跨程序訪問(AIDL服務)
我們都知道Service的主要的作用是後臺執行和跨程序訪問。
關於Service後臺執行請檢視鄙人的另外一篇文章Service基礎
本篇博文主要探討的是跨程序訪問~
什麼是AIDL
Android系統中的程序之間是不能共享記憶體,因此,需要提供一些機制在不同的程序之間進行資料通訊,Activity BroadCast 和 Content Provider都可以跨程序通訊,Service同樣也可以跨程序通訊。
其中Activity可以跨程序呼叫其他應用程式的Activity 看看這裡;還有這裡
Content Provider可以跨程序訪問其他應用程式中的資料(以Cursor物件形式返回),當然,也可以對其他應用程式的資料進行增、刪、改操 作;
Broadcast可以向android系統中所有應用程式傳送廣播,而需要跨程序通訊的應用程式可以監聽這些廣播;
Service和Content Provider類似,也可以訪問其他應用程式中的資料,但不同的是,Content Provider返回的是Cursor物件,而Service返回的是Java物件,這種可以跨程序通訊的服務叫AIDL服務。
為了使其他應用程式也可以訪問本應用程式提供的服務,Android系統採用了遠端過程呼叫(Remote Procedure Call,RPC)方式來實現。 與很多其他基於RPC的解決方案一樣,Android使用了一種介面定義語言(Interface Definition Lanuage)來公開服務的介面,因此可以將這種跨程序訪問的服務稱為 AIDL (Android Interface Definition Language);
建立AIDL的步驟
建立AIDL服務要比建立普通服務的步驟要複雜一些,工具:AS
具體步驟如下
看看這裡
看看這裡
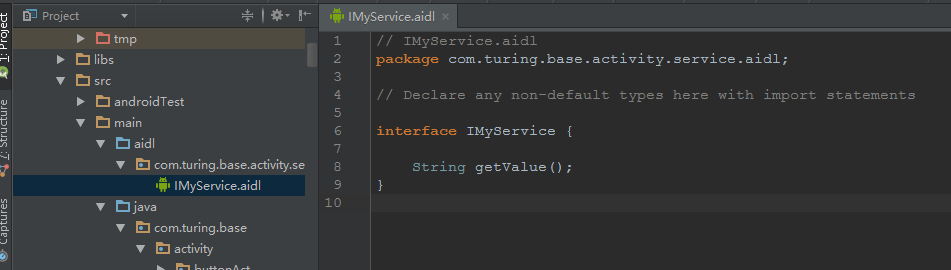
1. New —-AIDL—-AIDL File ,建立AIDL檔案
2. 如果aidl檔案正確,Build–Rebulild Project之後,會自動生成一個Java介面檔案
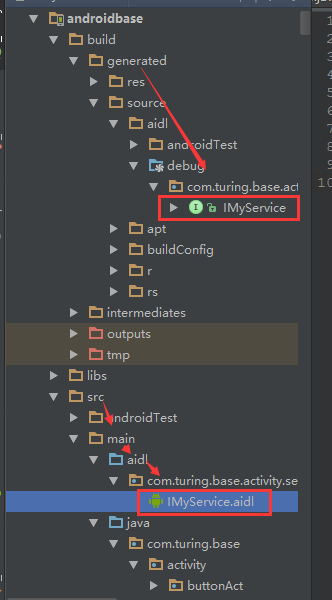
3. 建立一個服務類(Service子類)
4. 實現有aidl檔案生成的java介面
5. 在AndroidManifest.xml中配置AIDL服務,尤其要注意的是,action標籤中android:name的屬性值就是客戶端要引用該服務的id,也就是Intent類構造方法的引數值。
<service
android:name=".activity.service.aidl.AIDLService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.turing.base.activity.service.aidl.AIDLService" />
</intent-filter>
</service>建立AIDL服務
首先需要明確,兩個工程。ProjectAIDL 和ProjectAIDLClient 。這樣就可以實現跨程序訪問啦。
功能說明:
建立一個簡單的AIDL服務,這個AIDL服務只有一個getValue的方法,改方法返回一個字串, 在安裝完服務後,會在客戶端呼叫這個getValue方法,並將返回值在TextView控制元件顯示。
ProjectAIDL:
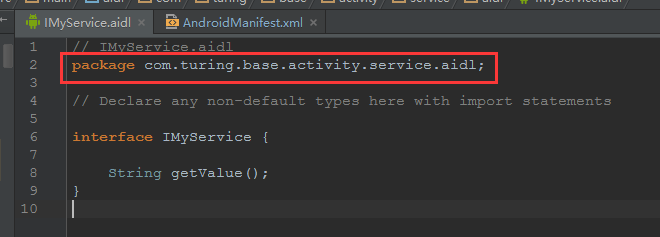
A. 建立AIDL檔案
// IMyService.aidl
package com.turing.base.activity.service.aidl;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface IMyService {
String getValue();
}
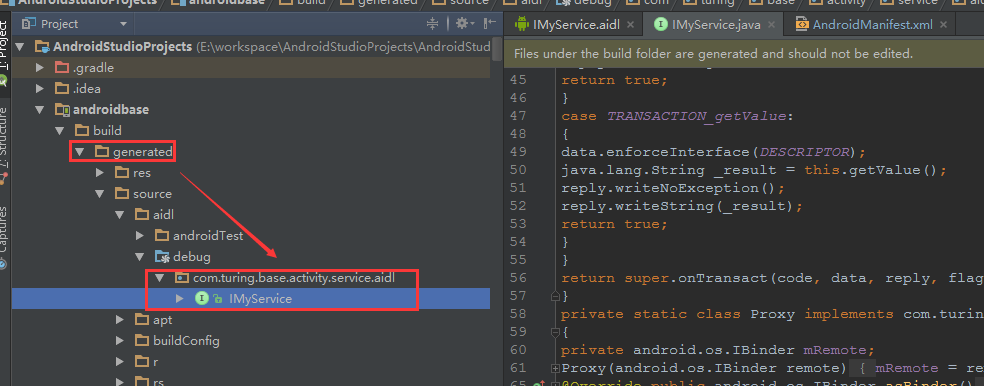
但是此時並沒有AIDL的java檔案產生,其實android studio也是帶有自動生成的,只不過需要確認一些資訊後才能生成。此時,我們可以在目錄 build–>generated–>source–>aidl–>test–>debug下面發現還沒有任何檔案
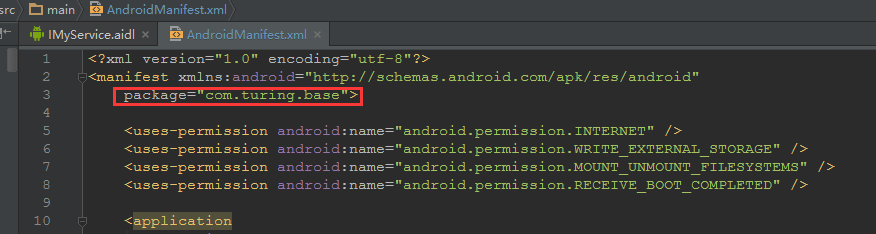
此時,開啟AndroidManifest.xml,確認package的值,
關鍵性的一步,確認aidl檔案所在的包名和AndroidMainifest.xml的package名是否一致。如果一致,點選
Build–>Make Project,生成相應的java檔案。
經驗證,貌似不一樣也沒問題
同樣生成了IMyService.java檔案
B. 編寫Service子類,在子類中定義一個內部類,該內部類繼承自 IMyService.Stub
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
public class AIDLService extends Service {
public class MyServiceImpl extends IMyService.Stub {
@Override
public String getValue() throws RemoteException {
return "AIDL.....";
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
}
注意事項:
I: IMyService.Stub是根據IMyService.aidl檔案自動生成的,一般不需要了解這個類的內容,只需要編寫一個繼承自IMyService.Stub的類即可
II:onBind方法必須返回MySeviceImpl物件,否則客戶端無法獲取服務物件。
C: 在AndroidManifest.xml中配置MyService類
<service
android:name=".activity.service.aidl.AIDLService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.turing.base.activity.service.aidl.AIDLService" />
</intent-filter>
</service>其中com.turing.base.activity.service.aidl.AIDLService是客戶端訪問AIDL服務的ID
至此 ,AIDL服務端的工作完成。
ProjectAIDLClient:
A. 建立AIDLClient工程,並將服務端自動生成的IMyService.java檔案連通同包目錄一起復制到該工程的src目錄下。
首先要拷貝AIDL檔案,這裡要保證檔案的內容一模一樣,包括包的名稱,比如本例子中伺服器端AIDL檔案所在包的名稱是com.sysu.aidlclient.aidlcilent,如何做到這一點,先新建一個專案,然後在:專案資料夾/app/src/main目錄下建立一個aidl資料夾,與java資料夾同級,在Android Studio中就可以看到這個目錄,在這個目錄上右鍵New>Package,建立一個com.sysu.aidlclient.aidlclient的包,再將aidl檔案拷進去。這樣才能保證生成的java介面檔案完全一樣,否則會提示找不到介面。
B 呼叫AIDL服務,首先要繫結服務,然後才可以獲得服務物件
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.turing.base.R;
public class AIDLActivityDemo extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private Button btn_bindAIDL, btn_callAIDL;
private TextView tv_aidlResult;
private IMyService myService ;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_aidlactivity_demo);
initView();
initEvents();
}
/**
* 初始化元件
*/
private void initView() {
btn_bindAIDL = (Button) findViewById(R.id.id_btn_aidl_bind);
btn_callAIDL = (Button) findViewById(R.id.id_btn_aidl_call);
// 現將呼叫AIDL按鈕設定為灰色禁用,等初始化AIDL服務之後在設定為可點選
btn_callAIDL.setEnabled(false);
tv_aidlResult = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.id_tv_aidl_result);
}
/**
* 按鈕註冊監聽事件
*/
private void initEvents() {
btn_bindAIDL.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_callAIDL.setOnClickListener(this);
tv_aidlResult.setOnClickListener(this);
}
/**
* 按鈕監聽事件
*
* @param v
*/
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.id_btn_aidl_bind:
bindService(new Intent("com.turing.base.activity.service.aidl.AIDLService"),
serviceConnection,
Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
break;
case R.id.id_btn_aidl_call:
// 呼叫服務端getValue方法
try {
tv_aidlResult.setText(myService.getValue().toString());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
case R.id.id_tv_aidl_result:
Toast.makeText(this,"鬧著玩",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// 獲取服務物件
myService = IMyService.Stub.asInterface(service);
btn_callAIDL.setEnabled(true);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
} ;
}
注意事項:
- 使用bindService方法繫結AIDL服務,其中需要使用Intent物件指定AIDL服務的ID,也就是action標籤中android:name屬性的值
- 在繫結時需要一個ServiceConnection物件,建立ServiceConnection物件的過程中如果繫結成功,系統會呼叫ServiceConnection.onServiceConnected方法,通過改方法的service引數值可以獲得AIDL服務物件。
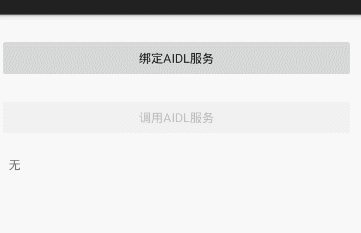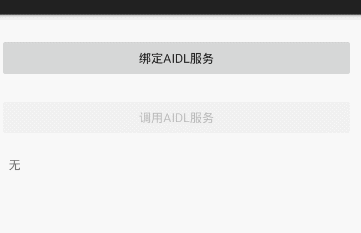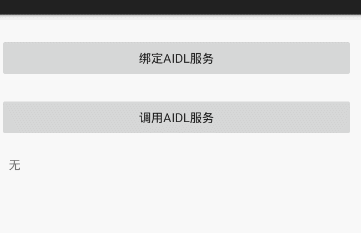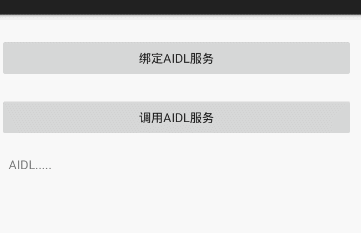
執行效果演示:
首先,執行AIDL服務程式,然後執行客戶端程式,單擊繫結AIDL服務按鈕,如果繫結成功,呼叫AIDL按鈕 會變成可點選狀態,單擊此按鈕,輸出getValue方法的返回值,
傳遞複雜資料的AIDL服務
AIDL服務只支援有限的資料型別,因此如果使用AIDL傳遞複雜的資料就需要做進一步的處理。
AIDL服務支援的資料型別
- Java簡單型別(int 、char 、boolean等),無需import
- String 和 CharSequence,無需import
- List 和 Map,但是List和Map物件的元素型別必須是AIDL服務支援的資料型別,不需要import
- AIDL指定生成的介面,需要import
- 實現android.os.Parcelable介面的類,需要import
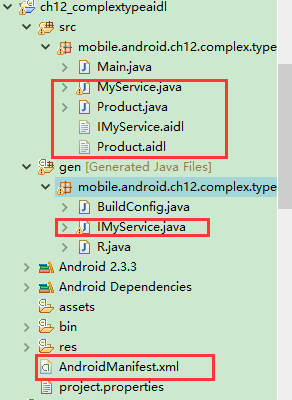
工程目錄:
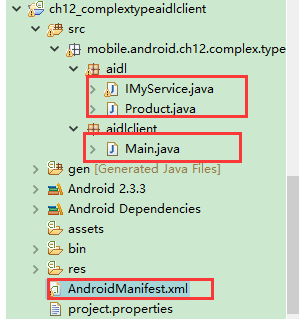
傳遞不需要import的資料型別值的方式相同,傳遞一個需要import的資料型別值(例如實現android.os.Parceable介面的類)的步驟略顯複雜,除了要建一個實現android.os.Parceable介面的類外,還需要為這個類單獨建立一個aidl檔案,並使用parceable關鍵字進行定義,具體的實現步驟如下:
ComplexTypeAIDL:
建立一個IMyService.aidl檔案
IMyService.aidl
package mobile.android.ch12.complex.type.aidl;
import mobile.android.ch12.complex.type.aidl.Product;
interface IMyService
{
Map getMap(in String country, in Product product);
Product getProduct();
} 注意事項:
- Product是一個實現了android.os.Parcelable介面的類,需要使用import匯入這個類
- 如果方法的型別是非簡單型別,例如String、List或者自定義的類,需要使用in 、out或者inout 進行修飾,其中in表示這個值被客戶端設定,out表示這個值被服務端設定;inout表示這個值既被客戶端設定,又要被服務端設定。 -
編寫Product類,該類用於傳遞的資料型別
Produt.java
package mobile.android.ch12.complex.type.aidl;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
public class Product implements Parcelable
{
private int id;
private String name;
private float price;
public static final Parcelable.Creator<Product> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<Product>()
{
public Product createFromParcel(Parcel in)
{
return new Product(in);
}
public Product[] newArray(int size)
{
return new Product[size];
}
};
public Product()
{
}
private Product(Parcel in)
{
readFromParcel(in);
}
@Override
public int describeContents()
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
public void readFromParcel(Parcel in)
{
id = in.readInt();
name = in.readString();
price = in.readFloat();
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags)
{
dest.writeInt(id);
dest.writeString(name);
dest.writeFloat(price);
}
public int getId()
{
return id;
}
public void setId(int id)
{
this.id = id;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public float getPrice()
{
return price;
}
public void setPrice(float price)
{
this.price = price;
}
}
注意事項:
- Product類必須實現android.os.Parcelable介面。該介面用於序列化物件。在Android中之所以使用Parcelable介面序列化,而不是使用java.io.Serializable介面,主要是為了提高效率。
- 在Product類中必須有一個靜態常量,常量名必須是CREATOR,而且CREATOR常量的資料型別必須是Parcelable.Creator.
public static final Parcelable.Creator<Product> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<Product>()
{
public Product createFromParcel(Parcel in)
{
return new Product(in);
}
public Product[] newArray(int size)
{
return new Product[size];
}
};- 在writeToParcel方法中需要將序列化的值寫入Parcel物件
public void readFromParcel(Parcel in)
{
id = in.readInt();
name = in.readString();
price = in.readFloat();
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags)
{
dest.writeInt(id);
dest.writeString(name);
dest.writeFloat(price);
}建立一個Proudct.aidl
Proudct.aidl
parcelable Product; 編寫MySevice類
MyService.java
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
public class MyService extends Service
{
public class MyServiceImpl extends IMyService.Stub
{
@Override
public Product getProduct() throws RemoteException
{
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(1234);
product.setName("汽車");
product.setPrice(31000);
return product;
}
@Override
public Map getMap(String country, Product product)
throws RemoteException
{
Map map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("country", country);
map.put("id", product.getId());
map.put("name", product.getName());
map.put("price", product.getPrice());
map.put("product", product);
return map;
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent)
{
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
}
在AndroidManifest.xml檔案中配置MyService類
<service android:name=".MyService" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="mobile.android.ch12.complex.type.aidl.IMyService" />
</intent-filter>
</service>至此,服務端的AIDL服務已經完成,下面看下客戶端的操作
ComplexTypeAIDLClient:
將IMyservice.java和Product.java檔案連同目錄一起復制到客戶端工程
繫結AIDL服務,並獲取AIDL服務,最後呼叫AIDL服務中的方法
Main.java
package mobile.android.ch12.complex.type.aidlclient;
import mobile.android.ch12.complex.type.aidl.IMyService;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class Main extends Activity implements OnClickListener
{
private IMyService myService = null;
private Button btnInvokeAIDLService;
private Button btnBindAIDLService;
private TextView textView;
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection()
{
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service)
{
// 獲取AIDL服務物件
myService = IMyService.Stub.asInterface(service);
btnInvokeAIDLService.setEnabled(true);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name)
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
};
@Override
public void onClick(View view)
{
switch (view.getId())
{
case R.id.btnBindAIDLService:
// 繫結AIDL服務
bindService(new Intent("mobile.android.ch12.complex.type.aidl.IMyService"),
serviceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
break;
case R.id.btnInvokeAIDLService:
try
{
String s = "";
// 呼叫AIDL服務中的方法
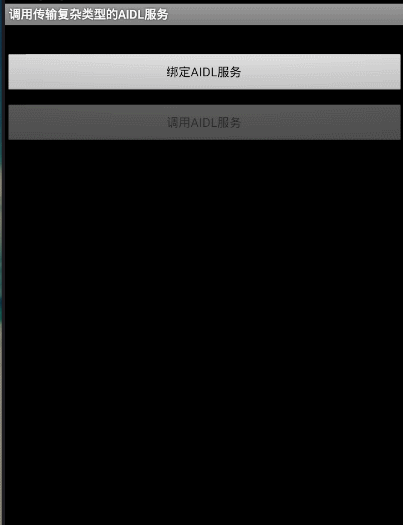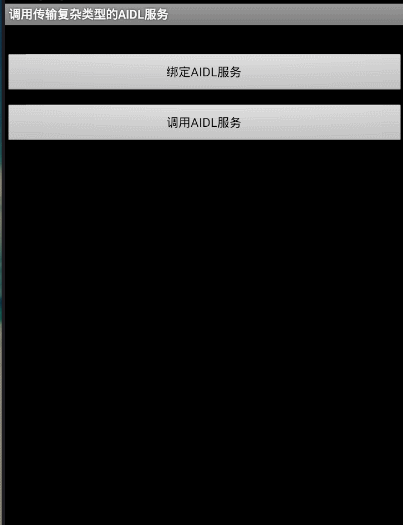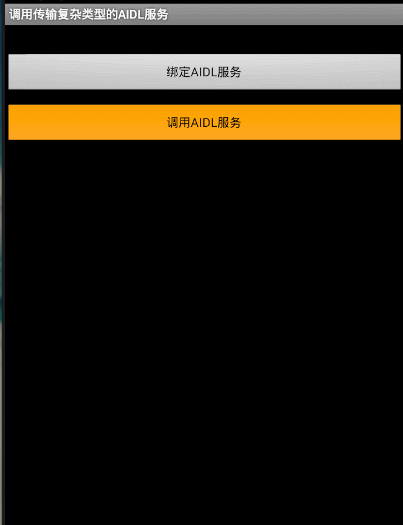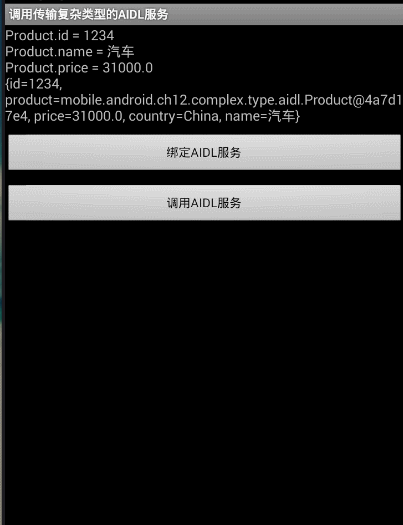
s = "Product.id = " + myService.getProduct().getId() + "\n";
s += "Product.name = " + myService.getProduct().getName()
+ "\n";
s += "Product.price = " + myService.getProduct().getPrice()
+ "\n";
s += myService.getMap("China", myService.getProduct()).toString();
textView.setText(s);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
}
break;
}
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
btnInvokeAIDLService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnInvokeAIDLService);
btnBindAIDLService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnBindAIDLService);
btnInvokeAIDLService.setEnabled(false);
textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textview);
btnInvokeAIDLService.setOnClickListener(this);
btnBindAIDLService.setOnClickListener(this);
}
}執行效果演示:
首選執行服務端,在執行客戶端,即可在客戶端獲取如下資訊
AIDL與來去電自動結束通話
真機親測有效
概述
雖然可以通過Activity Action來撥打電話,但是使用常規的方法卻無法結束通話電話,不過我們可以利用反射,使用AIDL檔案自動生成介面來實現。
在Android SDK 原始碼中可以找到如下介面
com.android.internal.telephony.ITelephony這個介面在外部是無法訪問的,只有將程式嵌入到Android SDK 內部才可以訪問,這個介面提供了一個endCall方法可以結束通話電話,現在我們就想辦法來呼叫ITelephony.endCall方法。
儘管不能直接訪問ITelephony介面,但是我們發現在TelephonyManager類中有一個getITelephhony方法,可以返回一個ITelephony物件,不過改方法是private方法,so..我們可以通過反射來呼叫改方法
private ITelephony getITelephony() {
return ITelephony.Stub.asInterface(ServiceManager.getService(Context.TELEPHONY_SERVICE));
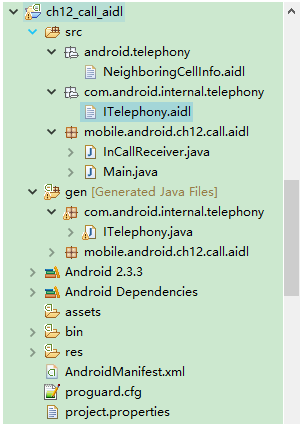
}在呼叫getITelephony方法獲得ITelephony物件之前,我們需要在SDK原始碼中找到 NeighboringCellInfo.aidl和 ITelephony.aidl,並將這兩個檔案連同所在的包複製到我們自己的工程中來。
目錄如下:
ADT會根據ITelephony.aidl檔案自動生成ITelephony.java檔案,在gen目錄下。
下面我們編寫一個接收來電的廣播接收器,並在這個廣播中自動結束通話指定號碼的來電,
Code
InCallReceiver.java
package mobile.android.ch12.call.aidl;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import com.android.internal.telephony.ITelephony;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.telephony.TelephonyManager;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class InCallReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver
{
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent)
{
TelephonyManager tm = (TelephonyManager) context
.getSystemService(Service.TELEPHONY_SERVICE);
switch (tm.getCallState())
{
case TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_RINGING: // 響鈴
// 獲得來電的電話號
String incomingNumber = intent
.getStringExtra("incoming_number");
if ("1234576".equals(incomingNumber))
{
try
{
// 獲取TelephoneManager物件
TelephonyManager telephonyManager = (TelephonyManager) context
.getSystemService(Service.TELEPHONY_SERVICE);
// 獲取TelephoneManager的class物件
Class<TelephonyManager> telephonyManagerClass = TelephonyManager.class;
// 獲得getITelephony方法
Method telephonyMethod = telephonyManagerClass
.getDeclaredMethod("getITelephony",
(Class[]) null);
// 允許訪問private方法
telephonyMethod.setAccessible(true);
// 呼叫getITelephony方法返回ITelephony物件
ITelephony telephony = (com.android.internal.telephony.ITelephony) telephonyMethod
.invoke(telephonyManager, (Object[]) null);
// 結束通話電話
telephony.endCall();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Toast.makeText(context, e.getMessage(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
break;
}
}
}
配置許可權
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CALL_PHONE"/>小結
服務除了可以在內部呼叫,還可以使用AIDL服務實現跨應用的呼叫,其中的AIDL檔案應用很廣泛,可以利用AIDL檔案自動生成介面檔案,並可以將相應的物件轉換成指定的介面,這大大方便了服務的呼叫。