ArrayList等常見集合的排序問題
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-04
對於ArrayList等常用的集合具體業務類,基本上都實現了Comparable介面,即可以用來比較裝載的物件實體。
主要用Collections.sort方法對集合類中的物件進行排序
Collections.sort的兩種過載方法
- Collections.sort(list, comparator)方法,通過comparator規則,實現對list的特定排序。
- Collections.sort(list),list中的物件自身實現comparator介面
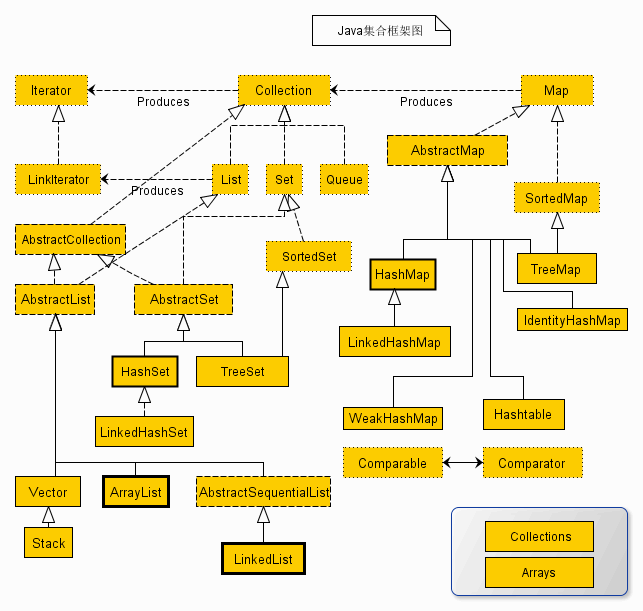
Java集合框架:
程式碼示例(演示Collections.sort(list, comparator)方法):
注意:本程式碼均已在
jdk1.6版本下通過測試
- model,Student類
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
/**
* @Title: Student
* @Description: TODO
* @param:
* @throws
*/
public Student(int id, String name, int age) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub - 測試類
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ArrayList<Student> arrayList = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student s1 = new Student(1, "jack", 20);
Student s2 = new Student(2, "jack", 20);
Student s3 = new Student(3, "lily", 29);
Student s4 = new Student(4, "tom", 30);
Student s5 = new Student(5, "rose", 31);
Student s6 = new Student(6, "crane", 20);
Student s7 = new Student(7, "jack", 25);
Student s8 = new Student(8, "rose", 27);
Student s9 = new Student(9, "lucy", 18);
arrayList.add(s1);
arrayList.add(s2);
arrayList.add(s3);
arrayList.add(s4);
arrayList.add(s5);
arrayList.add(s6);
arrayList.add(s7);
arrayList.add(s8);
arrayList.add(s9);
Comparator<Student> studentComparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
/**
*
* @Title: compare
* @Description: 先比較age,再比較name,最後比較id
* @param: @param o1
* @param: @param o2
* @param: @return
* @return: int
* @throws
*/
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (o1.getAge() != o2.getAge()) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
} else if (!o1.getName().equals(o2.getName())) {
return o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
} else if (o1.getId() != o2.getId()) {
return o1.getId() - o2.getId();
}
return 0;
}
};
Collections.sort(arrayList, studentComparator);
for (Student student : arrayList) {
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
}- 測試結果
Student [age=18, name=lucy, id=9]
Student [age=20, name=crane, id=6]
Student [age=20, name=jack, id=1]
Student [age=20, name=jack, id=2]
Student [age=25, name=jack, id=7]
Student [age=27, name=rose, id=8]
Student [age=29, name=lily, id=3]
Student [age=30, name=tom, id=4]
Student [age=31, name=rose, id=5]