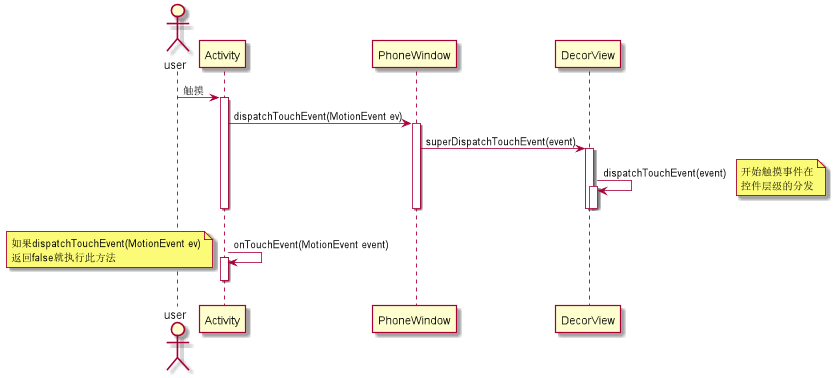
android觸控事件的分發
本文根據原始碼來梳理流程
一、觸控事件傳遞流程
使用者觸控式螢幕幕,Ativity是最先接觸到螢幕的,然後將觸控事件傳遞到DecorView,然後由DecorView處理具體的事件分發。
二.ViewGroup和View事件分發邏輯
ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)執行具體的事件分發。
1.觸控事件的down動作的執行分發流程。
首先會去清空mFirstTouchTarget和將當前ViewGroup的事件分發可以執行打斷方法的狀態標誌(即可以執行onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)方法),每個down動作都會清空之前事件儲存的狀態。
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) { //清空mFirstTouchTargetcancelAndClearTouchTargets(ev);
//設定mGroupFlags裡面可以執行onInterceptTouchEvent()方法的標誌位
resetTouchState();
}down動作可以執行下面程式碼,因為允許打斷
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0; if (!disallowIntercept) { intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev); ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed} else { intercepted = false; }else {
// There are no touch targets and this action is not an initial down // so this view group continues to intercept touches. intercepted = true; }
如果intercepted==false,ViewGroup不打斷事件傳遞,那麼就會像子控制元件分發down動作。
if (!canceled && !intercepted) { // If the event is targeting accessiiblity focus we give it to the// view that has accessibility focus and if it does not handle it // we clear the flag and dispatch the event to all children as usual. // We are looking up the accessibility focused host to avoid keeping // state since these events are very rare. View childWithAccessibilityFocus = ev.isTargetAccessibilityFocus() ? findChildWithAccessibilityFocus() : null;
//一定是要down動作或者滑鼠停留在Viewgroup才會執行下面程式碼
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) {
final int actionIndex = ev.getActionIndex(); // always 0 for down
final int idBitsToAssign = split ? 1 << ev.getPointerId(actionIndex)
: TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS;
// Clean up earlier touch targets for this pointer id in case they
// have become out of sync.
removePointersFromTouchTargets(idBitsToAssign);
final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount;
if (newTouchTarget == null && childrenCount != 0) {
final float x = ev.getX(actionIndex);
final float y = ev.getY(actionIndex);
// Find a child that can receive the event.
// Scan children from front to back.
final ArrayList<View> preorderedList = buildTouchDispatchChildList();
final boolean customOrder = preorderedList == null
&& isChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled();
final View[] children = mChildren; //遍歷迴圈
for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final int childIndex = getAndVerifyPreorderedIndex(
childrenCount, i, customOrder);
final View child = getAndVerifyPreorderedView(
preorderedList, children, childIndex);
// If there is a view that has accessibility focus we want it
// to get the event first and if not handled we will perform a
// normal dispatch. We may do a double iteration but this is
// safer given the timeframe.
if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != null) {
if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != child) {
continue;
}
childWithAccessibilityFocus = null;
i = childrenCount - 1;
}
//如果該子控制元件不是觸控
if (!canViewReceivePointerEvents(child)
|| !isTransformedTouchPointInView(x, y, child, null)) {
ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
continue;
}
newTouchTarget = getTouchTarget(child);
if (newTouchTarget != null) {
// Child is already receiving touch within its bounds.
// Give it the new pointer in addition to the ones it is handling.
newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign;
break;
}
resetCancelNextUpFlag(child);if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) { // Child wants to receive touch within its bounds. mLastTouchDownTime = ev.getDownTime(); if (preorderedList != null) { // childIndex points into presorted list, find original index for (int j = 0; j < childrenCount; j++) { if (children[childIndex] == mChildren[j]) { mLastTouchDownIndex = j; break; } } } else { mLastTouchDownIndex = childIndex; } mLastTouchDownX = ev.getX(); mLastTouchDownY = ev.getY(); newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign); alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true; break; } // The accessibility focus didn't handle the event, so clear // the flag and do a normal dispatch to all children. ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false); } if (preorderedList != null) preorderedList.clear(); } if (newTouchTarget == null && mFirstTouchTarget != null) { // Did not find a child to receive the event. // Assign the pointer to the least recently added target. newTouchTarget = mFirstTouchTarget; while (newTouchTarget.next != null) { newTouchTarget = newTouchTarget.next; } newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign; } } }以上程式碼,在向下分發事件的時候要呼叫dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()方法,它是真正控制分發事件是自己處理還是對應的子控制元件來處理。如果交給自己的父類dispatchTouchEvent()處理,就會執行onTouchEvent()方法,onTouchEvent()方法就是處理具體的觸控事件的。onTouchEvent()的執行是有條件的,要根據當前控制元件是否新增OnTouchListener和OnTouchListener.onTouch()是否消耗了此事件來決定的,可以檢視原始碼瞭解邏輯。使用者的新增的點選事件監聽和長按監聽也是在onTouchEvent()裡面處理的,所以自定義控制元件重寫OnTouchEvent()的時候需要注意。
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel, View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) { final boolean handled; // Canceling motions is a special case. We don't need to perform any transformations // or filtering. The important part is the action, not the contents. final int oldAction = event.getAction(); if (cancel || oldAction == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL) { event.setAction(MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL); if (child == null) { handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event); } else { handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event); } event.setAction(oldAction); return handled; } // Calculate the number of pointers to deliver. final int oldPointerIdBits = event.getPointerIdBits(); final int newPointerIdBits = oldPointerIdBits & desiredPointerIdBits; // If for some reason we ended up in an inconsistent state where it looks like we // might produce a motion event with no pointers in it, then drop the event. if (newPointerIdBits == 0) { return false; } // If the number of pointers is the same and we don't need to perform any fancy // irreversible transformations, then we can reuse the motion event for this // dispatch as long as we are careful to revert any changes we make. // Otherwise we need to make a copy. final MotionEvent transformedEvent; if (newPointerIdBits == oldPointerIdBits) { if (child == null || child.hasIdentityMatrix()) { if (child == null) { handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event); } else { final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft; final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop; event.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY); handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event); event.offsetLocation(-offsetX, -offsetY); } return handled; } transformedEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(event); } else { transformedEvent = event.split(newPointerIdBits); } // Perform any necessary transformations and dispatch. if (child == null) { handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent); } else { final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft; final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop; transformedEvent.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY); if (! child.hasIdentityMatrix()) { transformedEvent.transform(child.getInverseMatrix()); } handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent); } // Done. transformedEvent.recycle(); return handled; }
如果down動作被子控制元件給消耗掉了(返回true),就會執行下面的程式碼,會在addTouchTarget()方法裡面給mFirstTouchTarget賦值,alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true;
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) { // Child wants to receive touch within its bounds. mLastTouchDownTime = ev.getDownTime(); if (preorderedList != null) { // childIndex points into presorted list, find original index for (int j = 0; j < childrenCount; j++) { if (children[childIndex] == mChildren[j]) { mLastTouchDownIndex = j; break; } } } else { mLastTouchDownIndex = childIndex; } mLastTouchDownX = ev.getX(); mLastTouchDownY = ev.getY(); newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign); alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true; break; } // The accessibility focus didn't handle the event, so clear // the flag and do a normal dispatch to all children. ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false); } if (preorderedList != null) preorderedList.clear(); }
最後down動作會執行以下程式碼
if (alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget && target == newTouchTarget) { handled = true; }最後在dispatchTouchEvent()的最後會返回
return handled;如果down動作被攔截或者向下分發的時候不消耗此事件,這個時候mFirstTouchTarget == null。這個時候回去執行下面程式碼
if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) { // No touch targets so treat this as an ordinary view. handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null, TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS); }
上面child的引數是null,這個時候回去執行父類也就是Viewd的dispatchTouchEvent()方法,最後會呼叫到自己的onTouchEvent(),這也就是當ViewGroup的子控制元件不消費這個觸控事件的時候或者當前容器攔截了觸控事件就會執行自己的onTouchEvent()方法。
2.觸控事件的move和up動作的分發流程。
move和up動作在分發流程上大致是一致的,但是不會去遍歷子控制元件查詢對應的可以消耗此事件的子控制元件,這個操作之前的down動作已經做了。如果有子控制元件消耗了down事件就會將對應的子控制元件儲存在mFirstTouchTarget裡面。
當move和up動作在ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent()裡面開始執行的時候,有兩種情況,是根據之前move動作的執行結果而受到影響的,即mFirstTouchTarget是否為空。我們分這兩種情況來分析
(1).mFirstTouchTarget == null,即move動作的時候,被viewgroup打斷或者子控制元件不消費此事件。
開始的時候,如果使用者沒有修改mGroupFlags的攔截標誌位話,預設是會執行onInterceptTouchEvent();
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0; if (!disallowIntercept) { intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev); ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed } else { intercepted = false; }
因為只有down動作的時候才會去遍歷子控制元件分發分發事件,當是move和up動作的時候newTouchTarget == null,alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget == false;
接下來會執行下面程式碼
if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) { // No touch targets so treat this as an ordinary view. handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null, TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS); }
這個時候回去執行父類也就是Viewd的dispatchTouchEvent()方法,最後會呼叫到自己的onTouchEvent()。
(2).mFirstTouchTarget != null,即ViewGroup的子控制元件消耗了此事件。
開始的時候,如果使用者沒有修改mGroupFlags的攔截標誌位話,預設是會執行onInterceptTouchEvent();
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0; if (!disallowIntercept) { intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev); ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed } else { intercepted = false; }
因為只有down動作的時候才會去遍歷子控制元件分發分發事件,當是move和up動作的時候newTouchTarget == null,alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget == false;
這個時候就會執行如下程式碼,會將move、up事件通過dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev,cancekChild,target.child,target.pointerIdBits)傳遞個對應的子控制元件處理或者自己處理。
final boolean cancelChild = resetCancelNextUpFlag(target.child) || intercepted; if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, cancelChild, target.child, target.pointerIdBits)) { handled = true; } if (cancelChild) { if (predecessor == null) { mFirstTouchTarget = next; } else { predecessor.next = next; } target.recycle(); target = next; continue; }
3.觸控事件的cancel動作的執行流程
一般情況下cancel事件的產生是由於viewgroup向下分發事件的時候,之前的事件能正常傳遞到子控制元件,但是在中途某個事件被某個ViewGroup攔截了,這個VIewGroup要處理這個事件,那麼就需要向子控制元件傳遞cancel事件,讓子控制元件根據cancel做相應的處理。我們可以看這裡的程式碼
final boolean cancelChild = resetCancelNextUpFlag(target.child) || intercepted; if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, cancelChild, target.child, target.pointerIdBits)) { handled = true; }此時cancelChild = true,再到dispatchTransforedTouchEvent()裡面看程式碼。它會修改當前的事件的動作為cancel,然後向下傳遞給子控制元件,最後還原當前事件的動作。
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel, View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) { final boolean handled; // Canceling motions is a special case. We don't need to perform any transformations // or filtering. The important part is the action, not the contents. final int oldAction = event.getAction(); if (cancel || oldAction == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL) { event.setAction(MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL); if (child == null) { handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event); } else { handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event); } event.setAction(oldAction); return handled;
}
……
}
總結:
在Viewgroup的dispatchTouchEvent()裡面會預設執行onInterceptTouchEvent()方法。使用者可以通過呼叫requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent()來決定是否執行onInterceptToucheEvent()方法。
1.down事件在Viewgroup的dispatchTouchEvent()裡面做了遍歷查詢是否有子控制元件能消費此事件,如果消費了此事件就儲存子控制元件,如果沒有就自己消費,具體消費就是將觸控事件傳遞給自己的onTouchEvent()。
2.move和up事件在Viewgroup的dispatchTouchEvent()裡面直接根據有沒有子控制元件消費之前的down事件來來判斷是將事件傳遞給自己的onTouchEvent()還是傳遞給子控制元件的dispatchTouchEvent().
3.ViewGroup和View的dispatchTouchEvent()又要檢視原始碼。
4.ViewGroup的具體事件分發是由dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()來完成的。