【推薦】fastjson、gson、jackson 序列化和反序列化效能對比
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-30
第一部分:序列化測試
首先說一下結論。
1. 序列化測試結論
100個物件轉換,gson最快、fastjson其次、jackson最差 b.
10000個物件轉換,gson和fastjson耗時幾乎一樣,jackson最差
100000個物件轉換,fastjson最快、jackson其次、gson最差
2. 建議
資料處理量小的情況下使用gson,資料量大的情況下使用fastjson。
具體測試過程如下
1. pom.xml依賴如下
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/fastjson --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.31</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.google.code.gson/gson --> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId> <artifactId>gson</artifactId> <version>2.8.0</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.fasterxml.jackson.core/jackson-core --> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId> <version>2.8.5</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.9</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.fasterxml.jackson.core/jackson-databind --> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.7.3</version> </dependency>
2:序列化測試程式碼
/** * 測試fastjson gson jackson效能 */ @Test public void test1() throws JsonProcessingException { List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>(); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { User user = new User(); user.setId(i); user.setUsername("張三"+i); user.setBirthday(new Date()); users.add(user); } //測試gson用時 Gson gson = new Gson(); long start = new Date().getTime(); gson.toJson(users); long end = new Date().getTime(); System.out.println("gson轉換共用時:"+(end-start)+"ms"); //測試fastjson用時 long start1 = new Date().getTime(); JSON.toJSONString(users); long end1 = new Date().getTime(); System.out.println("fastjson轉換共用時:"+(end1-start1)+"ms"); //測試jackson用時 long start2 = new Date().getTime(); ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); mapper.writeValueAsString(users); long end2 = new Date().getTime(); System.out.println("jackson轉換共用時:"+(end2-start2)+"ms"); }
3. 測試結果
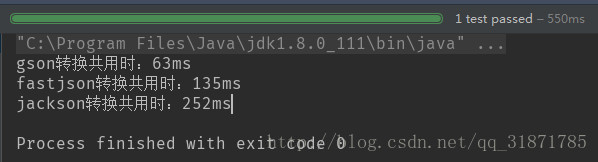
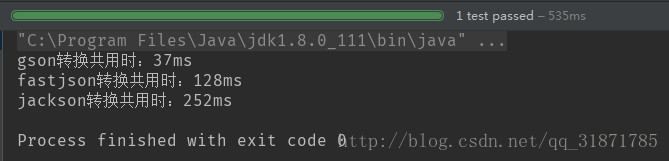
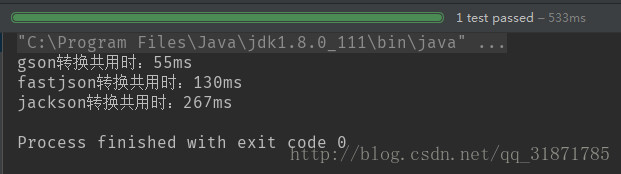
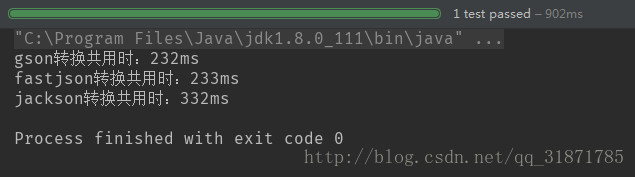
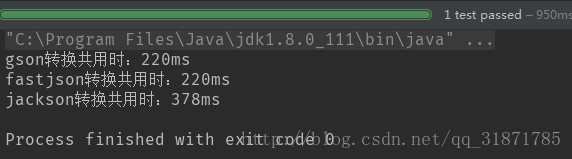
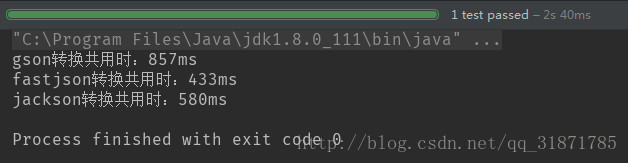
- 100個物件(測試3次結果)
- 第一次結果
- 第二次結果
- 第三次結果
- 第一次結果
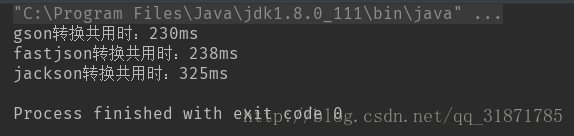
- 10000個物件
- 第一次結果
- 第二次結果
- 第三次結果
- 第一次結果
- 100000個物件
- 第一次結果
- 第二次結果
- 第三次結果
- 第一次結果
4. 測試結論
100個物件轉換,gson最快、fastjson其次、jackson最差 b.
10000個物件轉換,gson和fastjson耗時幾乎一樣,jackson最差
100000個物件轉換,fastjson最快、jackson其次、gson最差
5. 建議
資料處理量小的情況下使用gson,資料量大的情況下使用fastjson
第二部分:反序列化測試
程式碼和測試資料如下
/**
* 測試gson反序列化
*
* 測試結果如下:
* 1000000物件:
* 第一次4131ms
* 第二次4225ms
* 第三次4345ms
* 10000個物件:
* 第一次77ms
* 第二次78ms
* 第三次71ms
*/
@Test
public void testGsonDeserialization() {
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("f:/json1.json"));
String json = reader.readLine();
// 測試gson的反序列化
Gson gson = new Gson();
long start = new Date().getTime();
List<User> list = gson.fromJson(json, List.class);
long end = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println("使用gson:反序列化物件數目:" + list.size() + ", 用時:" + (end - start));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 測試fastjson反序列化
*
* 測試結果如下:
* 1000000物件:
* 第一次3679ms
* 第二次3783ms
* 第三次2972ms
* 10000物件:
* 第一次247ms
* 第二次229ms
* 第三次240ms
*/
@Test
public void testFastJsonDeserialization(){
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("f:/json1.json"));
String json = reader.readLine();
// 測試fastjson反序列化
long start1 = new Date().getTime();
List<User> list1= (List<User>) JSON.parse(json);
long end1 = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println("使用fastjson:反序列化物件數目:"+list1.size()+", 用時:"+(end1-start1));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 測試jackson反序列化
*
* 測試結果如下:
* 1000000個物件:
* 第一次4239ms
* 第二次4209ms
* 第三次3671ms
* 10000個物件:
* 第一次107ms
* 第二次114ms
* 第三次122ms
*/
@Test
public void testJacksonDeserialization(){
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("f:/json1.json"));
String json = reader.readLine();
// 測試jackson反序列化
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
long start2 = new Date().getTime();
List<User> list2 = objectMapper.readValue(json, List.class);
long end2 = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println("使用jackjson:反序列化物件數目:" + list2.size() + ", 用時:" + (end2 - start2));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}