LeetCode: Reverse Linked List 單鏈表的反轉
=======題目描述=======
題目連結:https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
題目內容:
Reverse Linked List
Reverse a singly linked list.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL=======演算法實現=======
4種常用的單鏈表翻轉的方法,分別是:開闢輔助陣列,新建表頭反轉,就地反轉,遞迴反轉。
①開闢輔助陣列
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution(object): def reverseList(self, head): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ ''' 時間消耗O(n),空間消耗O(n) ''' #邊界條件 if head == None or head.next == None: return head #新建陣列,用於儲存連結串列各元素 Arr = [] #將連結串列元素賦值給陣列 while head: Arr.append(head.val) head=head.next #建立新的單鏈表 newHead = ListNode(0) temp = newHead #倒著讀取陣列元素賦值給連結串列 for i in Arr[::-1]: #print(i) temp.next=ListNode(i) temp=temp.next return newHead.next
②新建表頭反轉
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution(object): def reverseList(self, head): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ ''' 以單鏈表的第一個元素為迴圈變數cur,並設定2個temp輔助變數,儲存資料; 時間消耗O(n),空間消耗O(1) ''' #邊界條件 if head == None or head.next == None: return head #定義迴圈變數 Cur=head #定義儲存資料的臨時變數 temp = None #建立新單鏈表的表頭 newHead = None while Cur: temp=Cur.next Cur.next = newHead #每次更新新連結串列的表頭 newHead = Cur Cur=temp return newHead
③就地反轉:從第2個節點到第N個節點,依次逐節點插入到第1個節點(head節點)之後,最後將第一個節點挪到新表的表尾。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
'''
開始以單鏈表的第二個元素為迴圈變數,用2個變數迴圈向後操作,並設定1個 輔助變數tmp,儲存資料;
時間消耗O(n),空間消耗O(1)
'''
#邊界條件
if head == None or head.next == None:
return head
#定義迴圈變數1
p1=head
#定義迴圈變數2
p2=head.next
temp = None
while p2:
temp=p2.next
p2.next = p1
p1=p2
p2=temp
#將第一個節點挪到新表的表尾
head.next=None
return p1
④遞迴反轉: (對於樹的大部分問題,基本可以考慮用遞迴來解決。對於單鏈表的一些問題,也可以使用遞迴。可以認為單鏈表是一顆永遠只有左(右)子樹的樹,因此可以考慮用遞迴來解決。或者說,因為單鏈表本身的結構也有自相似的特點,所以可以考慮用遞迴來解決)
1)如果head為空,或者只有head這一個節點,return head即可;
2)先遍歷head->next為首的連結串列,得到一個頭結點newHead;
3)把head賦值給head->next->next, head->next為空;
4)返回newHead。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
'''
遞迴操作,先將從第一個點開始翻轉轉換從下一個節點開始翻轉
直至只剩一個節點
時間消耗O(n),空間消耗O(1)
'''
#邊界條件
if head == None or head.next == None:
return head
else:
s = Solution()
#使用遞迴翻轉
## 呼叫自身的反轉函式,將頭結點後資料當成一個完成的單鏈表處理
##上下兩句是之前未執行成功的關鍵
newHead = s.reverseList(head.next)
#newHead = reverseList(head.next)
head.next.next=head
head.next=None
return newHead;
=======演算法筆記->單鏈表=======
1.單鏈表(From BaiDu)
單鏈表是一種鏈式存取的資料結構,用一組地址任意的儲存單元存放線性表中的資料元素。連結串列中的資料是以結點來表示的,每個結點的構成:元素(資料元素的映象) + 指標(指示後繼元素儲存位置),元素就是儲存資料的儲存單元,指標就是連線每個結點的地址資料。
連結串列是動態分配儲存空間的鏈式儲存結構。
其包括一個“頭指標”變數,其中第0個結點稱為整個連結串列的頭結點,頭結點中存放一個地址,該地址指向一個元素,頭結點一般不存放具體資料,只是存放第一個結點的地址。
連結串列中每一個元素稱為“結點”,每個結點都由兩部分組成:存放資料元素的資料域和儲存直接後繼儲存位置的指標域。指標域中儲存的即是連結串列的下一個結點儲存位置,是一個指標。多個結點連結成一個連結串列。
最後一個結點的指標域設定為空(NULL),作為連結串列的結束標誌,表示它沒有後繼結點。
使用結構體變數作為連結串列中的結點,因為結構體變數成員可以是數值型別,字元型別,陣列型別,也可以是指標型別,這樣就可以使用指標型別成員來存放下一個結點的地址,使其它型別成員存放資料資訊。
當一個序列中只含有指向它的後繼結點的連結時,就稱該連結串列為單鏈表。
單鏈表的示意圖如下:
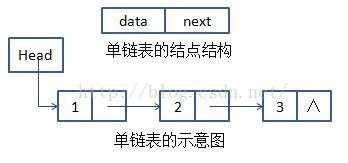
Head指標為單鏈表的頭指標,單鏈表的名字,也是其頭指標。連結串列中的最後一個結點的指標域定義為空指標(NULL)。
2.單鏈表基本操作:
單鏈表的基本操作包含:建立,插入,刪除,輸出等
#python作為面向物件程式設計的,可以使用建立一個Node類來實現連結串列,利用類的屬性引用來代替指標操作。
class Node(): # 初始化 建構函式
def __init__(self,value,next=None):
self.value=value
self.next=next def Creatlist(n):
if n<=0:
return False
if n==1:
# 只有一個節點
return Node(1)
else:
root=Node(1)
tmp=root
# 一個一個的增加節點
for i in range(2,n+1):
tmp.next=Node(i)
tmp=tmp.next
# 返回根節點
return root # 列印連結串列
def printlist(head):
p=head
while p!=None:
print p.value
p=p.next # 連結串列長度
def listlen(head):
c=0
p=head
while p!=None:
c=c+1
p=p.next
return c # 在n的前面插入元素
def insert(head,n):
if n<1 or n>listlen(head):
return
p=head
for i in range(1,n-1): # 迴圈m-2次到達 m-1
p=p.next
a=raw_input("Enter a value:")
t=Node(value=a)
t.next=p.next # 這裡注意
p.next=t
return head # 把m放在t的後面 t放在原先p的後面# 刪除連結串列
def dellist(head,n):
if n<1 or n>listlen(head):
return head
elif n is 1:
head=head.next # 刪除頭
else:
p=head
for i in range(1,n-1):
p=p.next # 迴圈到達 2次
q=p.next
p.next=q.next # 把5放在3的後面
return head 程式碼實現參考
https://blog.csdn.net/fanyun_01/article/details/79831877
http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangsyx/p/9005174.html
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008453411
