Dealing with Noisy Data in Data Science
We were working on a dataset for our data science project, where we saw that our model was not performing up to the mark. While performance is a subjective term and there can be many reasons for an under-performing model, our hunch was that this is because of the noise in the dataset.
We tried many approaches to identify and reduce this noise. Some of them worked, and some of them didn’t, because of the specific nature of the problem and the patterns in the data.
Based on my above experience, I am going to discuss various type of noise in data, and the approaches and methods to identify & reduce noise in a given dataset.
Understanding Noise in Data
Noise (in the data science space) is unwanted data items, features or records which don’t help in explaining the feature itself, or the relationship between feature & target. Noise often causes the algorithms to miss out patterns in the data.
Noise in tabular data can be of three types:
- Anomalies in certain data items (Noise 1: certain anomalies in features & target)
- Features that don’t help in explaining the target (Noise 2: irrelevant/weak features)
- Records which don’t follow the form or relation which rest of the records do (Noise 3: noisy records)

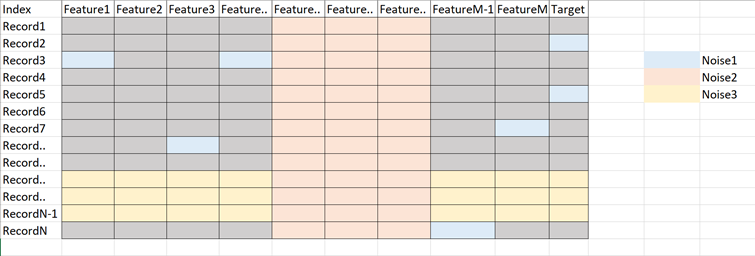
Benefits of identifying & treating noise in data:
- enables the DS algorithm to train faster.
- reduces the complexity of a model and makes it easier to interpret
- improves the accuracy of a model if the right subset is chosen
- reduces overfitting
These are the ways of dealing noise within data based on the type of noise:
Noise as an item
We can analyse the features & target and identify the noise in terms of outliers.


Outlier detection & treatment: either remove the records or put upper and lower ceiling.
Noise as a feature
This type of noise is introduced when there are features in the data which are not related to target or doesn’t help explaining target.
Feature Selection or Elimination

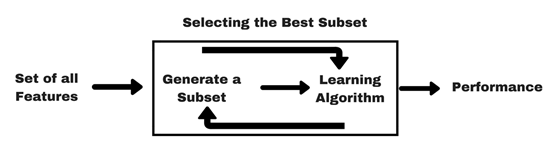
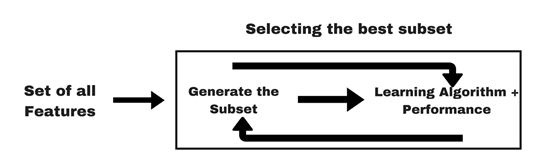
Not all features are important, so we can use various methods to find the best subset of features:
Filter method
We can perform various statistical tests between feature & response to identify which features are more relevant than others.

Please note that above methods don’t identify or deal with multicollinearity, we need to figure that out separately.
Wrapper method
Here we add/remove features to baseline model and compare the performance of the model:
- Forward selection
- Backward elimination
- Recursive elimination

Embedded Methods (Regularization)
This method make use of filter & wrapper method, it is implemented using algos which have its own built-in feature selection methods.

Noise as a record
In these methods, we can try to find the set of records which have noise.
K-fold validation
In this method, we can look at the cross validation score of each fold and analyse the folds which have poor CV scores, what are the common attributes of records having poor scores, etc.


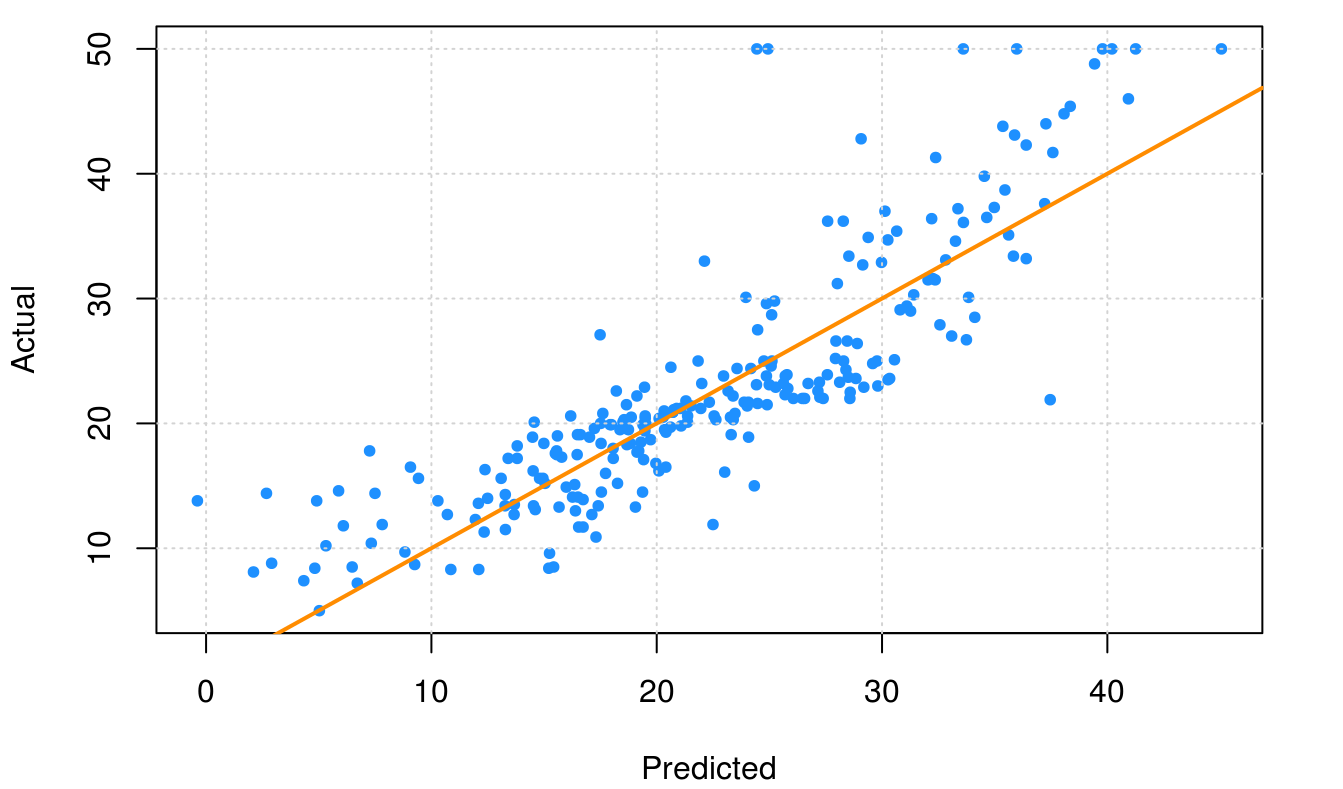
Manual method
Here we can evaluate CV of each record (predicted vs. actual) and filter/analyse the records having a poor CV score. This will help us in analyzing why this is happening in the first place.

Unsupervised Methods (Anomaly Detection)
We can also use unsupervised learning algorithms to identify anomalies in data, these are mostly categorized as Anomaly Detection techniques.
Density-based anomaly detection
This method assumes normal data points occur around a dense neighborhood and abnormalities are far away. i.e. kNN & LOF based methods
Clustering-based anomaly detection
Using clustering technique, we can analyse the clusters to analyse which has noise. Data instances falling outside the clusters can be marked as anomalies. i.e. k-Means clustering
SVM-based anomaly detection
This technique uses SVM to learn the soft boundary in the training set and tune on validation set to identify anomalies. In this approach, the need of large samples by the previous approach is reduced by using Support Vector Machine while maintaining the high quality of clustering-based anomaly detection methods. i.e. One-class SVM
Autoencoder-based anomaly detection
Auto-encoders are used in deep learning for unsupervised learning, we can use them for anomaly detection to identify noisy data-set. These methods are advanced and outperforms traditional anomaly detection methods. i.e. Variational Autoencoder based Anomaly Detection using Reconstruction Probability.
