CodeForces - 559B Equivalent Strings
Today on a lecture about strings Gerald learned a new definition of string equivalency. Two strings a and b of equal length are called equivalent in one of the two cases:
- They are equal.
- If we split string a into two halves of the same size a
1 and a2, and string binto two halves of the same size b1 and b2, then one of the following is correct:
- a1 is equivalent to b1, and a2 is equivalent to b2
- a1 is equivalent to b2, and a2 is equivalent to b
1As a home task, the teacher gave two strings to his students and asked to determine if they are equivalent.
Gerald has already completed this home task. Now it's your turn!
Input
The first two lines of the input contain two strings given by the teacher. Each of them has the length from 1 to 200 000 and consists of lowercase English letters. The strings have the same length.
Output
Print "YES" (without the quotes), if these two strings are equivalent, and "NO" (without the quotes) otherwise.
Examples
Input
aaba abaaOutput
YESInput
aabb ababOutput
NO
Note
In the first sample you should split the first string into strings "aa" and "ba", the second one — into strings "ab" and "aa". "aa" is equivalent to "aa"; "ab" is equivalent to "ba" as "ab" = "a" + "b", "ba" = "b" + "a".
In the second sample the first string can be splitted into strings "aa" and "bb", that are equivalent only to themselves. That's why string "aabb" is equivalent only to itself and to string "bbaa".
題目大意:給定兩個等長的字串a,b,問兩個字串是否是等價的,
等價的定義:1 如果兩個字串相等則是等價的,
2 如果字串長度為偶數,則將a分成兩個等長的字串a1,a2,將b分成兩個等長的字串b1,b2,如果滿足a1==b1&&a2==b2或者a1==b2&&a2==b1,則認為a,b等價
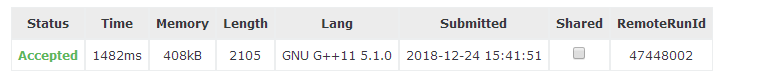
解題思路:可以用分治思想來做,如果當前兩個串相等,返回true,否則判斷當前串長度是否為偶數,是的話,將兩個串分成四個字串a1,a2,b1,b2,依次判斷是否符合定義,符合返回true,否則繼續進行上述操作,剛開始使用strncpy函式來將兩個串分成四個串,然後用strcmp函式進行判斷是否相等,不幸的是在第91組測試時TLE了,想了一想每一次遞迴是都要進行串的賦值,會花費很多的時間,所以我簡化了一下,每一次不用strncpy函式來分字串,用兩個變數來標記每一個串的起始位置和終止位置,然後在進行判斷,這樣就會省很多時間,題目時間限制是2000ms,簡化後用了1482ms過了,開心
簡化之前TLE的程式碼:

#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=2e5+100;
char a[maxn],b[maxn];
int judge(char a1[],char a2[],char b1[],char b2[])
{
if((!strcmp(a1,b1)&&!strcmp(a2,b2))||(!strcmp(a1,b2)&&!strcmp(a2,b1)))
return 1;
if(!strcmp(a1,b1))//a1==b1,但a2!=b2
return 2;
if(!strcmp(a2,b2))//a2==b2,但a1!=b1;
return 3;
if(!strcmp(a1,b2))//a1==b2,但a2!=b1;
return 4;
if(!strcmp(a2,b1))//a2==b1,但a1!=b2
return 5;
return 6;
}
bool solve(char a[],char b[],int n)
{
if(!strcmp(a,b))
return true;
if(n%2!=0)//奇數不等價
return false;
int mid=n/2;
if(mid)
{
char a1[mid+1],a2[mid+1],b1[mid+1],b2[mid+1];//四個子串
strncpy(a1,a,mid);
a1[mid]='\0';
strncpy(a2,a+mid,mid);
a2[mid]='\0';
strncpy(b1,b,mid);
b1[mid]='\0';
strncpy(b2,b+mid,mid);
b2[mid]='\0';
int term=judge(a1,a2,b1,b2);
switch(term)
{
case 1://相等
{
return true;
break;
}
case 2://a1==b1,但a2!=b2 這時只需判斷字a2和b2即可,下面情況相同
{
bool flag=solve(a2,b2,mid);
if(flag)
return true;
break;
}
case 3:
{
bool flag=solve(a1,b1,mid);
if(flag)
return true;
break;
}
case 4:
{
bool flag=solve(a2,b1,mid);
if(flag)
return true;
break;
}
case 5:
{
bool flag=solve(a1,b2,mid);
if(flag)
return true;
break;
}
case 6://分成的四個字串沒有相同的,就有四種情況,分別判斷
{
bool flag=solve(a1,b1,mid)&&solve(a2,b2,mid)||solve(a1,b2,mid)&&solve(a2,b1,mid);
if(flag)
return true;
break;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%s%s",a,b);
int n;
n=strlen(a);
if(!strcmp(a,b))
printf("YES\n");
else if(n%2!=0)
printf("NO\n");
else
{
bool flag=solve(a,b,n);
if(flag)
printf("YES\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
return 0;
}
簡化之後AC程式碼:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=2e5+100;
char a[maxn],b[maxn];
bool cmp(char a[],char b[],int f1,int L1,int f2,int L2)//判斷字串是否相同
{
bool flag=false;
int i=f1,j=f2;
while(i<L1&&j<L2)
{
if(a[i++]!=b[j++])
{
flag=true;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
int judge(char a[],char b[],int f1,int L1,int f2,int L2,int f3,int L3,int f4,int L4)
{
if((!cmp(a,b,f1,L1,f3,L3)&&!cmp(a,b,f2,L2,f4,L4))||(!cmp(a,b,f1,L1,f4,L4)&&!cmp(a,b,f2,L2,f3,L3)))
return 1;
if(!cmp(a,b,f1,L1,f3,L3))//a1==b1,但a2!=b2
return 2;
if(!cmp(a,b,f2,L2,f4,L4))//a2==b2,但a1!=b1;
return 3;
if(!cmp(a,b,f1,L1,f4,L4))//a1==b2,但a2!=b1;
return 4;
if(!cmp(a,b,f2,L2,f3,L3))//a2==b1,但a1!=b2
return 5;
return 6;
}
bool solve(char a[],char b[],int n,int f1,int L1,int f2,int L2)
{
if(!cmp(a,b,f1,L1,f2,L2))
return true;
if(n%2!=0)//奇數不等價
return false;
int mid=n/2;
if(mid)
{
int term=judge(a,b,f1,f1+mid,f1+mid,L1,f2,f2+mid,f2+mid,L2);
switch(term)// | 子串a1 | a2 | b1 | b2 /
{
case 1:
{
return true;
break;
}
case 2://a1==b1,但a2!=b2 這時只需判斷字a2和b2即可,下面情況相同
{
bool flag=solve(a,b,mid,f1+mid,L1,f2+mid,L2);
if(flag)
return true;
break;
}
case 3:
{
bool flag=solve(a,b,mid,f1,f1+mid,f2,f2+mid);
if(flag)
return true;
break;
}
case 4:
{
bool flag=solve(a,b,mid,f1+mid,L1,f2,f2+mid);
if(flag)
return true;
break;
}
case 5:
{
bool flag=solve(a,b,mid,f1,f1+mid,f2+mid,L2);
if(flag)
return true;
break;
}
case 6:
{
bool flag=solve(a,b,mid,f1,f1+mid,f2,f2+mid)&&solve(a,b,mid,f1+mid,L1,f2+mid,L2)||solve(a,b,mid,f1,f1+mid,f2+mid,L2)&&solve(a,b,mid,f1+mid,L1,f2,f2+mid);
if(flag)
return true;
break;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%s%s",a,b);
int n;
n=strlen(a);
if(!cmp(a,b,0,n,0,n))
printf("YES\n");
else if(n%2!=0)
printf("NO\n");
else
{
bool flag=solve(a,b,n,0,n,0,n);
if(flag)
printf("YES\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
return 0;
}
