Java 基礎-IO、stream 流、檔案操作
輸入輸出流的分類
在 java.io 包中,包含了輸入輸出操作所需的類。
I/O 流可以安裝不同的標準分類:
- 按照流的方向分類:
- 輸入流:將資訊從程式碼外部輸入程式碼
- 輸出流:將程式碼得到的資料輸出到檔案、網路、記憶體等地方
- 按照流的分工分類:
- 節點流:訪問磁碟、網路等獲取資料的流,可以直接例項化
- 處理流:對資訊進行加工轉換的流,需要基於節點流例項化
- 按處理資料的型別分類:
- 面向字元的流:處理字元資料,自動實現 Java 內部格式(16 bit char 型別)與外部格式(UTF-8 等)的轉換。基類是 Reader 和 Writer
- 面向位元組的流:處理一般資料,基類是 InputStream 和 OutputStream
輸入輸出流
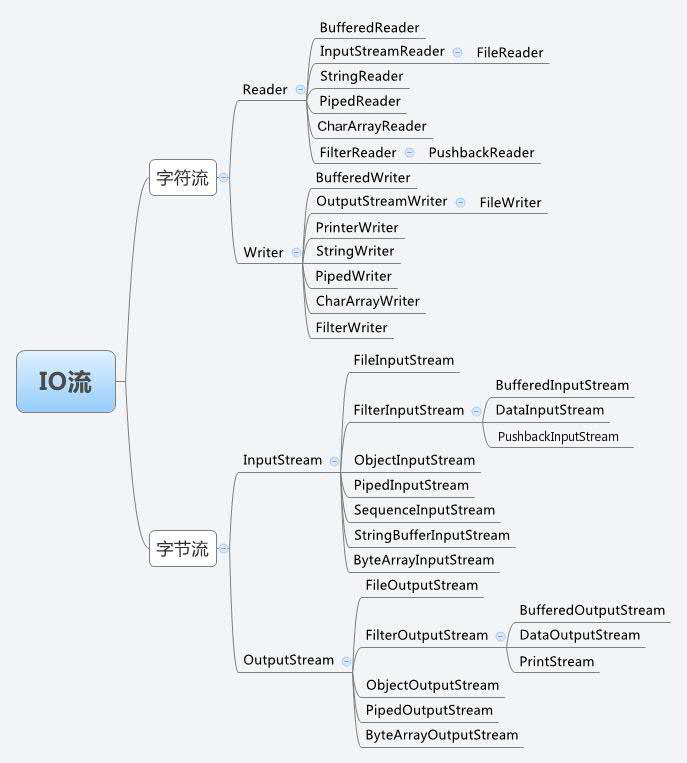
字元流
字元輸入流 Reader
所有的字元輸入流都繼承自 Reader 類。
常用的字元輸入流有:BufferedReader、InputStreamReader、FilterReader、StringReader、PipedReader、CharArrayReader。
字元輸出流 Writer
所有的字元輸出流都繼承自 Writer 類。
常用的字元輸出流有:BufferedWriter、OutputStreamWriter、FilterWriter、StringWriter、PipedWriter、CharArrayWriter。
位元組流
位元組輸入流 InputStream
所有的位元組輸入流都繼承自 Writer 類。
常用的位元組輸入流有:FileInputStream、FilterInputStream(子類 BufferedInputStream)、ByteArrayInputStream。
位元組輸出流 OutputStream
所有的位元組輸出流都繼承自 Writer 類。
常用的位元組輸出流有:FileOutputStream、FilterOutputStream(子類 BufferedOutputStream)、ByteArrayOutputStream。
常用的輸入輸出流
FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream
這兩個類用於按位元組讀寫檔案。
FileInputStream 從檔案讀取位元組資料
可以用用字串型別的檔名或檔案物件建立 FileInputStream 類的物件。
- 使用字串型別的檔名建立輸入流物件讀取檔案:
InputStream f = new FileInputStream("C:/java/hello");
- 使用檔案物件來建立輸入流物件讀取檔案。首先得使用 File() 方法來建立一個檔案物件:
File f = new File("C:/java/hello");
InputStream out = new FileInputStream(f);
FileInputStream 物件的常用方法:
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| public void close() throws IOException{} | 關閉此檔案輸入流並釋放與此流有關的所有系統資源 |
| protected void finalize()throws IOException {} | 清除與該檔案的連線。確保在不再引用檔案輸入流時呼叫其 close 方法 |
| public int read()throws IOException{} | 從 InputStream 物件讀取一個位元組的資料。返回為整數值。如果已經到結尾則返回-1。 |
| public int read(byte[] r) throws IOException{} | 從輸入流讀取r.length長度的位元組。返回讀取的位元組數。如果是檔案結尾則返回-1。 |
| public int available() throws IOException{} | 返回下一次對此輸入流呼叫的方法可以不受阻塞地從此輸入流讀取的位元組數。返回一個整數值。 |
FileOutputStream 向檔案寫位元組資料
如果檔案不存在,FileOutputStream 會先建立檔案。
- 使用字串型別的檔名來建立一個輸出流物件:
OutputStream f = new FileOutputStream("C:/java/hello")
- 使用一個檔案物件來建立一個輸出流來寫檔案。我們首先得使用File()方法來建立一個檔案物件:
File f = new File("C:/java/hello");
OutputStream f = new FileOutputStream(f);
FileOutputStream 物件的常用方法:
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| public void close() throws IOException{} | 關閉此檔案輸入流並釋放與此流有關的所有系統資源。丟擲IOException異常。 |
| protected void finalize()throws IOException {} | 這個方法清除與該檔案的連線。確保在不再引用檔案輸入流時呼叫其 close 方法。丟擲IOException異常。 |
| public void write(int w)throws IOException{} | 把指定的位元組寫到輸出流中。注意一次只能寫一位元組 |
| public void write(byte[] w) | 把指定陣列中w.length長度的位元組寫到OutputStream中。 |
示例
import java.io.*;
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
byte [] arr = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'w', 'o', 'r'};
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("test.txt");
for (byte i : arr) {
os.write(i); // 寫一個位元組到檔案
}
os.write(arr); // 寫位元組陣列到檔案
os.close();
File f = new File("test.txt");
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(f);
System.out.println(is.read()); // 顯示 104
byte [] arr2 = new byte[10];
is.read(arr2);
for (byte i : arr2) {
System.out.print((char)i);
}
is.close();
is = new FileInputStream(f);
int size = is.available();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print((char)(is.read()));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
上面程式的輸出為:
104
ello worhehello worhello wor
檔案 test.txt 內容為:
hello worhello wor
OutputStreamWriter 和 InputStreamReader
這兩個類用於轉換位元組流和字元流。
OutputStreamWriter
OutputStreamWriter 是將字元流轉為位元組流的橋樑,可以用指定的編碼將字元編碼為位元組。可以在構造方法中指定字符集,或者預設用作業系統字符集。
使用字串型別的檔名來建立一個輸出流物件:
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, CharsetEncoder enc)
OutputStreamWriter 物件的常用方法:
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| void close() | 關閉流,關閉之前會自動清空 |
| void flush() | 清空流 |
| String getEncoding() | 返回當前流的字元編碼 |
| void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 寫入字元陣列的一部分 |
| void write(int c) | 寫入一個字元 |
| void write(String str, int off, int len) | 寫入字串的一部分 |
InputStreamReader
將位元組流轉為字元流。讀取位元組並按照指定的字符集解碼為字元。
InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs)
FileOutputStream 物件的常用方法:
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| void close() | 關閉流並釋放相關的系統資源 |
| String getEncoding() | 返回當前流使用的字符集編碼 |
| int read() | 讀一個字元 |
| int read(char[] cbuf, int offset, int length) | 將字元讀到陣列的指定部分 |
| boolean ready() | 表示當前流是否就緒,可以隨時讀資料 |
示例
import java.io.*;
public class StreamTrans {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
char[] arr = new char[10];
isr.read(arr);
System.out.println(arr);
isr.close();
}
}
FileReader 和 FileWriter
用於按字元讀寫檔案。跟 FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream 類似。
BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter
這兩個類可以為 I/O 操作提供緩衝區,實現單個字元、陣列和字串的讀寫。
BufferedReader
繼承自 Reader。
比 FileReader 類多了個 readLine() 方法,可以一次讀取完整的一行(跨平臺)。
BufferedWriter
BufferedWriter 有個跨平臺的 newLine() 方法,可以在各個平臺實現統一的換行效果。
示例
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("test.txt"));
bw.newLine();
bw.write("hehe");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("hehe");
bw.flush();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("test.txt"));
String line = br.readLine();
while (line != null) {
System.out.println(line);
line = br.readLine();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
輸出:
hehe
hehe
DataOutputStream 和 DataInputStream
這兩個類具有寫各種基本資料型別的方法,且各種型別可以跨平臺。另外,可以用 size() 方法統計寫入的位元組數。
DataOutputStream
常用方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| void flush() | Flushes this data output stream. |
| int size() | 返回當前計數器的值,目前已經寫入這個流的位元組數 |
| void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 從指定的位元組陣列 off 偏移處,寫 len 個位元組到輸出流 |
| void write(int b) | 寫入指定的位元組(引數 b 的低8位)到輸出流 |
| void writeBoolean(boolean v) | 將布林資料作為1位元組的值寫到輸出流 |
| void writeByte(int v) | 將位元組資料作為1位元組的值寫到輸出流 |
| void writeBytes(String s) | 將字串作為位元組序列寫到輸出流 |
| void writeChar(int v) | 將字元資料作為2位元組的值寫到輸出流,高位在前 |
| void writeChars(String s) | 將字串作為字元序列寫到輸出流 |
| void writeDouble(double v) | 通過 Double 類中的 doubleToLongBits 方法將double型別引數轉為long 型別後,將其完整的8位元組寫入輸出流,高位元組在前 |
| void writeFloat(float v) | |
| void writeInt(int v) | |
| void writeLong(long v) | |
| void writeShort(int v) | |
| void writeUTF(String str) |
DataInputStream
可以按照指定的型別讀取資料。
示例
import java.io.*;
public class DataStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test.txt"));
dos.writeInt(666);
dos.writeBoolean(false);
dos.writeChars("hello world");
dos.flush();
System.out.println(dos.size()); // 總位元組數
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.txt"));
System.out.println(dis.readInt()); // 讀整型資料
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dis.readByte());
}
}
標準輸入輸出流
System 類的靜態成員變數,包括:
- System.in:InputStream 型別的標準輸入流,預設是鍵盤
- System.out:PrintStream 型別的標準輸出流,預設是顯示器
- System.err:PrintStream 型別的標準錯誤輸出流,預設也是輸出到顯示器
按型別輸入輸出資料
- printf 方法格式化輸出,其中多了
%n這個平臺無關的換行標誌 - Scanner 類從標準輸入流獲取指定型別的輸入,支援 nextLine()、nextByte() 等方法:
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int i = s.nextInt();
標準輸入輸出流重定向
可以將標準流重定向到檔案,這樣在使用標準輸出流時,實際使用的就是檔案了。
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.txt"));
OutputStream out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("out.txt"));
System.setIn(in);
System.setOut(out);
System.setErr(out);
File 類
File 類提供了檔案的相關操作,包括:
- 建立、刪除、重新命名檔案
- 判斷檔案是否存在
- 判斷檔案的讀寫許可權
- 設定和查詢檔案的最新修改時間
import java.io.*;
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("test.txt");
if (f.exists()) { // 判斷檔案或目錄是否存在
f.delete(); // 刪除檔案或目錄
} else {
try {
f.createNewFile(); // 建立檔案
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
}
物件序列化
如果需要在程式結束時儲存物件的資訊,可以將物件序列化後儲存到磁碟上。前提是物件已經實現了 Serializable 介面:
- ObjectOutputStream 可以用 writeObject 方法把物件寫入磁碟
- ObjectInputStream 可以用 readObject 方法把物件讀入程式
對於序列化時不想儲存的屬性,可以加 transient 修飾。另外 static 型別的變數,不屬於任何一個物件,所以也不會序列化。
RandomAccessFile 類
Java 把輸入輸出都當做位元組流處理,所以對隨機的檔案讀寫支援的不太好。
- 可跳轉到檔案的任意位置讀寫
- RandomAccessFile 類實現了 DataInput 和 DataOutput 介面,可以使用普通讀寫方法
