if語句(初學者)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-02
用if語句可以構成分支結構。它根據給定的條件進行判斷,以決定執行某個分支程式段。C語言的if語句有三種基本形式。
1、基本形式:if(表示式)語句
其語義是:如果表示式的值為真,則執行其後的語句,否則不執行該語句。其過程為
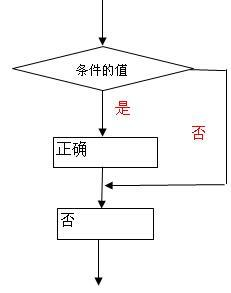
例:
#include<stdio.h> void main() { int a,b,max; printf("\n input two numbers;"); scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); max=a; if(max<b)max=b; printf("max=%d",max); }
2、if-else型
if(表示式)
語句1 ;
else
語句2;
其過程為:
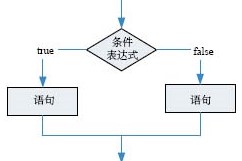
例:
#include<stdio.h> void main() { int a,b; printf("\n input two numbers;"); scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); if(a>b) printf("max=%d\n",a); else printf("max=%d\n",b); }
3、if-else-if型:前兩種形式的if語句一般都用於兩個分支的情況。當有多個分支選擇時,可採用if-else-if語句,其一般形式為:
if(表示式1)語句1
else if(表示式2)語句2
else if(表示式3)語句3
else if(表示式m)語句m
else 語句 n
在每個語句中,可以有多個語句,但需要加大括號。
具體流程圖:

例:
#include<stdio.h> voidmain() { char c; printf("input a character;"); c=getchar(); if(c<32) { printf("This is a control character\n"); } else if(c>='0'&&c<='9') { printf("This is a digit\n"); } else if(c>='A'&&c<='z') { printf("This is a capital letter\n"); } else if(c>='a'&&c<='z') { printf("This is a small letter\n"); } else { printf("This is an other character\n"); } }
