H.264解碼過程剖析-4
x264開源工程實現H.264的視訊編碼,但沒有提供對應的解碼器。ffmpeg開源多媒體編解碼集合彙集了市面上幾乎所有媒體格式的編解碼的原始碼。其中的H264.c就是一個能正常解碼x264編碼碼流的獨立的原始檔,其使用步驟也與上述的編碼或解碼CODEC應用案例基本相同。這一節通過自頂向下的方式,講述H264.c如何實現H.264視訊解碼過程。
H264.c原始檔有幾千行,程式碼量龐大,很不便於瀏覽、分析和移植。同時該檔案還依賴其他原始檔,組織結構較複雜,實現平臺由於不是基於Windows的VC++,對編譯、跟蹤等帶來了很多不便。光碟中“chapter7\ffmpeg_h264”目錄給出了一個從ffmpeg抽取的C語言實現H.264視訊解碼的專案案例“ffmpeg_h264”。“ffmpeg_h264”的檔案功能分類明確,在VC++2005平臺下編譯,且剔除了MMX的支援,純C語言工程便於嵌入式平臺的移植。下面從main主函式入手,逐步深入分析實現H.264視訊解碼的過程。
1 解碼主程式
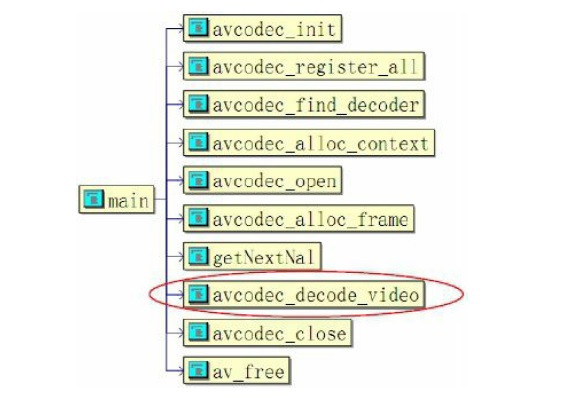
函式main實現H.264視訊解碼的控制檯應用,包括瞭解碼工作的所有過程。其函式呼叫關係如圖所示。
上述應用中,拓撲結構流程與前述的MPEG-1視訊解碼過程基本相同,包括了avcodec_init、avcodec_register_all、avcodec_find_decoder、avcodec_all_context、avcodec_open、avcodec_all_frame、avcodec_decode_video、avcodec_close等ffmpeg的幾大公共模組,其中avcodec_decode_video是解碼器的核心,在圖中做了標註。main函式的程式碼實現如下:
int main(){
FILE * inp_file;
FILE * out_file;
int i;
int nalLen; /*NAL 長度*/
unsigned char* Buf; /*H.264碼流*/
int got_picture; /*是否解碼一幀影象*/
int consumed_bytes; /*解碼器消耗的碼流長度*/
int cnt=0;
AVCodec *codec; /* 編解碼CODEC*/
AVCodecContext *c; /* 編解碼CODEC context*/ 上述過程中,步驟1~8為ffmpeg在編碼或解碼等工作時的基本步驟。分析函式名稱的特點會發現,CODEC的處理函式均以“avcodec_”為字首。為了使用H.264解碼器CODEC,首先需要定義CODEC,如下所示:
AVCodec h264_decoder = {
"h264", //解碼器名稱
CODEC_TYPE_VIDEO, //解碼器型別,視訊
CODEC_ID_H264, //解碼器ID
sizeof(H264Context), //解碼器上下文大小
decode_init, //解碼器初始化
NULL, //編碼器,禁用
decode_end, //銷燬解碼器
decode_frame, //解碼
0, //CODEC相容性,禁用
};因此,實際的解碼處理模組採用decode_init、decode_frame、decode_end三個本地函式來實現。而main函式中使用公共的函式介面訪問這裡的函式。例項如註冊CODEC。
/**
* simple call to register all the codecs.
*/
void avcodec_register_all(void)
{
static int inited = 0;
if (inited != 0)
return;
inited = 1;
register_avcodec(&h264_decoder);
//av_register_codec_parser(&h264_parser);
}所以,CODEC解碼器實際呼叫H264.c中的三個子函式來完成解碼任務。
2 配置解碼器
上述是註冊和定義解碼器,其中ffmpeg的avcodec_open模組開啟CODEC,並實際呼叫decode_init本地函式建立、配置H.264解碼器。
int avcodec_open(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVCodec *codec)
{
int ret;
if(avctx->codec) return -1; /*CODEC指標有效*/
avctx->codec = codec; /*指向codec*/
avctx->codec_id = codec->id; /*CODEC 名稱*/
avctx->frame_number = 0;
#if 1
if (codec->priv_data_size > 0) {/*CODEC的結構體不為0*/
/*為CODEC申請空間*/
avctx->priv_data = av_mallocz(codec->priv_data_size);
if (!avctx->priv_data)
return -ENOMEM;
} else {
avctx->priv_data = NULL;
}
#endif
/*CODEC的初始化*/
ret = avctx->codec->init(avctx);
/*若失敗,則釋放context結構體*/
if (ret < 0) {
av_freep(&avctx->priv_data);
return ret;
}
return 0;
}上述實現解碼器的初始化,包括設定預設的解碼引數、影象寬度和高度、I幀預測函式的初始化等;然後是畫素格式為I420的平面模式;最後為可變長度編碼VLC表的初始化。
3 H.264視訊解碼
視訊解碼模組由ffmpeg的avcodec_decode_video()來完成。由於H.264碼流是經過了NAL打包,所以在呼叫解碼器之前,需要呼叫getNextNal()模組以從碼流檔案中讀取分析一個NAL包,即尋找NAL的頭標識0x00 00 00 01,然後將兩個頭標識之間的資料傳給VCL解碼器avcodec_decode_video()實現解碼:
/**
* decode a frame.
* @param buf bitstream buffer, must be FF_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE larger then the actual read bytes
* because some optimized bitstream readers read 32 or 64 bit at once and could read over the end
* @param buf_size the size of the buffer in bytes
* @param got_picture_ptr zero if no frame could be decompressed, Otherwise, it is non zero
* @return -1 if error, otherwise return the number of
* bytes used.
*/
int avcodec_decode_video(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *picture,
int *got_picture_ptr,
uint8_t *buf, int buf_size)
{
int ret;
/*當前沒有解碼的標識*/
*got_picture_ptr= 0;
/*H.264解碼*/
ret = avctx->codec->decode(avctx, //解碼器上下文
picture, //解碼的影象
got_picture_ptr, //影象解碼標識
buf, //待解碼的碼流
buf_size); //碼流長度
/*如果使用了MMX等指令,需要呼叫該函式*/
emms_c();
/*解碼的是影象,不是頭資料*/
if (*got_picture_ptr)
avctx->frame_number++;
return ret;
}
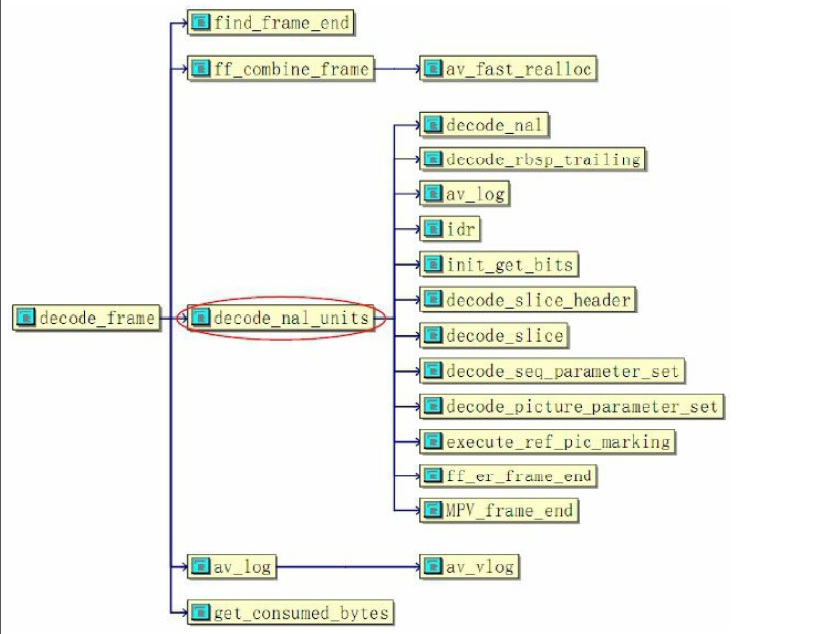
上述的VCL解碼器根據傳入的碼流及長度呼叫ffmpeg的公共函式介面decode,即實際的解碼函式decode_frame實現H.264的VCL解碼。若解碼過程中使用了MMX指令且退出後又要使用float/double型別,則需要使用emms指令(Empty mmx state)清空MMX狀態,以恢復以前的CPU狀態。實際的解碼函式decode_frame實現VCL的真正解碼工作,該模組的拓撲結構如圖所示。
圖中的decode_frame解碼視訊編碼層VCL資料,模組核心是decode_nal_units。
static int decode_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx, /*解碼器上下文*/
void *data, /*解碼影象的結構*/
int *data_size, /*結構大小*/
uint8_t *buf, /*碼流空間*/
int buf_size) /*碼流長度*/
{
H264Context *h = avctx->priv_data; /*解碼器上下文*/
MpegEncContext *s = &h->s; /*MpegEncContext指標*/
AVFrame *pict = data; /*影象空間*/
int buf_index; /*當前的碼流位置*/
s->flags= avctx->flags; /*CODEC的標誌*/
s->flags2= avctx->flags2; /*CODEC的標誌2*/
if (buf_size == 0) { /*碼流不為空*/
return 0;
}
/*截斷的碼流解碼*/
if(s->flags&CODEC_FLAG_TRUNCATED){
int next= find_frame_end(&s->parse_context, buf, buf_size);
if( ff_combine_frame(&s->parse_context, next, &buf, &buf_size) < 0 )
return buf_size;
}
/*碼流中特別資料的解碼*/
if(s->avctx->extradata_size && s->picture_number==0){
if(0 < decode_nal_units(h, s->avctx->extradata, s->avctx->extradata_size) )
return -1;
}
/*正常的解碼*/
buf_index=decode_nal_units(h, buf, buf_size);
if(buf_index < 0)
return -1;
#if 0 /*B幀*/
if(s->pict_type==B_TYPE || s->low_delay){
*pict= *(AVFrame*)&s->current_picture;
} else {
*pict= *(AVFrame*)&s->last_picture;
}
#endif
/*沒有解碼輸出影象,解碼頭資料*/
if(!s->current_picture_ptr){
av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "error, NO frame\n");
return -1;
}
/*有解碼影象輸出*/
*pict= *(AVFrame*)&s->current_picture;
assert(pict->data[0]);
/*表明解碼輸出*/
*data_size = sizeof(AVFrame);
/*返回當前消耗的碼流*/
return get_consumed_bytes(s, buf_index, buf_size);
}
上述解碼過程中,首先如果是截斷的碼流,則將解碼後的碼流與一幀影象組合;判斷碼流中是否有特殊的資料如Huffman表等;然後正常解碼NAL;最後輸出解碼影象及消耗的碼流長度。其中核心是NAL解碼decode_nal_units。
4 NAL包解碼
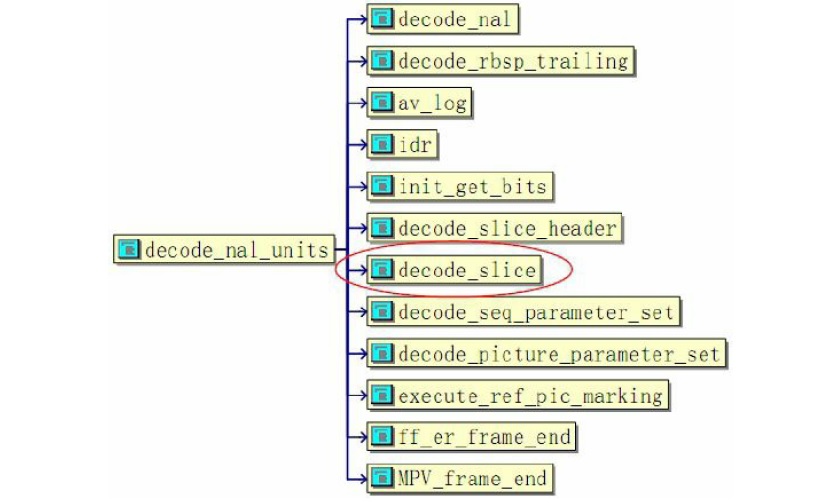
H.264碼流中的基本單位表現為各個獨立的NAL包,因此解碼的處理函式
decode_nal_units()實現解碼NAL包。該模組的拓撲結構如圖所示:
上圖中的NAL解碼主要包括序列引數集SPS、影象引數集PPS、即時解碼重新整理片IDR、影象片頭Slice_header、影象片Slice等結構的解碼decode_nal_units實現過程如下:
/*NAL單元解碼*/
static int decode_nal_units(H264Context *h, //解碼器控制代碼
uint8_t *buf, //碼流空間
int buf_size){ //碼流長度
MpegEncContext * const s = &h->s;
AVCodecContext * const avctx= s->avctx;
int buf_index=0;
/*迴圈解碼*/
for(;;){
int consumed; //消耗的長度
int dst_length; //目標長度
int bit_length; //位元長度
uint8_t *ptr; //臨時指標
/*搜尋字首開始碼:0x 00 00 01*/
for(; buf_index + 3 < buf_size; buf_index++){
/*在第一次搜尋時,必須成功,否則認為碼流出錯*/
if(buf[buf_index] == 0 && buf[buf_index+1] == 0 && buf[buf_index+2] == 1)
break;
}
/*後續仍然有資料*/
if(buf_index+3 >= buf_size) break;
/*索引後移*/
buf_index+=3;
/*網路抽象層NAL解包*/
ptr= decode_nal(h, buf + buf_index, &dst_length, &consumed, buf_size - buf_index);
if(ptr[dst_length - 1] == 0) dst_length--;
/*確定碼流的精確的結束位置*/
bit_length= 8*dst_length - decode_rbsp_trailing(ptr + dst_length - 1);
if(s->avctx->debug&FF_DEBUG_STARTCODE){
av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "NAL %d at %d length %d\n", h->nal_unit_type, buf_index, dst_length);
}
/*索引後移*/
buf_index += consumed;
if( s->hurry_up == 1 && h->nal_ref_idc == 0 )
continue;
switch(h->nal_unit_type){ /*根據NAL型別執行解碼*/
case NAL_IDR_SLICE: //IDR片
idr(h); //
case NAL_SLICE: //影象片SLICE解碼
/*初始化碼流指標*/
init_get_bits(&s->gb, ptr, bit_length);
h->intra_gb_ptr=
h->inter_gb_ptr= &s->gb;
s->data_partitioning = 0;
/*解碼影象片的頭*/
if(decode_slice_header(h) < 0) return -1;
if(h->redundant_pic_count==0 && s->hurry_up < 5 )
/*****************影象片資料解碼*/
decode_slice(h);
/*****************影象片資料解碼*/
break;
case NAL_DPA: //資料分割槽A
init_get_bits(&s->gb, ptr, bit_length);
h->intra_gb_ptr=
h->inter_gb_ptr= NULL;
s->data_partitioning = 1;
/*解碼影象片的頭*/
if(decode_slice_header(h) < 0) return -1;
break;
case NAL_DPB: //資料分割槽B
init_get_bits(&h->intra_gb, ptr, bit_length);
h->intra_gb_ptr= &h->intra_gb;
break;
case NAL_DPC: //資料分割槽C
init_get_bits(&h->inter_gb, ptr, bit_length);
h->inter_gb_ptr= &h->inter_gb;
if(h->redundant_pic_count==0 && h->intra_gb_ptr && s->data_partitioning && s->hurry_up < 5 )
decode_slice(h);
break;
case NAL_SEI: //補充增強資訊
break;
case NAL_SPS: //序列引數集SPS
/*初始化碼流*/
init_get_bits(&s->gb, ptr, bit_length);
/*SPS解碼*/
decode_seq_parameter_set(h);
if(s->flags& CODEC_FLAG_LOW_DELAY)
s->low_delay=1;
avctx->has_b_frames= !s->low_delay;
printf("decode SPS\n");
break;
case NAL_PPS: //影象引數集PPS
/*初始化碼流*/
init_get_bits(&s->gb, ptr, bit_length);
/*PPS解碼*/
decode_picture_parameter_set(h);
printf("decode PPS\n");
break;
case NAL_PICTURE_DELIMITER:
break;
case NAL_FILTER_DATA:
break;
default:
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Unknown NAL code: %d\n", h->nal_unit_type);
}
/*影象幀型別*/
s->current_picture.pict_type= s->pict_type;
/*關鍵幀型別初始化*/
s->current_picture.key_frame= s->pict_type == I_TYPE;
}
/*沒有解碼輸出影象*/
if(!s->current_picture_ptr) return buf_index; //no frame
/*修改影象序列POC*/
h->prev_frame_num_offset= h->frame_num_offset;
h->prev_frame_num= h->frame_num;
if(s->current_picture_ptr->reference){
h->prev_poc_msb= h->poc_msb;
h->prev_poc_lsb= h->poc_lsb;
}
/*標記參考幀*/
if(s->current_picture_ptr->reference)
execute_ref_pic_marking(h, h->mmco, h->mmco_index);
else
assert(h->mmco_index==0);
/*碼流容錯結束*/
ff_er_frame_end(s);
/*解碼一幀完畢,擴充套件影象*/
MPV_frame_end(s);
return buf_index;
}
上述過程首先解析得到NAL的字首碼0x 00 00 01,然後函式decode_nal()實現NAL解包,根據解析到的NAL型別執行不同的解碼:SPS、PPS、IDR、Slice_header、Slice等,解碼結束後,標記參考幀、碼流容錯結束,最後擴充套件解碼影象的邊界。NAL解碼的核心是函式decode_slice()。
5 影象片解碼
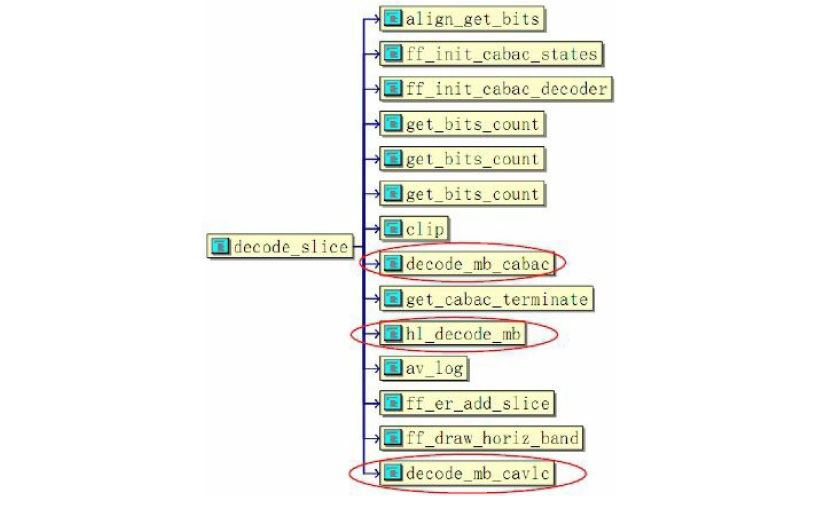
H.264的編碼是以片Slice為單位的,片的型別又分為I_TYPE、P_TYPE和B_TYPE等。ffmpeg的H.264解碼器在這一級的影象片解碼中是不分片型別的,即統一處理。因為H.264的熵編碼分為CABAC和CAVLC兩種,故對應的熵解碼也區別處理。模組decode_slice()實現影象片的解碼功能,該函式的拓撲結構如圖所示。
上圖中影象片解碼分為算術熵解碼CABAC和Huffman熵解碼CAVLC兩大型別,每種又主要包括熵解碼、反量化和反變換、運動補償等功能。decode_slice()模組的實現過程如下:
/*解碼影象片*/
static int decode_slice(H264Context *h){
MpegEncContext * const s = &h->s;
const int part_mask= s->partitioned_frame ? (AC_END|AC_ERROR) : 0x7F;
s->mb_skip_run= -1;
/*CABAC解碼*/
if( h->pps.cabac ) {
int i;
/* 規整碼流 */
align_get_bits( &s->gb );
/* 初始化CABAC 的狀態*/
ff_init_cabac_states( &h->cabac, ff_h264_lps_range, ff_h264_mps_state, ff_h264_lps_state, 64 );
/*填充碼流解碼結構*/
ff_init_cabac_decoder( &h->cabac,
s->gb.buffer + get_bits_count(&s->gb)/8,
( s->gb.size_in_bits - get_bits_count(&s->gb) + 7)/8);
/* 計算固定400的初始狀態 */
for( i= 0; i < 399; i++ ) {
int pre;
if( h->slice_type == I_TYPE )
pre = clip( ((cabac_context_init_I[i][0] * s->qscale) >>4 ) + cabac_context_init_I[i][1], 1, 126 );
else
pre = clip( ((cabac_context_init_PB[h->cabac_init_idc][i][0] * s->qscale) >>4 ) + cabac_context_init_PB[h->cabac_init_idc][i][1], 1, 126 );
if( pre <= 63 )
h->cabac_state[i] = 2 * ( 63 - pre ) + 0;
else
h->cabac_state[i] = 2 * ( pre - 64 ) + 1;
}
for(;;){
/*CABAC 巨集塊熵解碼、反量化*/
int ret = decode_mb_cabac(h);
/*返回片的結尾標記*/
int eos = get_cabac_terminate( &h->cabac ); /* End of Slice flag */
/*反變換、運動補償等*/
hl_decode_mb(h);
/* 幀或場自適應切換 */
if( ret >= 0 && h->sps.mb_aff ) { //FIXME optimal? or let mb_decode decode 16x32 ?
s->mb_y++;
ret = decode_mb_cabac(h);
eos = get_cabac_terminate( &h->cabac );
hl_decode_mb(h);
s->mb_y--;
}
/*解碼出錯或已經解碼到結尾*/
if( ret < 0 || h->cabac.bytestream > h->cabac.bytestream_end + 1) {
av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "error while decoding MB %d %d\n", s->mb_x, s->mb_y);
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x, s->mb_y, (AC_ERROR|DC_ERROR|MV_ERROR)&part_mask);
return -1;
}
/*一行巨集塊解碼結束,為提高Cache效率,保留水平方向內容*/
if( ++s->mb_x >= s->mb_width ) {
s->mb_x = 0;
ff_draw_horiz_band(s, 16*s->mb_y, 16);
/*根據巨集塊數目,解碼結束*/
if( ++s->mb_y >= s->mb_height ) {
tprintf("slice end %d %d\n", get_bits_count(&s->gb), s->gb.size_in_bits);
}
}
/*解碼完畢,新增影象片*/
if( eos || s->mb_y >= s->mb_height ) {
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x-1, s->mb_y, (AC_END|DC_END|MV_END)&part_mask);
return 0;
}
}
}
else{
/*CAVLC解碼*/
for(;;){
/*一個巨集塊熵解碼、反量化*/
int ret = decode_mb_cavlc(h);
/*反變換、運動補償等*/
hl_decode_mb(h);
/*巨集塊自適應幀、場編碼*/
if(ret>=0 && h->sps.mb_aff){ //FIXME optimal? or let mb_decode decode 16x32 ?
s->mb_y++;
ret = decode_mb_cavlc(h);
hl_decode_mb(h);
s->mb_y--;
}
/*解碼出錯*/
if(ret<0){
av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "error while decoding MB %d %d\n", s->mb_x, s->mb_y);
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x, s->mb_y, (AC_ERROR|DC_ERROR|MV_ERROR)&part_mask);
return -1;
}
/*一行巨集塊解碼結束,為提高Cache效率,保留水平區*/
if(++s->mb_x >= s->mb_width){
s->mb_x=0;
ff_draw_horiz_band(s, 16*s->mb_y, 16);
/*根據巨集塊數目,解碼完畢,新增影象片*/
if(++s->mb_y >= s->mb_height){
tprintf("slice end %d %d\n", get_bits_count(&s->gb), s->gb.size_in_bits);
if(get_bits_count(&s->gb) == s->gb.size_in_bits ) {
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x-1, s->mb_y, (AC_END|DC_END|MV_END)&part_mask);
return 0;
}else{
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x, s->mb_y, (AC_END|DC_END|MV_END)&part_mask);
return -1;
}
}
}
/*碼流消耗完畢,新增影象片*/
if(get_bits_count(&s->gb) >= s->gb.size_in_bits && s->mb_skip_run<=0){
if(get_bits_count(&s->gb) == s->gb.size_in_bits ){
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x-1, s->mb_y, (AC_END|DC_END|MV_END)&part_mask);
return 0;
}else{
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x, s->mb_y, (AC_ERROR|DC_ERROR|MV_ERROR)&part_mask);
return -1;
}
}
}
}
return -1; //正常情況下不會達到這裡
}
上述的影象片解碼中,熵解碼包含了反量化處理,預測、反變換和運動補償在模組hl_decode_mb()中實現。解碼中以巨集塊為迴圈單位,根據巨集塊遞增量以及碼流消耗的情況決定解碼結束,記錄解碼中的出錯狀態,填充影象塊,正常或報錯返回。
6 巨集塊熵解碼
熵編碼是完全可逆的無損編碼,H.264碼流首先經過熵解碼、反量化形成DCT變換的係數。在H.264編碼中熵編碼包括上下文自適應的可變長度編碼CAVLC、上下文自適應的二進位制算術編碼CABAC。相對應的熵解碼也包括decode_mb_cavlc和decode_mb_cabac兩種,這兩個模組的執行過程非常類似,限於篇幅,這裡只介紹CAVLC的解碼decode_mb_ cavlc,該函式的拓撲結構如圖所示。
在實施熵解碼前,需要首先確定巨集塊的預測模式Mode或運動向量MV,以及塊編碼模式CBP,然後再分別對亮度和色度執行熵解碼。巨集塊的CAVLC模組的執行過程如下。在介紹實現過程中,省略了部分無關緊要的程式碼,重點從功能上詳細說明實現步驟。具體內容詳見光碟中的“ffmpeg_h264\cavlc.c”檔案。
/**
* decodes a macroblock
* @returns 0 if ok, AC_ERROR / DC_ERROR / MV_ERROR if an error is noticed
*/
int decode_mb_cavlc(H264Context *h){
MpegEncContext * const s = &h->s;
const int mb_xy= s->mb_x + s->mb_y*s->mb_stride;
int mb_type, partition_count, cbp;
s->dsp.clear_blocks(h->mb); //FIXME avoid if allready clear (move after skip handlong?
tprintf("pic:%d mb:%d/%d\n", h->frame_num, s->mb_x, s->mb_y);
cbp = 0; /* avoid warning. FIXME: find a solution without slowing
down the code */
if(h->slice_type != I_TYPE && h->slice_type != SI_TYPE){
if(s->mb_skip_run==-1)
s->mb_skip_run= get_ue_golomb(&s->gb);
if (s->mb_skip_run--) {
int mx, my;
/* skip mb */
//FIXME b frame
mb_type= MB_TYPE_16x16|MB_TYPE_P0L0|MB_TYPE_P1L0;
memset(h->non_zero_count[mb_xy], 0, 16);
memset(h->non_zero_count_cache + 8, 0, 8*5); //FIXME ugly, remove pfui
if(h->sps.mb_aff && s->mb_skip_run==0 && (s->mb_y&1)==0){
h->mb_field_decoding_flag= get_bits1(&s->gb);
}
if(h->mb_field_decoding_flag)
mb_type|= MB_TYPE_INTERLACED;
fill_caches(h, mb_type); //FIXME check what is needed and what not ...
pred_pskip_motion(h, &mx, &my);
fill_rectangle(&h->ref_cache[0][scan8[0]], 4, 4, 8, 0, 1);
fill_rectangle( h->mv_cache[0][scan8[0]], 4, 4, 8, pack16to32(mx,my), 4);
write_back_motion(h, mb_type);
s->current_picture.mb_type[mb_xy]= mb_type; //FIXME SKIP type
s->current_picture.qscale_table[mb_xy]= s->qscale;
h->slice_table[ mb_xy ]= h->slice_num;
h->prev_mb_skiped= 1;
return 0;
}
}
if(h->sps.mb_aff /* && !field pic FIXME needed? */){
if((s->mb_y&1)==0)
h->mb_field_decoding_flag = get_bits1(&s->gb);
}else
h->mb_field_decoding_flag=0; //FIXME som ed note ?!
h->prev_mb_skiped= 0;
mb_type= get_ue_golomb(&s->gb);
if(h->slice_type == B_TYPE){
if(mb_type < 23){
partition_count= b_mb_type_info[mb_type].partition_count;
mb_type= b_mb_type_info[mb_type].type;
}else{
mb_type -= 23;
goto decode_intra_mb;
}
}else if(h->slice_type == P_TYPE /*|| h->slice_type == SP_TYPE */){
if(mb_type < 5){
partition_count= p_mb_type_info[mb_type].partition_count;
mb_type= p_mb_type_info[mb_type].type;
}else{
mb_type -= 5;
goto decode_intra_mb;
}
}else{
assert(h->slice_type == I_TYPE);
decode_intra_mb:
if(mb_type > 25){
av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "mb_type %d in %c slice to large at %d %d\n", mb_type, av_get_pict_type_char(h->slice_type), s->mb_x, s->mb_y);
return -1;
}
partition_count=0;
cbp= i_mb_type_info[mb_type].cbp;
h->intra16x16_pred_mode= i_mb_type_info[mb_type].pred_mode;
mb_type= i_mb_type_info[mb_type].type;
}
if(h->mb_field_decoding_flag)
mb_type |= MB_TYPE_INTERLACED;
s->current_picture.mb_type[mb_xy]= mb_type;
h->slice_table[ mb_xy ]= h->slice_num;
if(IS_INTRA_PCM(mb_type)){
const uint8_t *ptr;
int x, y;
// we assume these blocks are very rare so we dont optimize it
align_get_bits(&s->gb);
ptr= s->gb.buffer + get_bits_count(&s->gb);
for(y=0; y<16; y++){
const int index= 4*(y&3) + 64*(y>>2);
for(x=0; x<16; x++){
h->mb[index + (x&3) + 16*(x>>2)]= *(ptr++);
}
}
for(y=0; y<8; y++){
const int index= 256 + 4*(y&3) + 32*(y>>2);
for(x=0; x<8; x++){
h->mb[index + (x&3) + 16*(x>>2)]= *(ptr++);
}
}
for(y=0; y<8; y++){
const int index= 256 + 64 + 4*(y&3) + 32*(y>>2);
for(x=0; x<8; x++){
h->mb[index + (x&3) + 16*(x>>2)]= *(ptr++);
}
}
skip_bits(&s->gb, 384); //FIXME check /fix the bitstream readers
//FIXME deblock filter, non_zero_count_cache init ...
memset(h->non_zero_count[mb_xy], 16, 16);
s->current_picture.qscale_table[mb_xy]= s->qscale;
return 0;
}
fill_caches(h, mb_type);
//mb_pred
if(IS_INTRA(mb_type)){
if(IS_INTRA4x4(mb_type)){
int i;
for(i=0; i<16; i++){
const int mode_coded= !get_bits1(&s->gb);
const int predicted_mode= pred_intra_mode(h, i);
int mode;
if(mode_coded){
const int rem_mode= get_bits(&s->gb, 3);
if(rem_mode<predicted_mode)
mode= rem_mode;
else
mode= rem_mode + 1;
}else{
mode= predicted_mode;
}
h->intra4x4_pred_mode_cache[ scan8[i] ] = mode;
}
write_back_intra_pred_mode(h);
if( check_intra4x4_pred_mode(h) < 0)
return -1;
}else{
h->intra16x16_pred_mode= check_intra_pred_mode(h, h->intra16x16_pred_mode);
if(h->intra16x16_pred_mode < 0)
return -1;
}
h->chroma_pred_mode= get_ue_golomb(&s->gb);
h->chroma_pred_mode= check_intra_pred_mode(h, h->chroma_pred_mode);
if(h->chroma_pred_mode < 0)
return -1;
}else if(partition_count==4){
int i, j, sub_partition_count[4], list, ref[2][4];
if(h->slice_type == B_TYPE){
for(i=0; i<4; i++){
h->sub_mb_type[i]= get_ue_golomb(&s->gb);
if(h->sub_mb_type[i] >=13){
av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "B sub_mb_type %d out of range at %d %d\n", h->sub_mb_type[i], s->mb_x, s->mb_y);
return -1;
}
sub_partition_count[i]= b_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].partition_count;
h->sub_mb_type[i]= b_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].type;
}
}else{
assert(h->slice_type == P_TYPE || h->slice_type == SP_TYPE); //FIXME SP correct ?
for(i=0; i<4; i++){
h->sub_mb_type[i]= get_ue_golomb(&s->gb);
if(h->sub_mb_type[i] >=4){
av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "P sub_mb_type %d out of range at %d %d\n", h->sub_mb_type[i], s->mb_x, s->mb_y);
return -1;
}
sub_partition_count[i]= p_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].partition_count;
h->sub_mb_type[i]= p_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].type;
}
}
for(list=0; list<2; list++){
const int ref_count= IS_REF0(mb_type) ? 1 : h->ref_count[list];
if(ref_count == 0) continue;
for(i=0; i<4; i++){
if(IS_DIR(h->sub_mb_type[i], 0, list) && !IS_DIRECT(h->sub_mb_type[i])){
ref[list][i] = get_te0_golomb(&s->gb, ref_count); //FIXME init to 0 before and skip?
}else{
//FIXME
ref[list][i] = -1;
}
}
}
for(list=0; list<2; list++){
const int ref_count= IS_REF0(mb_type) ? 1 : h->ref_count[list];
if(ref_count == 0) continue;
for(i=0; i<4; i++){
h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i] ]=h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i]+1 ]=
h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i]+8 ]=h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i]+9 ]= ref[list][i];
if(IS_DIR(h->sub_mb_type[i], 0, list) && !IS_DIRECT(h->sub_mb_type[i])){
const int sub_mb_type= h->sub_mb_type[i];
const int block_width= (sub_mb_type & (MB_TYPE_16x16|MB_TYPE_16x8)) ? 2 : 1;
for(j=0; j<sub_partition_count[i]; j++){
int mx, my;
const int index= 4*i + block_width*j;
int16_t (* mv_cache)[2]= &h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[index] ];
pred_motion(h, index, block_width, list, h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[index] ], &mx, &my);
mx += get_se_golomb(&s->gb);
my += get_se_golomb(&s->gb);
tprintf("final mv:%d %d\n", mx, my);
if(IS_SUB_8X8(sub_mb_type)){
mv_cache[ 0 ][0]= mv_cache[ 1 ][0]=
mv_cache[ 8 ][0]= mv_cache[ 9 ][0]= mx;
mv_cache[ 0 ][1]= mv_cache[ 1 ][1]=
mv_cache[ 8 ][1]= mv_cache[ 9 ][1]= my;
}else if(IS_SUB_8X4(sub_mb_type)){