Java7新特性——新I/O
NIO.2是一組新的類和方法,主要存在於java.nio包內。
主要優點:
- 它完全取代了java.io.File與檔案系統的互動。
- 它提供了新的非同步處理類,讓你無需手動配置執行緒池和其他底層併發控制,便可在後臺執行緒中執行檔案和網路I/O操作。
- 它引入了新的Network-Channel構造方法,簡化了套接字(Socket)與通道的編碼工作。
檔案I/O的基石:Path
Path通常代表檔案系統中的位置,比如C:\Users\dell\Desktop\nio。NIO.2把位置(由Path表示)的概念和物理檔案系統的處理(比如複製一個檔案)分得很清楚,物理檔案系統的處理通常是由Files輔助類實現。
- Path:Path類中的方法可以用來獲取路徑資訊,訪問該路徑中的各元素,將路徑轉換為其他形式,或提取路徑中的一部分。有的方法還可以匹配路徑字串以及移除路徑中的冗餘項
- Paths:工具類,提供返回一個路徑的輔助方法,比如get(String first, String... more)和get(URI uri)
- FileSystem:與檔案系統互動的類,無論是預設的檔案系統,還是通過其統一資源標識(URI)獲取的可選檔案系統
- FIleSystems:工具類,提供各種方法,比如其中用於返回預設檔案系統的FIleSystems.getDefault()
Path不一定代表真實的檔案或目錄。
1、建立一個Path
Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio", "a.txt");
其實,等同於Path path = FileSystems.getDefault().getPath("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio", "a.txt");
2、從Path中獲取資訊
Path path = FileSystems.getDefault().getPath("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio", "a.txt");
System.out.println("File Name:" + path.getFileName());
System.out.println("Number of Name Elements in the Path:" + path.getNameCount());
System.out.println("Root of Path:" + path.getRoot());
System.out.println("Subpath from Root,2 elements deep:" + path.subpath(0, 2));
3、移除冗餘項
Path normalizePath = Paths.get("./PathTest.java").normalize();
此外,toRealPath()方法也很有效,它融合了toAbsolutePath()和normalize()兩個方法的功能,還能檢測並跟隨符號連線。
4、轉換Path
合併兩個Path之間的路徑:
Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\dell");
Path completePath = path.resolve("Desktop\\nio");
System.out.println(completePath);
取得兩個Path之間的路徑:
Path path1 = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\dell");
Path path2 = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio");
System.out.println(path1.relativize(path2));
比較
startsWith(Path prefix)、equals(Path path)、endsWith(Path suffix)。
5、NIO.2 Path和Java已有的FIle類
處理目錄和目錄樹
- java.io.File.toPath():把File轉化為Path
- java.nio.file.Path.toFile():把Path轉化為File
java.nio.file.DirectorySystem<T>介面和它的實現類提供了很多功能:
- 迴圈遍歷目錄中的子項,比如查詢目錄中的檔案
- 用glob表示式(比如*Foobar*)進行目錄子項匹配和基於MIME的內容檢測(比如text/xml)檔案
- 用walkFileTree方法實現遞迴移動、複製和刪除操作
1、在目錄中查詢檔案
Path dir = Paths.get("C:\\\\Users\\\\dell\\\\Desktop\\\\nio");
try (DirectoryStream<Path> stream = Files.newDirectoryStream(dir, "*.txt")) {
for (Path entry : stream) {
System.out.println(entry.getFileName());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
2、遍歷目錄樹
Java7可以很容易地搜尋目錄樹中的檔案,在子目錄中查詢,並對它們執行操作。
關鍵方法是:Path walkFileTree(Path start, FileVisitor<? super Path> visitor) throws IOException,其中visitor提供了一個預設實現類SimpleFileVisitor<T>。
/**
* Java7的新I/O
* @author z_hh
* @time 2018年8月16日
*/
public class Nio {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Path startingDir = Paths.get("D:\\eclipse_workspace\\zhh_src\\src");
Files.walkFileTree(startingDir, new FindJavaVisitor());
}
private static class FindJavaVisitor extends SimpleFileVisitor<Path> {
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
if (file.toString().endsWith(".java")) {
System.out.println(file.getFileName());
}
return FileVisitResult.CONTINUE;
}
}
}重寫了SimpleFileVisitor的visitFile方法來判斷檔名是否以.java結尾。
其它用例包括遞迴移動、複製、刪除或者修改檔案。
為了確保遞迴等操作的安全性,walkFileTree方法不會自動跟隨符號連結。
NIO.2的檔案系統I/O
檔案處理的基礎類
Files:讓你輕鬆複製、移動、刪除或處理檔案的工具類,有你需要的所有方法
WatchService:用來監視檔案或目錄的核心類,不管它們有沒有變化
1、建立和刪除檔案
// 建立檔案
Path txt = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio\\z.txt");
Path path = Files.createFile(txt);
// 建立檔案並分配許可權
Path jpg = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio\\h.jpg");
Set<PosixFilePermission> perms = PosixFilePermissions.fromString("r--r--r--");
FileAttribute<Set<PosixFilePermission>> attr = PosixFilePermissions.asFileAttribute(perms);
Files.createFile(jpg, attr);
// 刪除
Files.delete(jpg);
Files.deleteIfExists(jpg);2、檔案的複製和移動
Path source = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio\\z.txt");
Path target = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio\\dir");
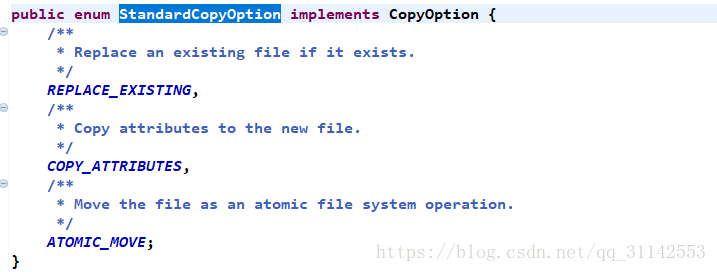
Files.copy(source, target, StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
Files.move(source, target, StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING, StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE);3、檔案的屬性
基本檔案屬性的支援
特定檔案屬性支援
try {
Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio\\a.txt");
// 獲取屬性範圍
PosixFileAttributes attrs = Files.readAttributes(path, PosixFileAttributes.class);
// 讀取訪問許可
Set<PosixFilePermission> posixPermissions = attrs.permissions();
// 消除訪問許可
posixPermissions.clear();
// 日誌資訊
String owner = attrs.owner().getName();
String perms = PosixFilePermissions.toString(posixPermissions);
System.out.format("%s %s%n", owner, perms);
// 設定新的訪問許可
posixPermissions.add(PosixFilePermission.OWNER_READ);
posixPermissions.add(PosixFilePermission.GROUP_READ);
posixPermissions.add(PosixFilePermission.OTHERS_READ);
posixPermissions.add(PosixFilePermission.OWNER_WRITE);
Files.setPosixFilePermissions(path, posixPermissions);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}符號連線
Path readSymbolicLink(Path link) throws IOException
4、快速讀寫資料
開啟檔案
- BufferedReader newBufferedReader(Path path, Charset cs) throws IOException
- BufferedReader newBufferedReader(Path path, Charset cs) throws IOException
簡化讀取和寫入
- List<String> readAllLines(Path path, Charset cs) throws IOException
- byte[] readAllBytes(Path path) throws IOException
5、檔案修改通知
java.nio.file.WatchService類用客戶執行緒監視註冊檔案或目錄的變化,並且在檢測到變化時返回一個事件。這種事件通知對於安全監測、屬性檔案中的資料重新整理等很多用例都很有用。是現在某些應用程式中常用的輪詢機制(相對而言效能較差)的理想替代品。(好像還有一種回撥的方式^_^)
try {
WatchService watcher = FileSystems.getDefault().newWatchService();
Path dir = FileSystems.getDefault().getPath("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio");
// 檢測變化
WatchKey key = dir.register(watcher, StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_MODIFY);
while (true) {
// 得到寫一個key及其事件
key = watcher.take();
for (WatchEvent<?> event : key.pollEvents()) {
// 檢查是否為建立事件
if (event.kind() == StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_MODIFY) {
System.out.println("Home dir has entry create!");
}
}
// 重置檢測key
key.reset();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}6、SeekableByteChannel
Java7引入SeekableByteChannel介面,是為了讓開發人員能夠改變位元組通道的位置和大小。比如,應用伺服器為了分析日誌中的某個錯誤碼,可以讓多個執行緒去訪問連線在一個大型日誌檔案上的位元組通道。
jdk中有一個java.nio.channels.SeekableByteChannel介面的實現類——java.nio.channels.FileChannel。這個類可以在檔案讀取或寫入時保持當前位置。
Path logFile = Paths.get("C:\\error.log");
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
FileChannel channel = FileChannel.open(logFile, StandardOpenOption.READ);
channel.read(buffer, channel.size() - 1000);非同步I/O操作
非同步I/O其實只是一種在讀寫操作結束前允許其他操作的I/O處理。
Java7中有三個新的非同步通道:
- AsynchronousFileChannel——用於檔案I/O
- AsynchronousSocketChannel——用於套接字I/O,支援超時
- AsynchronousServerSocketChannel——用於套接字接受非同步連線
使用新的非同步I/O API時,主要有兩種形式,將來式和回撥式。
1、將來式
Path file = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio\\a.txt");
// 非同步開啟檔案
AsynchronousFileChannel channel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(file);
// 讀取100,000位元組
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(100_000);
Future<Integer> result = channel.read(buffer, 0);
while (!result.isDone()) {
// 乾點別的事情
System.out.println("睡個覺!");
}
// 獲取結果
Integer byteRead = result.get();
System.out.println("Bytes read:" + byteRead);AsynchronousFileChannel會關聯執行緒池,它的任務是接收I/O處理事件,並分發給負責處理通道中I/O操作結果的結果處理器。跟通道中發起的I/O操作關聯的結果處理器確保是由執行緒池中的某個執行緒產生的。
2、回撥式
Path file = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\nio\\a.txt");
// 以非同步方式開啟檔案
AsynchronousFileChannel channel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(file);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(100_000);
// 從通道中讀取資料
channel.read(buffer, 0, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
// 獲取完成時的回撥方法
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
System.out.println("Byte read:" + result);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
System.out.println("fail:" + exc.getMessage());
}
});以上兩個離職都是基於檔案的,但也同樣適合AsynchronousSocketChannel和AsynchronousServerSocketChannel。
Socket和Channel的整合
NetworkChannel
java.nio.channels.NetworkChannel代表一個連線到網路套接字通道的對映。
SelectorProvider provider = SelectorProvider.provider();
try {
// 將NetworkChannel繫結到3080上
NetworkChannel socketChannel = provider.openSocketChannel();
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(3080);
socketChannel = socketChannel.bind(address);
// 檢查套接字選項
Set<SocketOption<?>> socketOptions = socketChannel.supportedOptions();
System.out.println(socketOptions.toString());
// 設定套接字的Tos(服務條款)選項
socketChannel.setOption(StandardSocketOptions.IP_TOS, 3);
// 獲取SO_KEEPALIVE選項
Boolean keepAlive = socketChannel.getOption(StandardSocketOptions.SO_KEEPALIVE);
// ...
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}MulticastChannel
多播(或組播)表示一對多的網路通訊,通常用來指代IP多播。使用java.nio.channels.MulticastChannel及其預設實現類DatagramChannel可以輕鬆地對多播發送和接收資料。
// 選擇網路介面
NetworkInterface networkInterface = NetworkInterface.getByName("net1");
// 開啟DatagramChannel
DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open(StandardProtocolFamily.INET);
// 將通道設定為多播
dc.setOption(StandardSocketOptions.SO_REUSEADDR, true)// 鏈式呼叫
.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080))
.setOption(StandardSocketOptions.IP_MULTICAST_IF, networkInterface);
// 加入多播組
InetAddress group = InetAddress.getByName("180.90.4.12");
MembershipKey key = dc.join(group, networkInterface);到此為止,我們對NIO.2 API的初步研究已經結束了。希望你喜歡這次行色匆匆的旅程!