Java倆種形式實現氣泡排序
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-02
資料排序的重要性在實際專案開發中的重要性不言而喻,無論是資料整理還是分析都離不開排序這道工序。
-------------------------------------
氣泡排序——
是一種比較簡單的排序方法,也是在資料結構課程中我們學習到的第一種排序方法。但是氣泡排序在簡單排序中屬於時間複雜度較高的方法,用大O表示法為O(N*N)。可是雖然如此,這種排序的思想仍然需要我們去很好的掌握,而且由於其在理解上較為容易,所以在資料量較少(此數量級基本上感覺不到氣泡排序的笨拙)的情況下使用起來也是相當順手的。
排序思想:
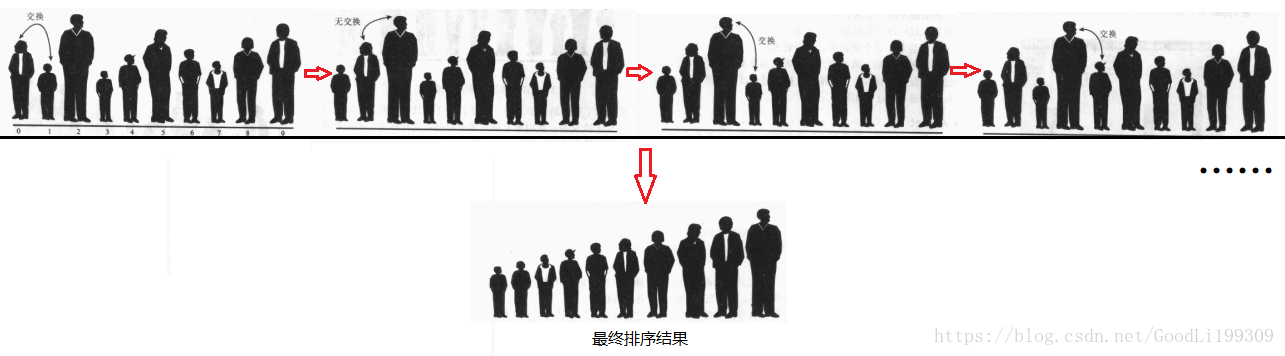
此處藉助《Java資料結構和演算法》一書中的形象例子來呈現:
我們從這幅圖中可以很清楚的找到氣泡排序的思想,即從左向右依次倆倆比較,較大者向右移動,若比較時較大者本在右側則不做右移操作,也因為此操作使得實際的比較次數>交換次數。經過N*(N-1)/2次的比較後完成排序操作(若有10個數要進行9+8+7+6+5+4+3+2+1次比較)。
程式碼實現——
我們將通過使用者指定輸入的陣列大小,自動產生一個整數型別的陣列,然後進行氣泡排序。
import java.util.Random; import java.util.Scanner; public class BubbleSort{ //test the bubbleSort public static void main(String[] aegs){ Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); int[] array=null; //produce a array ArrayUtil util=new ArrayUtil(); System.out.println("Please set array`s size:"); int size=sc.nextInt(); array=util.produce(size); System.out.println("Before sort!"); util.show(array); Sort s=new Sort(array); array=s.sortArray(); //show sorted array System.out.println("After sort!"); util.show(array); System.out.format("compairsion_times:%d--exchange_times:%d",s.getComparisiontimes(),s.getExchangetimes()); } } class Sort{ private int[] arr=null; private int EXCHANGE_TIMES=0; private int COMPIRASION_TIMES=0; public Sort(int[] array){ arr=array; } public int[] sortArray(){ //this array is not empty if(arr!=null&&arr.length>0){ //sort array int temp=0; int index=0; int count=0; //method1(根據冒泡思想衍生出的另一種書寫方式,while+for實現) while(true){ for(int i=index+1;i<arr.length-count;i++){ if(arr[index]>arr[i]){ temp=arr[i]; arr[i]=arr[index]; arr[index]=temp; EXCHANGE_TIMES++; } COMPIRASION_TIMES++; index++; } index=0; count++; if(count==arr.length-1){ break; } } //method2 /*(方法二,也是我們書本上常見的書寫方式,通過倆層for迴圈完成排序) for(int i=arr.length-1;i>1;i--){ for(int j=0;j<i;j++){ if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){ EXCHANGE_TIMES++; temp=arr[j+1]; arr[j+1]=arr[j]; arr[j]=temp; } COMPIRASION_TIMES++; } } */ return arr; }else{ return null; } } //get exchange times(獲取排序時交換次數) public int getExchangetimes(){ return EXCHANGE_TIMES; } //get comparision times(獲取排序時比較次數) public int getComparisiontimes(){ return COMPIRASION_TIMES; } } //tool class(此類完成陣列的自動生成和陣列資料的顯示) class ArrayUtil{ private int[] arr=null; //make a array(產生指定大小的陣列) public int[] produce(int num){ Random rand=new Random(500); arr=new int[num]; for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ arr[i]=rand.nextInt(100); } return arr; } //show array(顯示陣列資料) public void show(int[] array){ if(array!=null){ for(int a:array){ if(a==array[array.length-1]){ System.out.format("%d\n",a); }else{ System.out.format("%d->",a); } } } } }
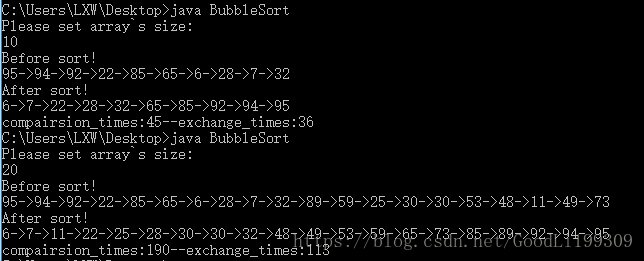
執行效果: