P4196 [CQOI2006]凸多邊形 半平面交
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-30
\(\color{#0066ff}{題目描述}\)
逆時針給出n個凸多邊形的頂點座標,求它們交的面積。例如n=2時,兩個凸多邊形如下圖:

則相交部分的面積為5.233。
\(\color{#0066ff}{輸入格式}\)
第一行有一個整數n,表示凸多邊形的個數,以下依次描述各個多邊形。第i個多邊形的第一行包含一個整數mi,表示多邊形的邊數,以下mi行每行兩個整數,逆時針給出各個頂點的座標。
\(\color{#0066ff}{輸出格式}\)
輸出檔案僅包含一個實數,表示相交部分的面積,保留三位小數。
\(\color{#0066ff}{輸入樣例}\)
2 6 -2 0 -1 -2 1 -2 2 0 1 2 -1 2 4 0 -3 1 -1 2 2 -1 0
\(\color{#0066ff}{輸出樣例}\)
5.233\(\color{#0066ff}{資料範圍與提示}\)
100%的資料滿足:2<=n<=10,3<=mi<=50,每維座標為[-1000,1000]內的整數
\(\color{#0066ff}{題解}\)
半平面交裸題
開兩個結構體儲存點和線
根據輸入方式,自己定義直線方向,那麼半平面的方向就確定了
程式碼中規定的方向是向量左邊
兩個向量求交(\(AC, BE\))
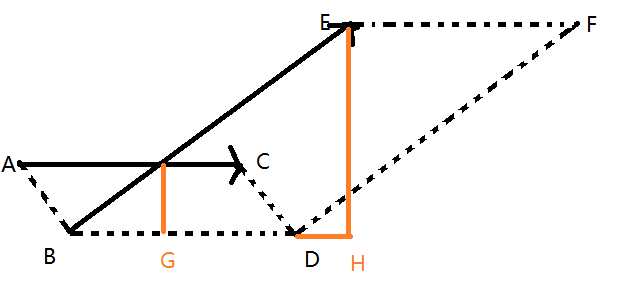
做出這樣的平行四邊形
過E作EH,過p(交點)作PG
顯然BPG,BEH相似,而且作的兩條線為平行四邊形的高
又因為兩個平行四邊形的底相等
所以高之比等於相似比?
通過叉積可以獲得面積比(相似比)
然後\(p = B + k * v_2\)
以上為向量求交點
我們維護一個雙端佇列
每次來一跳新的直線,把收到影響的隊首,隊尾彈出
最後佇列裡就是有效直線
把相鄰的交點都求出來,那麼這個多邊形的面積就是半平面交的面積
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define LL long long LL in() { char ch; int x = 0, f = 1; while(!isdigit(ch = getchar()))(ch == '-') && (f = -f); for(x = ch ^ 48; isdigit(ch = getchar()); x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48)); return x * f; } const int maxn = 505; double eps = 1e-8; int T(double x) { if(x > eps) return 1; if(x < -eps) return -1; return 0; } struct node { double x, y; node(double x = 0, double y = 0): x(x), y(y) {} node operator + (const node &b) const { return node(x + b.x, y + b.y); } node operator - (const node &b) const { return node(x - b.x, y - b.y); } double operator ^ (const node &b) const { return x * b.y - y * b.x; } double jj() const { return atan2(y, x); } node operator * (double b) const { return node(x * b, y * b); } }e[maxn]; struct line { node from, to; line(node from = node(), node to = node()): from(from), to(to) {} double jj() const { return (to - from).jj(); } bool operator < (const line &b) const { return T(jj() - b.jj()) == 0? T((to - from) ^ (b.to - from)) > 0 : T(jj() - b.jj()) < 0; } }a[maxn], q[maxn]; int n, head, tail, ji; node to(line i, line j) { node x = i.to - i.from, y = j.to - j.from, z = j.from - i.from; return j.from + y * ((z ^ x) / (x ^ y)); } bool jud(line x, line y, line z) { node p = to(x, y); return ((z.to - z.from) ^ (p - z.from)) < 0; } void work() { std::sort(a + 1, a + ji + 1); int cnt = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= ji; i++) { if(T(a[i].jj() - a[i - 1].jj())) cnt++; a[cnt] = a[i]; } head = 1, tail = 0; q[++tail] = a[1], q[++tail] = a[2]; for(int i = 3; i <= cnt; i++) { while(head < tail && jud(q[tail - 1], q[tail], a[i])) tail--; while(head < tail && jud(q[head + 1], q[head], a[i])) head++; q[++tail] = a[i]; } while(head < tail && jud(q[tail - 1], q[tail], q[head])) tail--; while(head < tail && jud(q[head + 1], q[head], q[tail])) head++; q[tail + 1] = q[head]; ji = 0; for(int i = head; i <= tail; i++) e[++ji] = to(q[i], q[i + 1]); } int main() { n = in(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { int F = in(); for(int j = 1; j <= F; j++) e[j].x = in(), e[j].y = in(); e[F + 1] = e[1]; for(int j = 1; j <= F; j++) a[++ji] = line(e[j], e[j + 1]); } work(); double ans = 0; e[ji + 1] = e[1]; if(ji > 2) for(int i = 1; i <= ji; i++) ans += (e[i] ^ e[i + 1]); printf("%.3f", fabs(ans) / 2.0); return 0; }
