Spring boot 官網學習筆記 - logging
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-01
- 調整日誌級別
- Log Level:
ERROR,WARN,INFO,DEBUG, orTRACE. - Logback does not have a
FATALlevel. It is mapped toERROR. - The default log configuration echoes messages to the console as they are written. By default,
ERROR-level,WARN-level, andINFO-level messages are logged. You can also enable a “debug” mode by starting your application with a--debugflag. -
$ java -jar myapp.jar --debug
- Alternatively, you can enable a “trace” mode by starting your application with a
--traceflag (ortrace=truein yourapplication.properties).
- Log Level:
- 日誌檔案
- By default, Spring Boot logs only to the console and does not write log files. If you want to write log files in addition to the console output, you need to set a
logging.fileorlogging.pathproperty (for example, in yourapplication.properties). - Log files rotate when they reach 10 MB and, as with console output,
ERROR-level,WARN-level, andINFO-level messages are logged by default. Size limits can be changed using thelogging.file.max-sizeproperty. Previously rotated files are archived indefinitely unless thelogging.file.max-historyproperty has been set. - Logging properties are independent of the actual logging infrastructure. As a result, specific configuration keys (such as
logback.configurationFilefor Logback) are not managed by spring Boot. 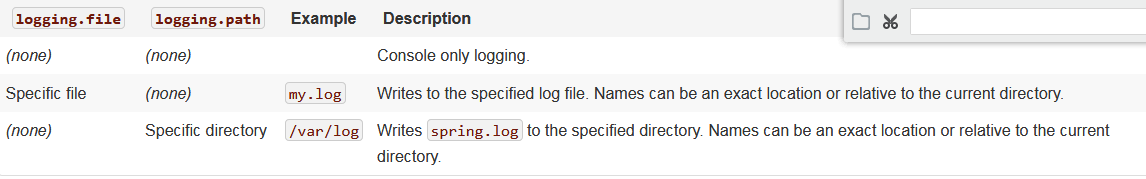
- By default, Spring Boot logs only to the console and does not write log files. If you want to write log files in addition to the console output, you need to set a
