FFmpeg實時解碼H264
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-31
ffmpeg的解碼過程在前面已經稍微總結了下,這裡主要是測試一下用ffmpeg如何進行實時的解碼。
在解碼之前,我們先做好準備工作,呼叫攝像頭。編碼的過程中,進行入隊出隊操作,出隊後的資料交給解碼器,進行解碼。
接下來依次介紹各個模組。
1.呼叫攝像頭:
怎麼利用opencv呼叫攝像頭,這裡不做過多介紹,可以參考這裡:點選開啟連結。VideoCapture capture(0); int w = capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH); int h = capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT); int yuv_bufLen = w * h * 3 / 2; unsigned char* pYuvBuf = new unsigned char[yuv_bufLen]; cout << "Frame size : " << w << " x " << h << endl; namedWindow("opencamera", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); while (1) { Mat frame; capture >> frame; imshow("opencamera", frame); if (waitKey(30) == 27) break; }
2.編碼過程:
DWORD WINAPI x264_encode(LPVOID lparam) { VideoCapture capture(0); if (!capture.isOpened()) { cout << "Cannot open the video cam" << endl; return -1; } int w = capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH); int h = capture.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT); result_link_type* result_link = (result_link_type*)lparam; int yuv_bufLen = w * h * 3 / 2; //unsigned char* pYuvBuf = new unsigned char[yuv_bufLen]; //int fps =25; size_t yuv_size = w * h * 3 / 2; x264_t *encoder; x264_picture_t pic_in, pic_out; uint8_t *yuv_buffer; x264_param_t param; //x264_param_default_preset(¶m, "veryfast", "zerolatency"); //為結構體param賦預設值 x264_param_default_preset(¶m, "veryfast", "animation"); //param.i_threads = 1; //並行編碼多幀 param.i_width = w; //視訊影象的寬 param.i_height = h; // param.i_fps_num = fps; //幀率分子 //param.i_fps_den = 1; //幀率分母 , fps_num / fps_den = 幀率 //param.i_keyint_max = 50; //IDR幀之間的間隔 //param.b_intra_refresh = 1; //是否使用週期幀內重新整理IDR幀 //param.b_annexb = 1; //加字首碼0x00000001 //param.rc.b_mb_tree = 0; //實時編碼必須為0,否則有延遲 //param.b_sliced_threads = 0; //x264_param_apply_profile(¶m, "baseline"); //編碼器的引數,使用baseline編碼,可以跟上面的引數做衝突比較 encoder = x264_encoder_open(¶m); //開啟編碼器,初始化param #if 1 x264_picture_alloc(&pic_in, X264_CSP_I420, w, h); //為pic_in分配記憶體 yuv_buffer = (uint8_t*)malloc(yuv_size); //給yuv_buffer分配記憶體 pic_in.img.plane[0] = yuv_buffer; //pic_in的三通道分別賦值 pic_in.img.plane[1] = pic_in.img.plane[0] + w * h; pic_in.img.plane[2] = pic_in.img.plane[1] + w * h / 4; int64_t i_pts = 0; x264_nal_t *nals; int nnal; FILE *fp_out = fopen("test.h264", "wb"); if (!fp_out) { printf("Could not open output 264 file\n"); return -1; } #if 1 FILE* pFileOut = fopen("test.yuv", "w+"); if (!pFileOut) { printf("Could not open input yuv file\n"); return -1; } #endif cout << "Frame size : " << w << " x " << h << endl; namedWindow("opencamera", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); Mat frame; while (1) { capture >> frame; //攝像頭處抓取一幀 imshow("opencamera", frame); //顯示 //if (waitKey(30) == 27) break; waitKey(1); cv::Mat yuvImg; cv::cvtColor(frame, yuvImg, CV_BGR2YUV_I420); //YUV轉RGB memcpy(yuv_buffer, yuvImg.data, yuv_bufLen*sizeof(unsigned char)); //YUV資料複製到yuv_buffer中 //fwrite(yuv_buffer, yuv_bufLen*sizeof(unsigned char), 1, pFileOut); //YUV寫入本地 //while (fread(yuv_buffer, 1, yuv_size, inf) > 0) //{ pic_in.i_pts = i_pts++; x264_encoder_encode(encoder, &nals, &nnal, &pic_in, &pic_out); //編碼一幀資料 x264_nal_t *nal; int j = 0; struct result_node_datatype *result_node = new struct result_node_datatype; result_node->result = new unsigned char[800000]; memset(result_node->result, '\0', 800000); result_node->size = 0; for (nal = nals; nal < nals + nnal; nal++) { //fwrite(nal->p_payload, 1, nal->i_payload, fp_out); //產生的NAL儲存在本地 //result_node->size += nal->i_payload; //memcpy(result_node->result, nal->p_payload, nal->i_payload); //cout << "nal->i_payload = " <<nal->i_payload<< endl; //j = j + nal->i_payload; //result_push(result_link, result_node); //cout << "in for(nal): j = "<<j << endl; memcpy(result_node->result + j, nal->p_payload, nal->i_payload); j = j + nal->i_payload; } result_node->size = j; cout << "result_node->size = " << result_node->size << endl; result_push(result_link, result_node); } x264_encoder_close(encoder); //關閉編碼器 //fclose(inf); //free(yuv_buffer); //fclose(pFileOut); //delete[] pYuvBuf; //Sleep(100); #endif return NULL; }
X264編碼的過程可以參考這裡:點選開啟連結。
需要注意的是,我們定義了一個為0的值j。編碼產生後的NAL單元個數是nnal,編碼後資料的起始地址是nal->p_payload,長度是nal->i_payload。增加j的原因是想把得到的一個個NAL單元累加在一起,組成一個完整幀的資料,最後一幀的長度就是j,然後將得到的一幀資料與長度送入佇列,這是一個執行緒函式。對解碼器來說,只有接收到完整的一幀,才能成功解碼。
3.佇列函式:
void result_push(result_link_type* result_link, result_node_datatype * result_node) //入隊操作 { if (result_link->head == NULL) { result_link->head = result_node; result_link->end = result_link->head; result_link->result_num++; // cout << "0: result_link->result_num++" << endl; } else { result_link->end->next = result_node; result_link->end = result_node; result_link->result_num++; // cout << "1: result_link->result_num++" << endl; } } struct result_node_datatype* result_pop(result_link_type* result_link) //出隊操作 { struct result_node_datatype* tmp_node; if (result_link->head == NULL) return NULL; else if (result_link->head == result_link->end) { // cout << "result_link->head == result_link->end " << endl; return NULL; } else { tmp_node = result_link->head; result_link->head = result_link->head->next; result_link->result_num--; //cout << "result_link->result_num--" << endl; return tmp_node; } }
4.解碼過程:
解碼之前,要新增標誌位0001。
bool get_h264_data(uchar* buf,int in_len,uchar* out_buf, int &out_len)
{
char nalu[4] = { 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01 };
memcpy(out_buf, nalu, 4);
out_buf += 4;
memcpy(out_buf, buf, in_len);
out_len = in_len + 4;
// cout << "out_len = " <<out_len<< endl;
return true;
}解碼過程:
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
HANDLE thread1;
result_link_type *result_link = new result_link_type;
result_link->head = result_link->end = NULL;
result_link->result_num = 0;
thread1 = CreateThread(NULL, 0, x264_encode, (LPVOID)result_link, 0, NULL);
Sleep(1);
//system("pause");
#if 1
Mat pCvMat;
AVCodec *pCodec;
AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx = NULL;
AVCodecParserContext *pCodecParserCtx = NULL;
int frame_count;
FILE *fp_in;
FILE *fp_out;
AVFrame *pFrame, *pFrameYUV;
uint8_t *out_buffer;
// const int in_buffer_size = 4096;
const int in_buffer_size = 800000;
//uint8_t in_buffer[in_buffer_size + FF_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE] = { 0 };
uint8_t in_buffer[in_buffer_size];
memset(in_buffer, 0, sizeof(in_buffer));
uint8_t *cur_ptr;
int cur_size;
AVPacket packet;
int ret, got_picture;
int y_size;
AVCodecID codec_id = AV_CODEC_ID_H264;
// char filepath_in[] = "test.h264";
// char filepath_out[] = "1.yuv";
int first_time = 1;
struct SwsContext *img_convert_ctx;
//av_log_set_level(AV_LOG_DEBUG);
avcodec_register_all();
pCodec = avcodec_find_decoder(codec_id);
if (!pCodec) {
printf("Codec not found\n");
return -1;
}
pCodecCtx = avcodec_alloc_context3(pCodec);
if (!pCodecCtx){
printf("Could not allocate video codec context\n");
return -1;
}
pCodecParserCtx = av_parser_init(codec_id);
if (!pCodecParserCtx){
printf("Could not allocate video parser context\n");
return -1;
}
if (pCodec->capabilities&CODEC_CAP_TRUNCATED)
pCodecCtx->flags |= CODEC_FLAG_TRUNCATED; /* we do not send complete frames */
if (avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec, NULL) < 0) {
printf("Could not open codec\n");
return -1;
}
#if 0
//Input File
fp_in = fopen(filepath_in, "rb");
if (!fp_in) {
printf("Could not open input stream\n");
return -1;
}
//Output File
fp_out = fopen(filepath_out, "wb");
if (!fp_out) {
printf("Could not open output YUV file\n");
return -1;
}
#endif
pFrame = av_frame_alloc();
av_init_packet(&packet);
AVFrame* pFrameBGR = av_frame_alloc(); //儲存解碼後轉換的RGB資料
// 儲存BGR,opencv中是按BGR來儲存的
int size;
//cout << "pCodecCtx->width = " << pCodecCtx->width << "\npCodecCtx->height = " << pCodecCtx->height << endl;
//pCvMat.create(cv::Size(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height), CV_8UC3);
struct result_node_datatype *result_node2 = NULL;
int out_len;
while (1)
{
// cur_size = fread(in_buffer, 1, in_buffer_size, fp_in);
// cout << "result_link->size = " << result_link->result_num << endl;
result_node2 = result_pop(result_link);
if (result_node2 == NULL)
{
Sleep(1);
// cout << "result_node2 is NULL" << endl;
continue;
}
//cur_size = result_node2->size;
//cout<<"after result_pop()" << endl;
get_h264_data(result_node2->result, result_node2->size, in_buffer, out_len);
//cur_size = result_node2->size;
cur_size = out_len;
cout << "cur_size = " << cur_size << endl;
if (cur_size == 0)
break;
cur_ptr = in_buffer;
//cur_ptr = result_node2->result;
while (cur_size>0){
int len = av_parser_parse2(
pCodecParserCtx, pCodecCtx,
&packet.data, &packet.size,
cur_ptr, cur_size,
AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AV_NOPTS_VALUE);
cur_ptr += len;
cur_size -= len;
if (packet.size == 0)
continue;
//Some Info from AVCodecParserContext
printf("Packet Size:%6d\t", packet.size);
switch (pCodecParserCtx->pict_type){
case AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I: printf("Type: I\t"); break;
case AV_PICTURE_TYPE_P: printf("Type: P\t"); break;
case AV_PICTURE_TYPE_B: printf("Type: B\t"); break;
default: printf("Type: Other\t"); break;
}
printf("Output Number:%4d\t", pCodecParserCtx->output_picture_number);
printf("Offset:%8ld\n", pCodecParserCtx->cur_offset);
ret = avcodec_decode_video2(pCodecCtx, pFrame, &got_picture, &packet);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("Decode Error.(解碼錯誤)\n");
return ret;
}
if (got_picture) {
if (first_time){
printf("\nCodec Full Name:%s\n", pCodecCtx->codec->long_name);
printf("width:%d\nheight:%d\n\n", pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height);
//SwsContext
//img_convert_ctx = sws_getContext(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, pCodecCtx->pix_fmt,
// pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, PIX_FMT_YUV420P, SWS_BICUBIC, NULL, NULL, NULL);
img_convert_ctx = sws_getContext(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, AV_PIX_FMT_BGR24, SWS_BICUBIC, NULL, NULL, NULL);
//pFrameYUV = av_frame_alloc();
//out_buffer = (uint8_t *)av_malloc(avpicture_get_size(PIX_FMT_YUV420P, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height));
//avpicture_fill((AVPicture *)pFrameYUV, out_buffer, PIX_FMT_YUV420P, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height);
//y_size = pCodecCtx->width*pCodecCtx->height;
//size = avpicture_get_size(AV_PIX_FMT_BGR24, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height);
size = avpicture_get_size(AV_PIX_FMT_BGR24, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height);
out_buffer = (uint8_t *)av_malloc(size);
avpicture_fill((AVPicture *)pFrameBGR, out_buffer, AV_PIX_FMT_BGR24, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height); // allocator memory for BGR buffer
cout << "pCodecCtx->width = " << pCodecCtx->width << "\npCodecCtx->height = " << pCodecCtx->height << endl;
pCvMat.create(cv::Size(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height), CV_8UC3);
first_time = 0;
}
printf("Succeed to decode 1 frame!\n");
//sws_scale(img_convert_ctx, (const uint8_t* const*)pFrame->data, pFrame->linesize, 0, pCodecCtx->height,pFrameYUV->data, pFrameYUV->linesize);
sws_scale(img_convert_ctx, (const uint8_t* const*)pFrame->data, pFrame->linesize, 0, pCodecCtx->height, pFrameBGR->data, pFrameBGR->linesize);
//fwrite(pFrameYUV->data[0], 1, y_size, fp_out); //Y
//fwrite(pFrameYUV->data[1], 1, y_size / 4, fp_out); //U
//fwrite(pFrameYUV->data[2], 1, y_size / 4, fp_out); //V
cout << "size = " << size << endl;
memcpy(pCvMat.data, out_buffer, size);
imshow("RGB", pCvMat);
waitKey(1);
}
}
}
system("pause");
//Flush Decoder
packet.data = NULL;
packet.size = 0;
#if 0
while (1){
ret = avcodec_decode_video2(pCodecCtx, pFrame, &got_picture, &packet);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("Decode Error.(解碼錯誤)\n");
return ret;
}
if (!got_picture)
break;
if (got_picture) {
printf("Flush Decoder: Succeed to decode 1 frame!\n");
sws_scale(img_convert_ctx, (const uint8_t* const*)pFrame->data, pFrame->linesize, 0, pCodecCtx->height,
pFrameYUV->data, pFrameYUV->linesize);
fwrite(pFrameYUV->data[0], 1, y_size, fp_out); //Y
fwrite(pFrameYUV->data[1], 1, y_size / 4, fp_out); //U
fwrite(pFrameYUV->data[2], 1, y_size / 4, fp_out); //V
}
}
#endif
// fclose(fp_in);
// fclose(fp_out);
sws_freeContext(img_convert_ctx);
av_parser_close(pCodecParserCtx);
//av_frame_free(&pFrameYUV);
av_frame_free(&pFrameBGR);
av_frame_free(&pFrame);
avcodec_close(pCodecCtx);
av_free(pCodecCtx);
#endif
return 0;
}解碼流程以及基本引數和函式的意義,可以參考連結:點選開啟連結。
解碼成功後,got_picture為非零值,在這個判斷裡面,解碼出的資料轉為RGB格式,並用opencv顯示出來。
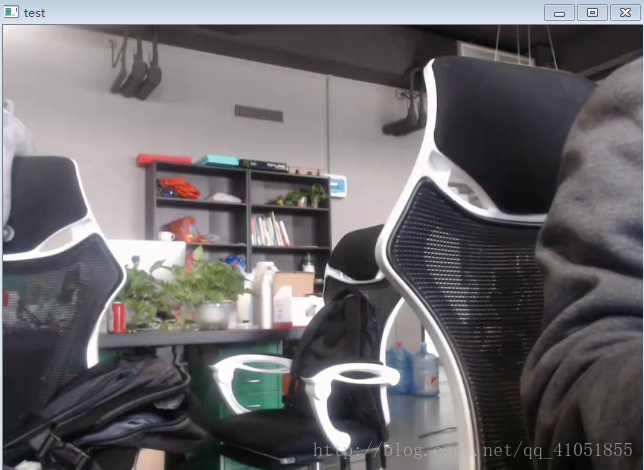
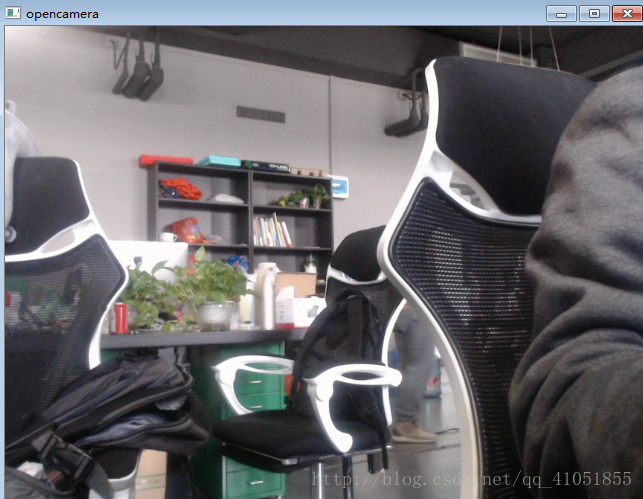
執行效果圖:
執行的過程中,對比上面的效果圖,發現解碼後的影象比攝像頭要延遲幾秒鐘,這是因為在編碼的過程,我們使用了引數animation,編碼開始前會快取幾幀,再開始,這樣幀間編碼效果好,壓縮效率高。如果使用zerolatency(零延時),基本不會有延時效果,但是壓縮效果不太好。
完整測試專案的程式碼下載地址:點選開啟連結