Intro: What is Blockchain and how does it work?
Intro: What is Blockchain and how does it work?


Unless you were hibernating for past 7–8 months, I can assure you that you have encountered words like Bitcoin, Blockchain and Ethereum more than once in your routine life and the reason behind this is simple, these words are in constant buzz all over the world and various governments, people and economic bodies are taking huge interests in them.
This article is will help you understand some key basics of Blockchain and will provide you better understanding of various aspects of Blockchain. So let’s try to understand Blockchain Block by Block.
Necessity is the mother of invention.
English proverb
It means, roughly, that the primary driving force for most new inventions is a need.
So before getting into intricate details of Blockchain and its working, let’s try to understand why it is needed.
Need of Blockchain
Trust is factor which has lead to development of Blockchain. Today we depend on third-parties to establish the trust between us. When I send some amount of cash to my friend using xyz payment wallet I need to trust the wallet company that the amount will reach my friend safely.
But trusting them blindly can lead to major problems some of them are listed below.
- These intermediaries use Registers, Ledgers, Spreadsheets and databases to store the data. Although these methods seems to be safe but the data stored in this manner can easily be modified or deleted easily without any one getting notified.
- The information stored by such intermediaries is in form of central database, so there is a possibility that the data in database can become corrupt or may be lost due to technical bug or catastrophic accident.
So to overcome this we need to design a system wherein the users can transact directly with each other without the need intermediaries. Yup you got it right this is where Blockchain come into the picture, it provides an architecture where in group of people can come along and transact with each other directly (peer to peer) without any involvement of third parties.
How does Blockchain work?
Consider a Hypothetical case wherein you and your friends are on a trip and you have decided to play a game where you will keep a track of all transactions that occur during the trip. Everybody on-board has a bag, some books and some cash. Everytime any two of your friends transact with each other everybody makes an entry about all the details of transaction in their own books. When the pages in book are completely filled everyone compares it with the entries made by others and if it is verified by all then everyone places the book in their bag where they can refer it in future if needed.
This explanation was a naive approach for explaining the workflow of Blockchain, now let’s dig into the technical part and understand how Blockchain works.
- Nodes are the basic units of a blockchain and each node can be distinguished with an unique identity (generally public keys), any computer that connects to the Blockchain network is called a node. Your friends were playing the part of node in the example discussed above.
- Ledgers are used to hold transactions, pages of books are like ledgers and a complete book is like a single Block in Blockchain .
- Blockchain are collection of blocks linked logically through a value here Bag can be considered a blockchain wherein we keep all our books (Blocks).
Blockchain are formed by a group of nodes which take part in it, every time a transaction occurs between any of the nodes it is broadcasted to each node. Every node which listens to a transaction makes an entry of the it in the ledger present with it locally. Every time a transaction is added its hash is found and it is appended along with the entry.The process of addition of transactions continues till the ledgers are completely filled, every time when the capacity of ledger reaches it’s maximum limit, each node in the blockchain starts computing the header and the hash for the block.
General structure of a header is;
Block Header Previous hash Timestamp Merkle root Nonce

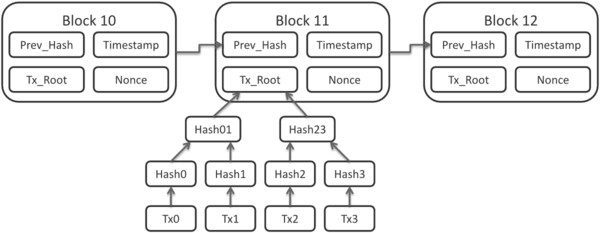
- Previous hash — as the name suggests “previous hash” contains the hash of previous block in the blockchain.
- Timestamp — is the timestamp at which the block was created.
- Merkle root — it is a combined hash value of all the hashes of individual transactions. It contains the value of root element of merkle tree created by all transactions.
- Nonce — The “nonce” in a blockchain block is a 32-bit (4-byte) field whose value is set so that the hash of the block will contain a run of leading zeros. The rest of the fields may not be changed, as they have a defined meaning.
Hash of a block is found by passing the values of the content of the block plus the block header to the hash function.
The computation of hash for block is a processor intensive task. The first node to compute the this broadcasts the information generated by its computation which is then verified by the other nodes. If a hash generated by node is verified by majority it is chosen is the hash for that block and the block is appended to the blockchain. If a node gets a different hash than one accepted for the block, that node is forced to discard its ledger and copy a genuine ledger from its peer. The reason for incorrect value hash may be a result of invalid entries or any other discrepancy in the data entered in ledger.
Storing the data on the blockchain in this manner enables secure storage and verification of all transaction. The data is immutable now and can be verified easily whenever required.
Now you would be thinking why should I spend my electricity and my computer’s processing power for the sake of a community who wants a third party free economy. Well wait then, because each blockchain rewards you for doing all the processing work on the network so every time you find a successful hash you are rewarded with a pre-decided amount by the creators of that blockchain, and this process is termed as mining you can carry out mining of various crypto-currencies using various softwares available in market and a computer with higher specifications or a mining rig.
Now one may think of modifying the contents of the data stored in blockchain but it is not possible to change the contents of the data stored in the blockchain because even a minor change in data will make them useless as the hash of that block won’t match if the change is applied. If any discrepancy is found the entire data is discarded and then it is copied form the nearest node.


The above picture depicts the arrangement of blocks in a blockchain first block in a block chain is called Genesis block and it stores all the information about the Blockchain. Every blockchain has a Genesis Block by default and all other blocks are appended after this block. The chain keeps on growing as the number of transaction increases and this is how the data is maintained and synchronized in a public distributed system.
Application of Blockchain
Blockchain as a technology is very robust and flexible we will discuss various applications that are possible using it.
- Decentralized cryptocurrencies — At its simplest, cryptocurrencies, or digital coins, are coins that are passed through a blockchain. Some famous cryptocurrencies are Bitcoin, Ethereum, Dash, Ripple etc.
- Blockchain Healthcare — Personal health records could be encoded and stored on the blockchain with a private key which would grant access only to specific individuals.
- Blockchain music — This technology can connect music artist to end users directly removing the requirement of middle man like i tunes saavn, gaana, spotify for distribution and generation of revenue.
- Blockchain polling — Blockchain can be deployed for elections and each eligible and verified user can vote form home using his identity no cases of fraud will be there because each vote can be checked and verified in Blockchain.
- Digital wallets- cryptocurrencies will have digital wallets that support that management and tracking of balaces of an individual for a particular cryptocurrency.
Blockchain can contribute significantly in simplifying, distributed cloud storage, decentralized application deployment, stock tradings etc.
These are some of the possible implementations of Blockchain some of them are already implemented and we will see may new applications using Blockchain in upcoming years.
Advantages of Blockchain
- Durability, reliability, longevity — Due to decentralized networks, Blockchain does not have a central point of failure and is better able to withstand attacks.
- Transparency and Immutability — changes to public Blockchain are publicly viewable by everybody creating transparency, and all transaction are immutable means they cannot be changed.
- Lower transaction cost — by removing third parties from picture we are reducing the overhead for exchanging assets, Blockchain have the potential to greatly reduce transactional fee.
- High data quality — Blockchain data is complete consistent, accurate, and available 24/7.
- Faster transactions — as the data is available to each node the transactions are fasted when compared to conventional systems.
Disadvantage of Blockchain
- Overhead and redundancy — Block chain performs same task across nodes which leads to redundancy and the computation of various hash is a big overhead when compared to conventional system.
- Blockchain may get corrupt — Suppose a scenario where in 51% of nodes become corrupt and start making false entries as they are in majority the chain will include data that is not genuine this case is very rare but it is a possible condition wherein the Blockchain fails.
Conclusion
In the end I would like to conclude that Blockchain are decentralized networks which are capable of synchronizing distributed databases which contains various informations of transactions amongst peers without the need of third parties.
What the internet did for communications, blockchain will do for trusted transactions.
Ginni Rometty
Hope you find this article informative. We will be discussing various applications of Blockchain technology in upcoming articles.
