內部排序演算法比較(超詳解)
一、題目描述
通過隨機資料比較各排序演算法的關鍵字比較次數和關鍵字移動次數,以 及執行時間,取得直觀感受。
二、設計要求
一、需求分析
實現各排序演算法,分別進行以下各組比較,並進行總結。
一、各演算法在不同規模下的比較。
1)比較範圍:直接插入排序、冒泡法排序、簡單選擇排序、快速排序1(自己實現)、快速排序2(呼叫STL)、歸併排序。
2)比較指標:a)關鍵字操作次數(比較次數和移動次數之和),b)排序時間。每個指標採用多次重複取平均數記錄,重複次數不小於100。注:1次關鍵字對換按3次移動計算。
3)資料規模:分別為50,100,500,1000,5000,10000;
4)資料型別:隨機資料
二、演算法在不同資料型別下的比較
1)比較範圍:直接插入排序、冒泡法排序、簡單選擇排序、快速排序1(自己實現)、快速排序2(呼叫STL)、歸併排序。
2)比較指標:a)關鍵字操作次數(比較次數和移動次數之和),b)排序時間。每個指標採用多次重複取平均數記錄,重複次數不小於100。注:1次關鍵字對換按3次移動計算。
3)資料規模:10000;
4)資料型別:隨機資料、正序資料、逆序資料;
三、程式碼要求
1、必須要有異常處理,比如刪除空連結串列時需要丟擲異常;
2、保持良好的程式設計的風格:
程式碼段與段之間要有空行和縮近
識別符號名稱應該與其代表的意義一致
函式名之前應該添加註釋說明該函式的功能 、關鍵程式碼應說明其功能
3、遞迴程式注意呼叫的過程,防止棧溢位
四、演算法分析
#include<iostream>
#include<time.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//關鍵次數初始化 六、結果截圖
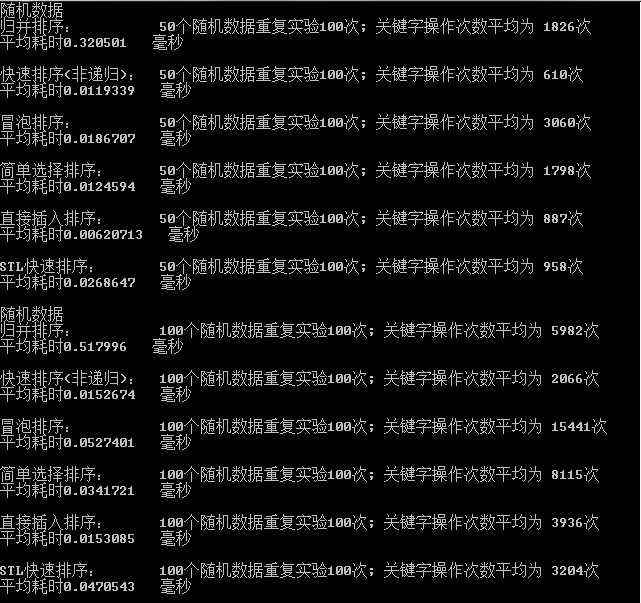
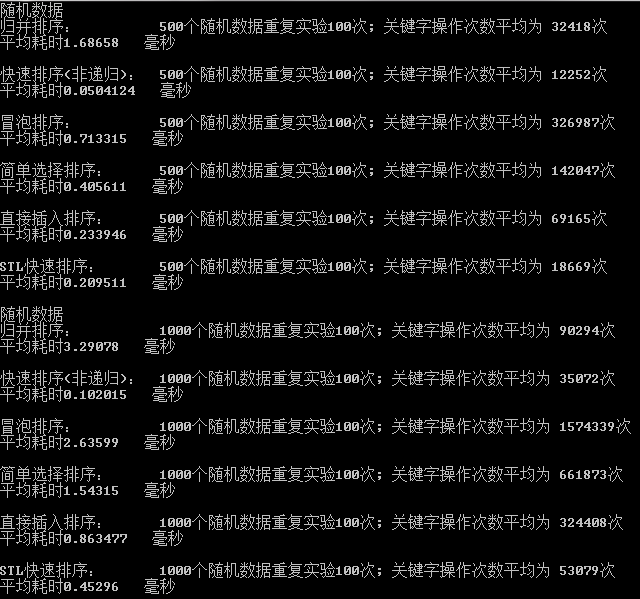
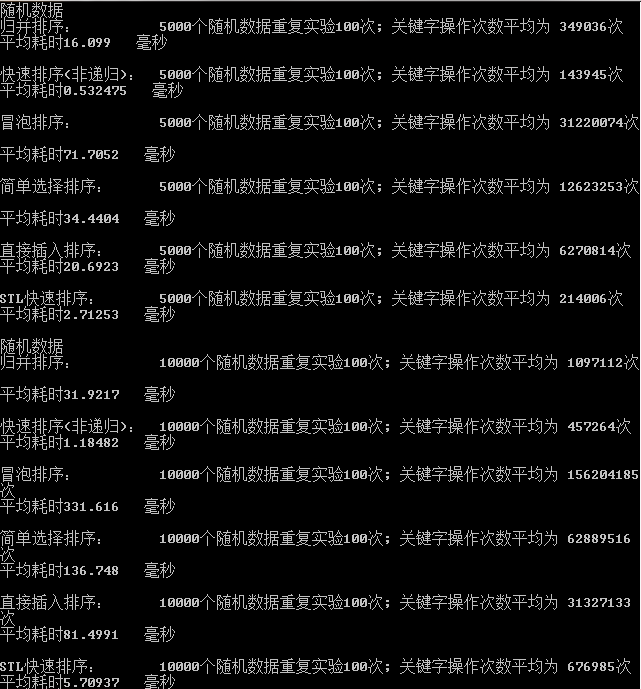


七、結果分析:
1、隨機資料比較:資料規模分別為50,100,500,1000,5000,10000,我們經過驗證可以得出初步結論:
在資料基本無序的狀態下且資料較多:排序效率比較如下:
快速排序法>STL快速排序法>歸併排序法>直接插入排序法>簡單選擇法>
氣泡排序法
在資料基本無序的狀態下且資料較少:排序效率比較如下:
快速排序法>STL快速排序法>直接插入排序法簡單選擇法>氣泡排序法>
歸併排序法
在資料更少的情況下,直接插入法也有奇效。
2、正序資料比較:資料規模為10000,我們經過驗證可以得出初步結論:
在資料基本有序且為正序的狀態下:排序效率如下:
直接插入排序>STL快速排序法>歸併排序>快速排序>簡單選擇排序>
氣泡排序法
3、逆序資料比較:資料規模為10000,我們經過驗證可以得出初步結論:
在資料基本有序且為正序的狀態下:排序效率如下:
STL快速排序法>歸併排序>快速排序>直接插入排序>簡單選擇排序>
氣泡排序法
八、總結
1、涉及遞迴的有歸併排序以及快速排序,這兩個都是我編寫程式的時候感覺最艱難的。
2、歸併排序使用的陣列除了中間要合併用的那個rf2用的是靜態陣列,其他都是動態陣列new建立的,堆建立陣列本來是挺好的,可是這裡卻因為資料規模較大的時候,遞迴太深rf2又無法delete[],只能用陣列,建立了一個rf2[10001].
3、快速排序我寫了兩種方法,一種是遞迴的,一種是非遞迴的,遞迴真的理解是最簡單的,可是對堆疊真的要求太高了,遞迴本來是崩潰的,不過忽然找到了方法:因為快排遞迴需要堆疊太大,一般電腦需要調整堆疊,我改動的為5032768位元組(隨便,夠大就好)
4、時間精度的問題也好解決,用的是QueryPerformance,這個精度非常好,學到的好東西。
