json轉換成bean物件
fastJson對於json格式字串的解析主要用到了一下三個類:
JSON:fastJson的解析器,用於JSON格式字串與JSON物件及javaBean之間的轉換。
JSONObject:fastJson提供的json物件。
JSONArray:fastJson提供json陣列物件。
我們可以把JSONObject當成一個Map<String,Object>來看,只是JSONObject提供了更為豐富便捷的方法,方便我們對於物件屬性的操作。我們看一下原始碼。

同樣我們可以把JSONArray當做一個List<Object>,可以把JSONArray看成JSONObject物件的一個集合。

此外,由於JSONObject和JSONArray繼承了JSON,所以說也可以直接使用兩者對JSON格式字串與JSON物件及javaBean之間做轉換,不過為了避免混淆我們還是使用JSON。
首先定義三個json格式的字串,作為我們的資料來源。
//json字串-簡單物件型 private static final String JSON_OBJ_STR = "{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12}"; //json字串-陣列型別 private static final String JSON_ARRAY_STR = "[{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12},{\"studentName\":\"lucy\",\"studentAge\":15}]";//複雜格式json字串 private static final String COMPLEX_JSON_STR = "{\"teacherName\":\"crystall\",\"teacherAge\":27,\"course\":{\"courseName\":\"english\",\"code\":1270},\"students\":[{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12},{\"studentName\":\"lucy\",\"studentAge\":15}]}";
示例1:JSON格式字串與JSON物件之間的轉換。
示例1.1-json字串-簡單物件型與JSONObject之間的轉換
/** * json字串-簡單物件型與JSONObject之間的轉換 */ public static void testJSONStrToJSONObject(){ JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR); //JSONObject jsonObject1 = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR); //因為JSONObject繼承了JSON,所以這樣也是可以的 System.out.println(jsonObject.getString("studentName")+":"+jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge")); }
示例1.2-json字串-陣列型別與JSONArray之間的轉換
/** * json字串-陣列型別與JSONArray之間的轉換 */ public static void testJSONStrToJSONArray(){ JSONArray jsonArray = JSON.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR); //JSONArray jsonArray1 = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR);//因為JSONArray繼承了JSON,所以這樣也是可以的 //遍歷方式1 int size = jsonArray.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){ JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i); System.out.println(jsonObject.getString("studentName")+":"+jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge")); } //遍歷方式2 for (Object obj : jsonArray) { JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) obj; System.out.println(jsonObject.getString("studentName")+":"+jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge")); } }
示例1.3-複雜json格式字串與JSONObject之間的轉換
/** * 複雜json格式字串與JSONObject之間的轉換 */ public static void testComplexJSONStrToJSONObject(){ JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR); //JSONObject jsonObject1 = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR);//因為JSONObject繼承了JSON,所以這樣也是可以的 String teacherName = jsonObject.getString("teacherName"); Integer teacherAge = jsonObject.getInteger("teacherAge"); JSONObject course = jsonObject.getJSONObject("course"); JSONArray students = jsonObject.getJSONArray("students"); }
示例2:JSON格式字串與javaBean之間的轉換。
首先,我們針對資料來源所示的字串,提供三個javaBean。
public class Student { private String studentName; private Integer studentAge; public String getStudentName() { return studentName; } public void setStudentName(String studentName) { this.studentName = studentName; } public Integer getStudentAge() { return studentAge; } public void setStudentAge(Integer studentAge) { this.studentAge = studentAge; } }
public class Course { private String courseName; private Integer code; public String getCourseName() { return courseName; } public void setCourseName(String courseName) { this.courseName = courseName; } public Integer getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(Integer code) { this.code = code; } }
public class Teacher { private String teacherName; private Integer teacherAge; private Course course; private List<Student> students; public String getTeacherName() { return teacherName; } public void setTeacherName(String teacherName) { this.teacherName = teacherName; } public Integer getTeacherAge() { return teacherAge; } public void setTeacherAge(Integer teacherAge) { this.teacherAge = teacherAge; } public Course getCourse() { return course; } public void setCourse(Course course) { this.course = course; } public List<Student> getStudents() { return students; } public void setStudents(List<Student> students) { this.students = students; } }
json字串與javaBean之間的轉換推薦使用 TypeReference<T> 這個類,使用泛型可以更加清晰,當然也有其它的轉換方式,這裡就不做探討了。
示例2.1-json字串-簡單物件型與javaBean之間的轉換
/** * json字串-簡單物件與JavaBean_obj之間的轉換 */ public static void testJSONStrToJavaBeanObj(){ Student student = JSON.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR, new TypeReference<Student>() {}); //Student student1 = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR, new TypeReference<Student>() {});//因為JSONObject繼承了JSON,所以這樣也是可以的 System.out.println(student.getStudentName()+":"+student.getStudentAge()); }
示例2.2-json字串-陣列型別與javaBean之間的轉換
/* * json字串-陣列型別與JavaBean_List之間的轉換 */ public static void testJSONStrToJavaBeanList(){ ArrayList<Student> students = JSON.parseObject(JSON_ARRAY_STR, new TypeReference<ArrayList<Student>>() {}); //ArrayList<Student> students1 = JSONArray.parseObject(JSON_ARRAY_STR, new TypeReference<ArrayList<Student>>() {});//因為JSONArray繼承了JSON,所以這樣也是可以的 for (Student student : students) { System.out.println(student.getStudentName()+":"+student.getStudentAge()); } }
示例2.3-複雜json格式字串與與javaBean之間的轉換
/** * 複雜json格式字串與JavaBean_obj之間的轉換 */ public static void testComplexJSONStrToJavaBean(){ Teacher teacher = JSON.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, new TypeReference<Teacher>() {}); //Teacher teacher1 = JSON.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, new TypeReference<Teacher>() {});//因為JSONObject繼承了JSON,所以這樣也是可以的 String teacherName = teacher.getTeacherName(); Integer teacherAge = teacher.getTeacherAge(); Course course = teacher.getCourse(); List<Student> students = teacher.getStudents(); }
對於TypeReference<T>,由於其構造方法使用 protected 進行修飾,所以在其他包下建立其物件的時候,要用其實現類的子類:new TypeReference<Teacher>() {}
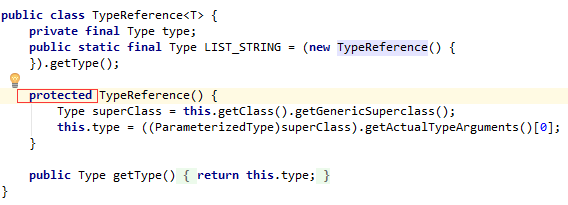
此外的:
1,對於JSON物件與JSON格式字串的轉換可以直接用 toJSONString()這個方法。
2,javaBean與JSON格式字串之間的轉換要用到:JSON.toJSONString(obj);
3,javaBean與json物件間的轉換使用:JSON.toJSON(obj),然後使用強制型別轉換,JSONObject或者JSONArray。
最後說一點,我們作為程式設計師,研究問題還是要仔細深入一點的。當你對原理了解的有夠透徹,開發起來也就得心應手了,很多開發中的問題和疑惑也就迎刃而解了,而且在面對其他問題的時候也可做到觸類旁通。當然在開發中沒有太多的時間讓你去研究原理,開發中要以實現功能為前提,可等專案上線的後,你有大把的時間或者空餘的時間,你大可去刨根問底,深入的去研究一項技術,為覺得這對一名程式設計師的成長是很重要的事情。
