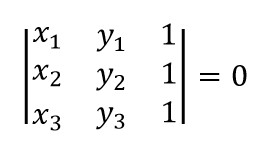
行列式的求法不用多說吧,不會的話回去翻線性代數,當初少打點刀塔不就好啦~
C++ 解法三:
class Solution { public: int maxPoints(vector<Point>& points) { int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) { int duplicate = 1; for (int j = i + 1; j < points.size(); ++j) { int cnt = 0; long long x1 = points[i].x, y1 = points[i].y; long long x2 = points[j].x, y2 = points[j].y; if (x1 == x2 && y1 == y2) {++duplicate; continue;} for (int k = 0; k < points.size(); ++k) { int x3 = points[k].x, y3 = points[k].y; if (x1 * y2 + x2 * y3 + x3 * y1 - x3 * y2 - x2 * y1 - x1 * y3 == 0) { ++cnt; } } res = max(res, cnt); } res = max(res, duplicate); } return res; } };
Java 解法三:
public class Solution { public int maxPoints(Point[] points) { int res = 0, n = points.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int duplicate = 1; for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) { int cnt = 0; long x1 = points[i].x, y1 = points[i].y; long x2 = points[j].x, y2 = points[j].y; if (x1 == x2 && y1 == y2) {++duplicate;continue;} for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k) { int x3 = points[k].x, y3 = points[k].y; if (x1*y2 + x2*y3 + x3*y1 - x3*y2 - x2*y1 - x1 * y3 == 0) { ++cnt; } } res = Math.max(res, cnt); } res = Math.max(res, duplicate); } return res; } }
參考資料:
