The Many Faces of Bitcoin
John Nash, a Nobel Prize economist who made significant contributions to game theory such as the Nash Equilibrium and Bargaining Problem, believed that although Keynesian economic policies were, in theory, intended to be for solely noble objectives and general welfare of the people, in practice these policies simply gave governments the ability to literally print money, collecting seigniorage by way of inflation of the money supply. Nash often likened Keynesians to Bolshevik Communists, as he saw that both groups gave credence to the notions of a centrally managed system and a lack of transparency surrounding decisions, especially with regards to the nation-state’s currency issuance.
Nash wrote that by discussing inflation targeting, central banking officials are essentially revealing that is possible to control inflation by controlling the supply of money. Central banks, in their calculations, use a cost-of-living index made up of domestic prices for goods in a given region of their nation-state. Nash introduced a notion he called the Industrial Consumer Price Index, or ICPI, which would provide an international standard for value comparison of goods via a formula incorporating differing prices of goods in a variety of locations.
Nash believed that a return to the Gold Standard was sub-optimal, because he believed that technological changes would result in increasing unpredictability of the future cost of gold production. He also considered the locations of gold mines to not be “politically appealing” nor ideal, and that a return to the Gold Standard would arbitrarily enhance the economic importance of those particular areas.
Nash’s Ideal Money proposal, in a nutshell, is an idea that although we cannot design a perfectly stable money, a money that approaches ‘stable’ would also approach a limit that would be comparable to an optimally chosen basket of commodity prices. While an ICPI would be a step on the path towards Nash’s vision of an Ideal Money, pegging a currency to the ICPI is not a solution, as it could fluctuate with changes in the supply or demand of commodities chosen for the index, thus necessitating an adjustment process that would be prone to political pressure.
Currently, global reserve currencies face the Triffin Dilemma, resulting in a conflict of interest between short-term domestic and long-term international objectives, such as a desire to increase inflation to spur economic growth, versus keeping a strong domestic currency with stability of purchasing power. Nash believed that money would be stronger if it were put on a stage of competition where it must compete to survive, and improve itself. Nowadays, however, currencies don’t really compete in a typical way like that which results in better products over time, but rather, they sometimes compete in a race to devalue. For Nash, rather than focusing on the utility of money for everyday transactions, of paramount importance was for the global economy to arrive at the same incorruptible value standard.
Bitcoin is seen by some as the catalyst for the evolution of global monetary systems toward something that would resemble stabilizing a currency versus an optimally chosen basket of commodity prices. Some believe that Nash’s writings from 1960’s may have even predicted the emergence of something like Bitcoin. Nash wrote: “Here I am thinking of a politically neutral form of a technological utility. To be quite respectable, in a Gresham-advised sense, money needs only to be as good as other material commodities that might be hoarded.”
Coincidentally, over the last several years, a global consensus over the nature of Bitcoin has slowly been converging on phrases like “digital gold”. Bitcoin has all the characteristics to acquire a global monetary premium, much the same as gold. The relation between scarcity and new supply is actually more important than scarcity of supply. In the next several years, bitcoin’s stock-to-flow ratio, the relation of its scarcity to its new supply, will drop below that of gold. Bitcoin’s annual inflation will continue to decrease. Many believe that during this time, bitcoin will draw growing interest as an inflation hedge from many around the world.
It is plausible that if Bitcoin continues seeing infrastructural improvements and growing place in the market, central banks and fiat currencies will themselves be forced to compete with Bitcoin in the future for relevance. It is likely that citizens of nation-states will put pressure on their central bank to print less money of a superior quality, resulting in a slower rate of inflation.If this were to occur, Bitcoin would likely usher similar effects to value stabilizing a currency versus an optimally chosen basket of commodity prices, without ever implementing an actual ICPI. This would force fiat currencies closer to Nash’s vision of Ideal Money. Nash’s goal is believed by some to be near, as Bitcoin represents competition to the nation-state control of money for the first time in centuries.
***
Fourth Theory: Bitcoin is an information and energy black hole that will result in the evolution of traditional money
Tenets: Perfect information and computational markets. Bitcoin is fractal and the sum of its forks. Peer-to-peer, censorship-resistant, borderless, cheap transfer of value, without middlemen. High on-chain throughput and on-chain utility.

“Bitcoin isn’t money. It’s past money, which is scary because it’s actually a new paradigm. We’ve never had access to perfect market information before, so the concept of money will have to evolve to fit reality, not stay the same because legacy deems it so.” — anonymous
There is also a niche number of individuals, the most prominent of which are George Gilder, author of a number of books on the monetary system and capitalism, Andrew DeSantis, former engineer at the Bitcoin startup 21.co, now earn.com, and Mark Wilcox, Director of Strategy at Nyriad, that discuss Bitcoin primarily as interpreted by Claude Shannon’s information theory. In simplistic terms, information is defined as surprise under information theory.


This group believes Bitcoin is a breakthrough in information theory because it allows anyone to conduct verifiable, timestamped, tamper-proof and transparent transactions without any third parties. Information theory says creativity requires a stable medium to experience fractal growth, and these individuals view Bitcoin as an extremely stable medium for doing so. In Knowledge and Power, Gilder argues “it takes a low-entropy carrier (no surprises) to bear high-entropy information (full of surprisal).” This camp also agrees with Bitcoin’s deflationary policy because they view capitalism and technological progress as a fundamentally deflationary system.



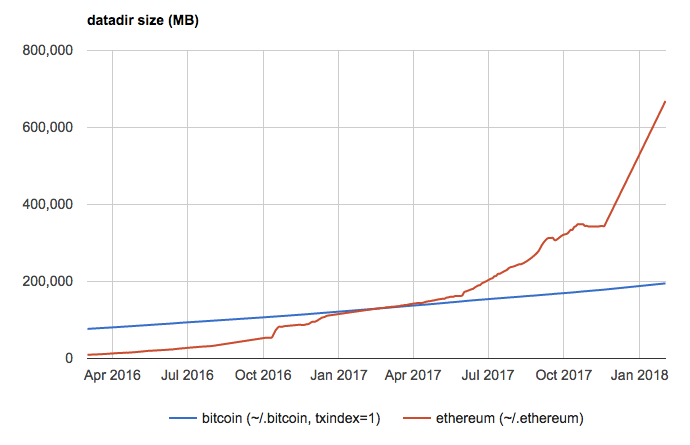

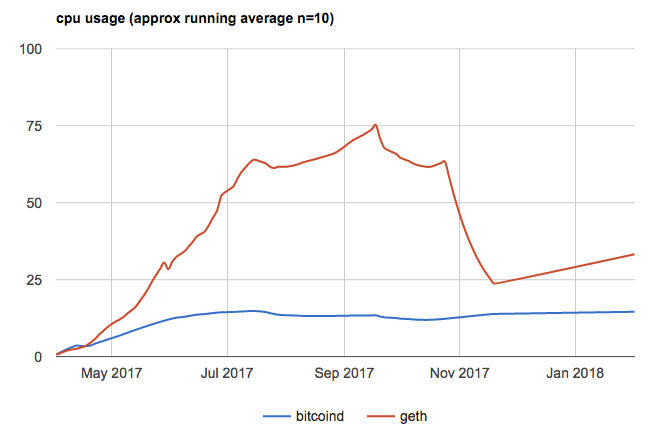
Similarly to Bitcoin Cash supporters, these individuals favor pushing Bitcoin to its limits to maximize the utility of an open data layer, and they are not fond of a future of Bitcoin where throughput is limited so that all users can verify transactions with a full node. This group views one use case of Bitcoin as an oracle machine to prove that a specific piece of data existed at a given point in time, and the bitcoin scripting language as much more capable than Ethereum in the long run due to the parallel nature of Bitcoin in comparison to the current serial execution forced by contracts on the Ethereum platform. They also believe Bitcoin will “wake up” in the future as a superintelligent AI and allow intelligence augmentation for humans.


This group views Bitcoin as a platform to re-build computer software and the web upon. For example, they are interested in the parallels between Ted Nelson’s Project Xanadu, the first hypertext project, and Bitcoin. Project Xanadu was envisioned to bring about a highly interconnected, parallel universe of documents for reading, writing, learning, and earning through hypertext, “non-sequential writing — text that branches and allows choices to the reader, best read at an interactive screen.” Xanadu was to operate through worldwide distributed servers and facilitate micro-transactions across the web.


As discussed in “Blockchain Control Flow,” Ethereum has made design decisions that allow the network to have control over contract execution, and thus users’ money. Wilcox writes “For a peer-to-peer network to be politically decentralised, it needs to have decentralised control, so we should at all times try to keep control completely in the private section.” He also writes that the “limitations” of Bitcoin as cited by Vitalik Buterin in the Ethereum Whitepaper are protections not limitations.

Individuals within this camp generally have negative opinions towards the Lightning Network and other secondary-layer solutions. DeSantis states the “Lightning Network makes the base chain strict, or predictable,” and thus reduces Bitcoin’s information theoretic value by constraining experimentation space and reducing the chances of surprise discovery. Wilcox views the Lightning Network as “a scam designed to function as an abstraction layer between you and the miners.”

When Wilcox discusses transaction processing, he is referring to verifying a transaction and hashing it into the merkle tree. Transaction processing can refer to almost anything, and he proposed a thesis that the same economic incentives that allowed Bitcoin’s hashrate to grow exponentially over the last nine years could be used to exponentially grow transaction processing, which is currently done serially on a CPU.


Nyriad, the company Wilcox co-founded, created the Nsulate for the Square Kilometre Array project, the world’s largest radio telescope. The Nsulate innovatively uses the GPU as a storage controller and makes processing and storing data the same thing. It has built in blockchain support through cryptographic hash algorithms, which would allow miners to process transactions in parallel.
Many of Wilcox’s arguments, therefore, are based on seeing Bitcoin as a platform to enable competitive general purpose computational markets where users and companies submit transaction puzzles via scripts for miners to compete to solve using GPUs and write-on chain to seek rewards. Transaction puzzles can mean nearly anything here, from deep learning to CRISPR searches.
With on-chain computational markets on Bitcoin, a user looking to submit computations to miners will care a lot about efficiency, to get the most computation per unit of reward they are including in a puzzle, and hashrate, to ensure the system they are submitting to is as secure as possible.
It is worth noting that similar projects can be built on secondary and third layer solutions, as well. For example, a “Layer 3” project called Fabric Protocol, led by former Blockstream engineer Eric Martindale, is aiming to become a distributed supercomputer and decentralized operating system using Bitcoin as a trust anchor, a Fabric sidechain, and payment channels.

Wilcox and DeSantis typically argue against the traditional supply and demand outlook of economic markets for blockchains, as described in the tweet above insinuating that hashrate will be price in the future. Wilcox discusses the implications of Proof of Work for transaction processing and scalability in his blog, including Fundamental Misconceptions. Computational markets sitting atop Bitcoin are particularly likely to expand if they prove to achieve cheaper and more efficient computation than established behemoths of the industry.
Conclusion
The four schools of thought presented in this article do not necessarily contradict one another, and, in fact, oftentimes overlap. In particular, the First Theory — Bitcoin being like a digital gold — and the Third Theory — Bitcoin leading to Nash’s Ideal Money — run pretty much in parallel to one another, with the key difference being that the latter states that fiat currencies survive and adjust, while the former states that hyperbitcoinization will disrupt fiat currencies entirely, with everyone eventually demanding payment for their goods, services, and labor in bitcoin.
Similarly, the Second Theory — Bitcoin Cash being a dominant peer-to-peer digital cash — and the Fourth Theory — Bitcoin being the key element in further developing information theory — have many of the same supporting points and arguments, with the key difference being that the latter is not fork-biased and believes that any possible fork that can happen, will happen, and they will compete against each other.
Thanks to armor123123 and others for giving us feedback on earlier versions of this post.
