浙大《java語言》學習筆記(第一週)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-02
1.1用類製造物件

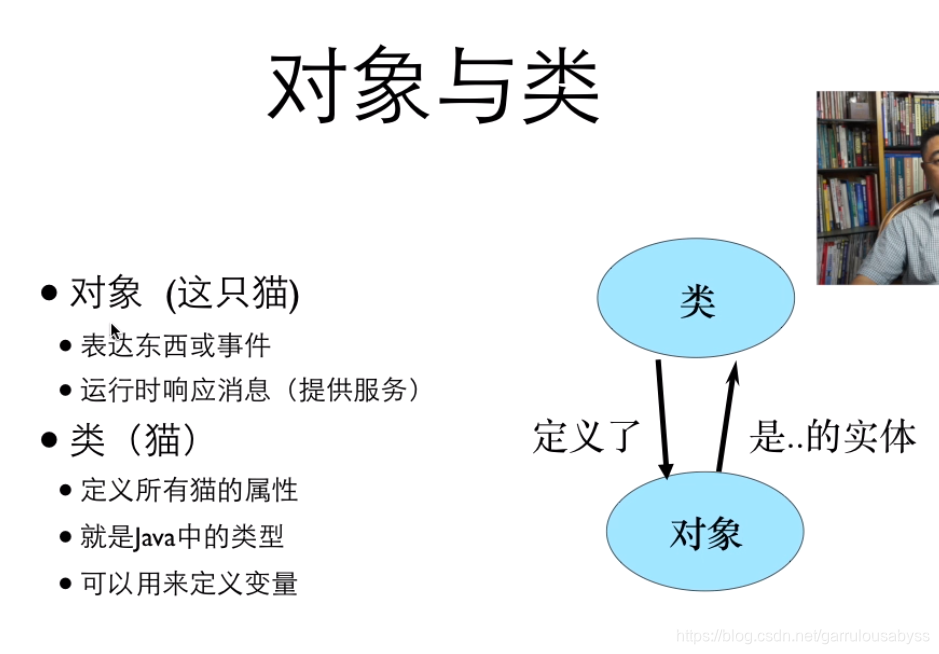
1.2定義類
這裡我們定義了一個類


這裡我們寫一個VendingMachine的類
package vendingmachine; public class VendingMachine { int price = 80; int balance; int total; void showPrompt() { System.out.println("Welcome"); } void insertMoney(int amount) { balance = balance + amount; } void showBalance() { System.out.println(balance); } void getFood() { if(balance >= price) { System.out.println("Here you are!"); balance = balance - price; total = total + price; } } public static void main(String[] args) { VendingMachine vm = new VendingMachine(); vm.showPrompt(); vm.showBalance(); vm.insertMoney(100); vm.getFood(); vm.showBalance(); VendingMachine vm1 = new VendingMachine(); vm1.insertMoney(200); vm.showBalance(); vm1.showBalance(); } }
執行結果
Welcome
0
Here you are!
20
20
200
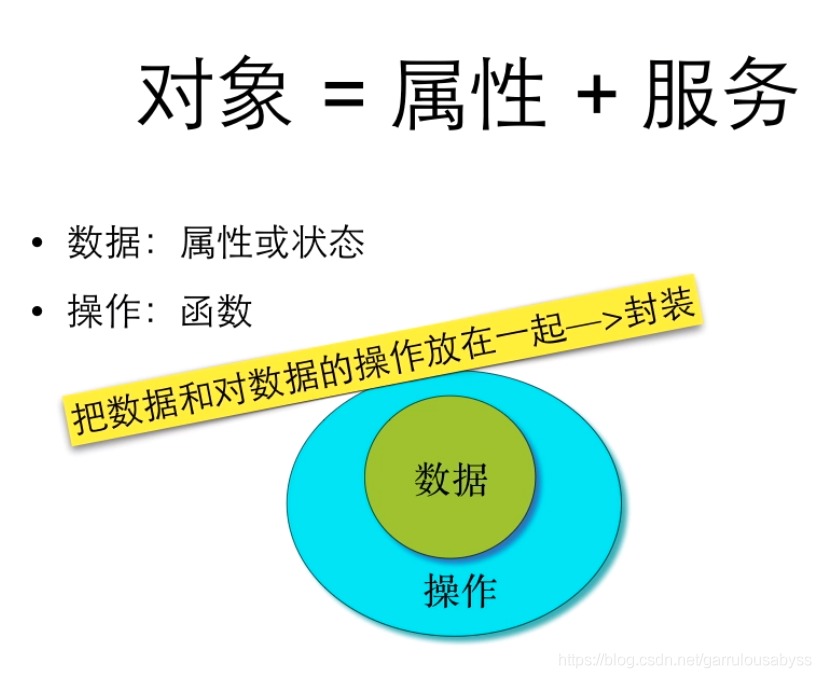
1.3 成員變數和成員函式

關於this的使用,在剛才那個程式的基礎上,我們修改了一下,注意當中的showPrice()和setPrice()
package vendingmachine; public class VendingMachine { int price = 80; int balance; int total; void setPrice(int price) { this.price = price; } void showPrice() { System.out.println(this.price); } void showPrompt() { System.out.println("Welcome"); } void insertMoney(int amount) { balance = balance + amount; } void showBalance() { System.out.println(this.balance); } void getFood() { if(balance >= price) { System.out.println("Here you are!"); balance = balance - price; total = total + price; } } public static void main(String[] args) { VendingMachine vm = new VendingMachine(); vm.showPrice(); vm.setPrice(55); vm.showPrice(); } }


1.4物件初始化

package vendingmachine; public class VendingMachine { int price = 80; int balance; int total; //建構函式 VendingMachine(){ total = 0; } //建構函式 //過載 VendingMachine(int price) { this.price = price; } void setPrice(int price) { this.price = price; } void showPrice() { System.out.println(this.price); } void showPrompt() { System.out.println("Welcome"); } void insertMoney(int amount) { balance = balance + amount; } void showBalance() { System.out.println(this.balance); } void getFood() { if(balance >= price) { System.out.println("Here you are!"); balance = balance - price; total = total + price; } } public static void main(String[] args) { VendingMachine vm = new VendingMachine(); vm.showPrice(); vm.setPrice(55); vm.showPrice(); VendingMachine vm1 = new VendingMachine(100); vm1.showPrice(); } }

1.5 本章練習
package week1;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Fraction a = new Fraction(in.nextInt(), in.nextInt());
Fraction b = new Fraction(in.nextInt(),in.nextInt());
a.print();
b.print();
a.plus(b).print();
a.multiply(b).plus(new Fraction(5,6)).print();
a.print();
b.print();
in.close();
}
}
class Fraction {
int up;
int down;
Fraction(int a,int b){
this.up = a;
this.down = b;
}
double toDouble() {
return (double)(this.up/this.down);
}
Fraction plus(Fraction o){
boolean found = false;
int num=this.down*o.down;
int up_new = o.down*this.up +this.down*o.up;
Fraction fra = new Fraction(up_new,num);
return fra;
}
Fraction multiply(Fraction o){
int up_new = this.up * o.up;
int down_new = this.down * o.down;
Fraction fra = new Fraction(up_new,down_new);
return fra;
}
void print() {
if(this.up%this.down ==0) {
System.out.println(this.up/this.down);
}
//這裡的一個問題是要最簡化分式,然後輸出
//自然想到輾轉相除法
//參考
//int GCD(int a,int b)
//{
// return b==0?a:GCD(b,a%b);
//}
else {
int a = this.up;
int b = this.down;
int c = 0;
while(b!=0) {
c = b;
b = a%b;
a = c;
}
System.out.println(this.up/a+"/"+this.down/a);
}
}
}
