Python+Django+MySQL進行增刪查操作
1.環境
1.安裝Django
pip 命令安裝方法
pip install Django```
## 2.是否安裝成功
進入cmd,輸入python,輸入以下字元,如果沒有錯誤提示,證明按照成功
import django
進入你的工作空間,開啟cmd輸入
會出現一堆
Usage: django-admin.py subcommand [options] [args]
Options:
-v VERBOSITY, --verbosity=VERBOSITY
Verbosity level; 0=minimal output, 1=normal output,
2=verbose output, 3=very verbose output
–settings=SETTINGS The Python path to a settings module, e.g.
“myproject.settings.main”. If this isn’t provided, the
DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE environment variable will be
used.
–pythonpath=PYTHONPATH
A directory to add to the Python path, e.g.
“/home/djangoprojects/myproject”.
–traceback Raise on exception
–version show program’s version number and exit
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Type 'django-admin.py help ’ for help on a specific subcommand.
Available subcommands:
[django]
check
cleanup
compilemessages
createcachetable
……省略部分……
沒報錯,就可以 ## 3.建立第一個專案 使用 django-admin.py 來建立 HelloWorld 專案: ```django-admin.py startproject HelloWorld``` 最新版的 Django 請使用 django-admin 命令: ```django-admin startproject HelloWorld``` 建立完成後我們可以檢視下專案的目錄結構:
$ cd HelloWorld/
$ tree
.
|-- HelloWorld
| |-- init.py
| |-- settings.py
| |-- urls.py
| -- wsgi.py– manage.py
目錄說明:
HelloWorld: 專案的容器。
manage.py: 一個實用的命令列工具,可讓你以各種方式與該 Django 專案進行互動。
HelloWorld/init.py: 一個空檔案,告訴 Python 該目錄是一個 Python 包。
HelloWorld/settings.py: 該 Django 專案的設定/配置。
HelloWorld/urls.py: 該 Django 專案的 URL 宣告; 一份由 Django 驅動的網站"目錄"。
HelloWorld/wsgi.py: 一個 WSGI 相容的 Web 伺服器的入口,以便執行你的專案。
接下來我們進入 HelloWorld 目錄輸入以下命令,啟動伺服器:
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000```
訪問專案 localhost:8000
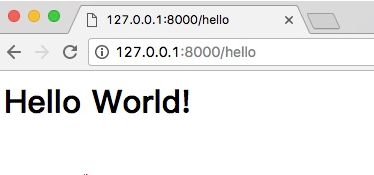
如果出現正常的歡迎頁面,就證明建立專案成功
4.HelloWorld
檢視和 URL 配置
在先前建立的 HelloWorld 目錄下的 HelloWorld 目錄新建一個 view.py 檔案,並輸入程式碼:
HelloWorld/HelloWorld/view.py 檔案程式碼:
from django.http import HttpResponse
def hello(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello world ! ")
```
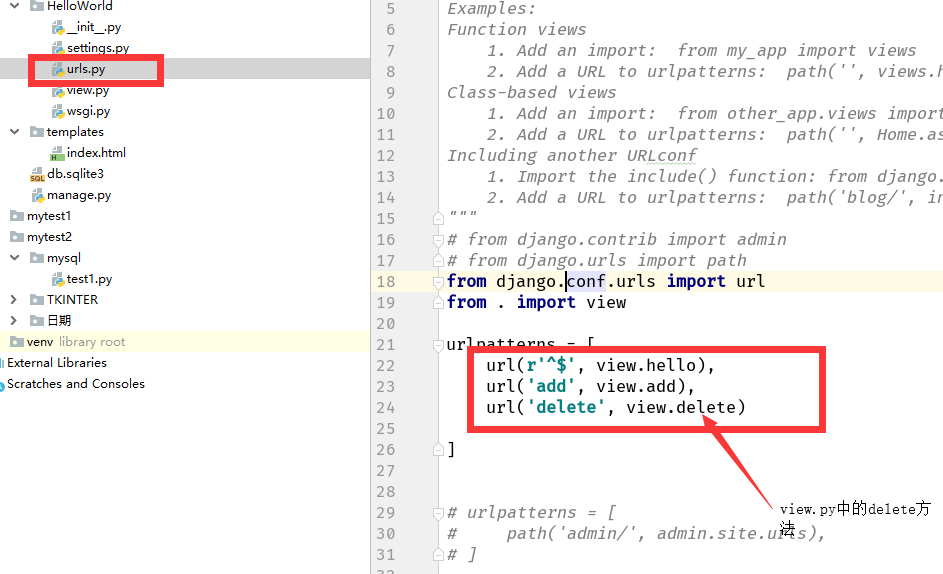
接著,繫結 URL 與檢視函式。開啟 urls.py 檔案,刪除原來程式碼,將以下程式碼複製貼上到 urls.py 檔案中:
`HelloWorld/HelloWorld/urls.py` 檔案程式碼:
from django.conf.urls import url
from . import view
urlpatterns = [
url(r’^$’, view.hello),
]
# 2.建立模板
`PS:一句話,模板就是靜態頁面`
在 HelloWorld 目錄底下建立 templates 目錄並建立 hello.html檔案,整個目錄結構如下:
HelloWorld/
|-- HelloWorld
| |-- init.py
| |-- init.pyc
| |-- settings.py
| |-- settings.pyc
| |-- urls.py
| |-- urls.pyc
| |-- view.py
| |-- view.pyc
| |-- wsgi.py
| -- wsgi.pyc |-- manage.py– templates
`-- hello.html
html裡面寫
{{ hello }}
```HelloWorld/HelloWorld/settings.py 檔案程式碼:
注意註釋地方,改這一處即可
...TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [BASE_DIR+"/templates",], # 修改位置
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]
HelloWorld/HelloWorld/view.py 檔案程式碼:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.shortcuts import render
def hello(request):
context = {}
context['hello'] = 'Hello World!'
return render(request, 'hello.html', context)
我們這裡使用 render 來替代之前使用的 HttpResponse。render 還使用了一個字典 context 作為引數。
context 字典中元素的鍵值 “hello” 對應了模板中的變數 “{{ hello }}”。
再訪問訪問 http://127.0.0.1:8000/hello,可以看到頁面
3.調整頁面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
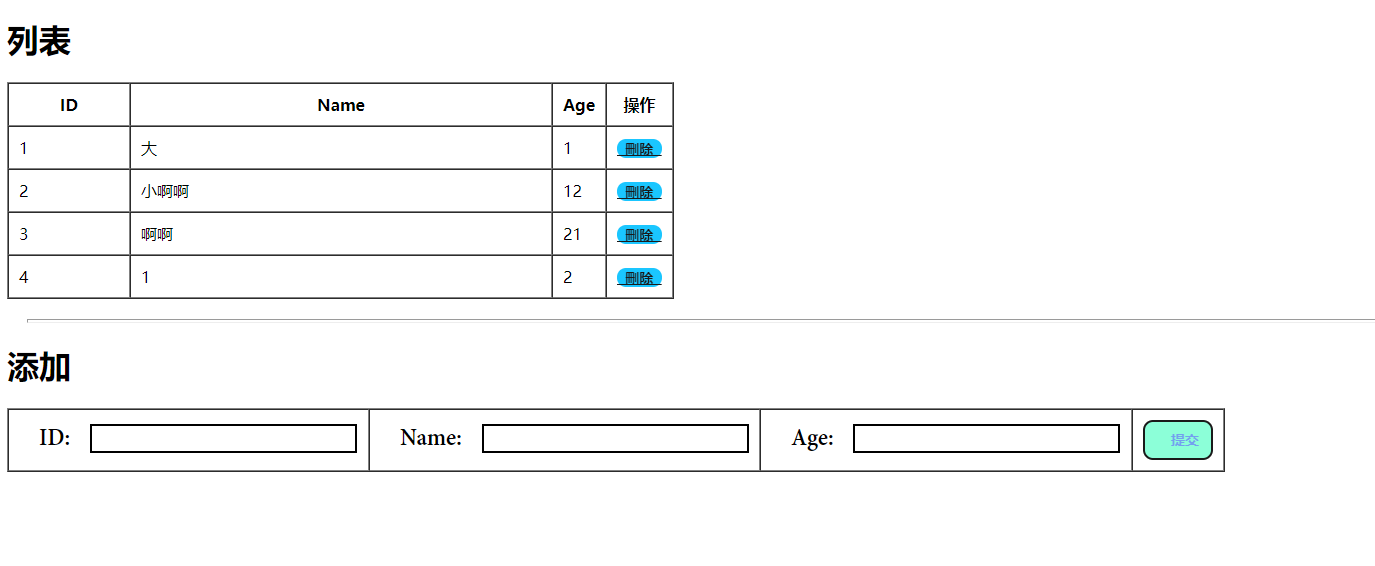
<h1>列表</h1>
<table border="1px" cellpadding="10px" cellspacing="0px">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
{% for user in userList %}
<tr>
<td width="100px">{{ user.ID }}</td>
<td width="400px">{{ user.USER_NAME }}</td>
<td width="20px">{{ user.USER_AGE }}</td>
<td><a href="/delete?id={{user.ID}}"> 刪除 </a></td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</div>
<hr/>
<div>
<h1>新增</h1>
<form action="/add" method="get">
{% csrf_token %}
<table border="1px" cellpadding="10px" cellspacing="0px">
<tr>
<td><span>ID:</span><input type="text" name="id"></td>
<td><span>Name:</span><input type="text" name="name"></td>
<td><span>Age:</span><input type="text" name="age"></td>
<td><input class="button" type="submit"></input></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<style>
input{
border: 2px solid black;
padding-left: 20px;
font-size: 20px;
}
span{
padding: 20px;
font-family: "Adobe Devanagari";
font-weight: bolder;
font-size: 25px;
}
.button{
width: 70px;
height: 40px;
background-color: aquamarine;
color: cornflowerblue;
font-weight: bolder;
font-size: 14px;
opacity: 0.9;
border-radius: 10px;
}
hr{
width: 80%;
height: 2px;
margin: 20px;
}
a{
width: 220px;
height: 40px;
background-color: deepskyblue;
color: black;
font-weight: bolder;
font-size: 14px;
opacity: 0.9;
border-radius: 10px;
}
</style>
4.寫邏輯程式碼
#from django.http import HttpResponse
import pymysql # 資料庫驅動
from django.http import HttpResponse # http響應
from django.shortcuts import render #跳轉頁面
from django.views.decorators import csrf
#資料庫連線
connection = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root',
password='root', db='test',charset='utf8',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
#建立資料庫連線“執行”物件
cur = connection.cursor()
#當我第一次進頁面的時候,查詢全部
def hello(request):
context = {} #封裝返回引數
sql = "SELECT * FROM user_py"
# 執行SQL語句
cur.execute(sql)
# 獲取所有記錄列表
results = cur.fetchall() #查詢所有
context['userList'] = results #存入集合
return render(request, 'index.html', context) #request,地址,引數
# 無視這個方法
def test():
print("test -- ")
# 新增
def add(request):
request.encoding = 'utf-8'
fuck = str(request) #這邊獲取的是url
values = fuck.split('?')[-1].rstrip("'>") #對url進行處理
param_list = values.split('&') # 獲取請求引數集合list
print(param_list[1]) # 不獲取第0個,第0個為token,從第一個獲取
print(param_list[2])
print(param_list[3])
id = param_list[1].split('=')[1] #這邊進行分割,因為原始字串為 “id=1”
name = param_list[2].split('=')[1]
age = param_list[3].split('=')[1]
print(id,name,age)
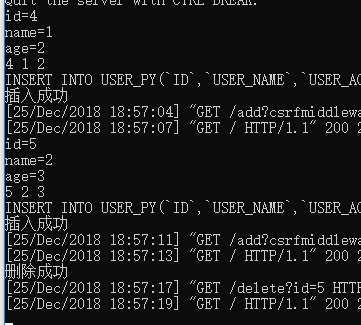
insert_sql = f"""INSERT INTO USER_PY(`ID`,`USER_NAME`,`USER_AGE`)values({id},"{name}",{age})"""
print(insert_sql)
cur.execute(insert_sql)
connection.commit() # 這邊注意一定要提交
print("插入成功")
return HttpResponse(request)
# 刪除
def delete(request):
request.encoding = 'utf-8'
fuck = str(request)
values = fuck.split('?')[-1].rstrip("'>")
param_list = values.split('&')
id = param_list[0].split('=')[1]
delete_sql = "DELETE FROM USER_PY WHERE ID = " + id
cur.execute(delete_sql)
print("刪除成功")
connection.commit()
return HttpResponse(request)
# def hello(request):
# return HttpResponse("Hello world ! ")
5.頁面
6.配置路由
附上一個表結構
CREATE TABLE `user_py` (
`ID` int(11) NOT NULL,
`USER_NAME` char(20) NOT NULL,
`USER_AGE` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
作者的話
這邊做的比較簡陋,點選刪除,跳的是空頁,新增也是,新增完成後要重新整理主頁面才會出現新的資料,資料庫裡面是已經新增成功的。
工作之餘做的,望理解,修改未做,邏輯清楚修改已經不是問題
全套crud請看《python對mysql增刪改查+計算器+九九乘法表》 該篇文章
如果感覺不錯,請點贊,讚賞下哦,點選下面讚賞