Android開發--便籤(一)
我的上一篇部落格http://blog.csdn.net/callmesp/article/details/52895630 講的是ListView和RecyclerView,起因就是想開發一個便籤的時候才遇到的問題。在學習了RecyclerView之後呢,在今天上午花了一段時間把這個app寫了出來(水平有限),來與大家分享。
專案地址為
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 前面的AppBarLayout就是建立project時候自動生成的不用去管它,也可以在toolbar上設定一個按鈕來增添一個編輯功能(這個功能還沒實現,目前還沒學會..等實現了再回來寫一個Android開發–便籤(二),有什麼建議的話也可以告訴我)。下面兩個控制元件就是重點了,一個RecyclerView負責顯示資訊和一個FloatingActionButton懸浮的按鈕來觸發增加便籤的事件。不明白的可以看我上一篇部落格這裡就不詳細的說了。
下面是list_item
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior"
tools:context="com.example.notes_2.MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<android.support.v7.widget.CardView
xmlns:card_view="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
card_view:cardBackgroundColor="#FFFFB9"
card_view:cardCornerRadius="10dp"
card_view:cardPreventCornerOverlap="true"
card_view:cardUseCompatPadding="true"
card_view:contentPadding="10dp">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingLeft="10sp"
android:paddingRight="10sp"
android:paddingTop="15sp"
android:singleLine="true"
android:id="@+id/time" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:paddingLeft="10sp"
android:paddingRight="10sp"
android:paddingTop="15sp"
android:paddingBottom="15sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</android.support.v7.widget.CardView>
</LinearLayout>
這裡用了一個CardView
<android.support.v7.widget.CardView
xmlns:card_view="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
card_view:cardBackgroundColor="#FFFFB9"
card_view:cardCornerRadius="10dp"
card_view:cardPreventCornerOverlap="true"
card_view:cardUseCompatPadding="true"
card_view:contentPadding="10dp">也是一個比較新的控制元件,這是今天才學會的,這裡就是簡單的呼叫一下,也沒什麼好說的,如果有時間的話會深入的研究一下,研究一下各種自定義,然後專門寫一篇部落格。現在,值得注意的一點就是我在裡面嵌套了一個LinearLayout然後才在裡面寫了兩個TextView,為什麼要這樣多此一舉而不是直接就寫兩個TextView呢?這裡其實我一開始也沒加,不過在測試的時候發現兩個TextView重合起來了,我感覺這個CardView就相當於一個改了style改了background的一個FrameLayout,所以要先巢狀然後再使用,總比什麼都要自定義要方便的多了。然後兩個TextView一個用來顯示時間一個顯示內容。
下面就開始上主要的內容了。
DBHelper.java
package com.example.notes_2;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
import android.util.Log;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Created by my on 2016/10/23.
*/
public class DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private final static String DB_NAME="my.db";
private final static int DB_VERSION=1;
private final static String TABLE_NAME="info";
private final static String CONTENT="content";
private final static String TIME="date";
private final static String ID="_id";
SQLiteDatabase database=getWritableDatabase();
public DBHelper(Context context){
super(context,DB_NAME,null,DB_VERSION);
}
//paramSQLiteDatabase.execSQL("create table " + NAME + "(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,title TEXT,date TEXT,content TEXT)");
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase database){
database.execSQL("create table " + TABLE_NAME + "(_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,date TEXT,content TEXT)");
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
}
public long insert(String text){
ContentValues contentValues=new ContentValues();
contentValues.put("content",text);
//獲取系統時間
SimpleDateFormat formatter=new SimpleDateFormat("yy-MM-dd HH:mm");
Date curDate = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
String time=formatter.format(curDate);
contentValues.put("date",time);
long row=database.insert(TABLE_NAME,null,contentValues);
Log.e("time:", time);
Log.e("content", text);
return row;
}
public void update(int _id,String text){
ContentValues contentValues=new ContentValues();
contentValues.put("content",text);
database.update(TABLE_NAME,contentValues,ID+"=?",new String[]{Integer.toString(_id)});
}
public void delete(int _id){
database.delete(TABLE_NAME, ID + "=?", new String[]{Integer.toString(_id)});
}
public Cursor select(){
Cursor cursor=database.query(TABLE_NAME,null,null,null,null,null,null);
return cursor;
}
}
/*
public long add(SQLiteDatabase paramSQLiteDatabase, Notepad paramNotepad) {
ContentValues localContentValues = new ContentValues();
localContentValues.put("title", paramNotepad.getTitle());
localContentValues.put("date", paramNotepad.getdata());
localContentValues.put("content", paramNotepad.getContent());
long l = paramSQLiteDatabase.insert(table, null, localContentValues);
paramSQLiteDatabase.close();
return l;
}
*/這個就是這個專案的核心了,一個數據庫幫助類,這裡用的是SQLite一個輕量級資料庫,後面我會專門詳細的寫一篇部落格來講它的。這裡先簡單的認識一下就可以。它有幾個引數,也是在構造的時候需要的,資料庫名字,資料庫版本,表名,id,還有就是表裡面的內容了,可以隨意設定。
SQLiteDatabase database=getWritableDatabase();這裡用了一個基礎類獲取讀寫資料庫的許可權,否則是會閃退的。然後就是對它的各種功能的重寫,新增,刪除,插入,更新等等。放入內容的時候用了ContentValues,一個鍵值對。比如contentValues.put(“content”,text);就是把text的內容賦予表裡面的“content”這一列。別的也沒什麼了。
然後是寫一個介面卡adpter來適配我們的RecyclerView。
package com.example.notes_2;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by my on 2016/10/23.
*/
public class MyRecyclerAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyRecyclerAdapter.MyViewHolder> {
private List<String> mDatas;
private Context mContext;
private LayoutInflater inflater;
private Cursor mmcursor;
private DBHelper mmDbhelper;
int k=0;
private OnItemClickListener mOnItemClickListener;
public MyRecyclerAdapter(Context context,Cursor cursor,DBHelper dbHelper){
this.mContext=context;
this.mmcursor=cursor;
this.mmDbhelper=dbHelper;
inflater= LayoutInflater. from(mContext);
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return mmcursor.getCount();
}
//填充onCreateViewHolder方法返回的holder中的控制元件
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(MyViewHolder holder, final int position) {
mmcursor.moveToPosition(mmcursor.getCount()-position-1);
holder.tv_time.setText(mmcursor.getString(1));
holder.tv_content.setText(mmcursor.getString(2));
//實現介面
if( mOnItemClickListener!= null){
holder.itemView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
mOnItemClickListener.onClick(position);
}
});
}
}
//重寫onCreateViewHolder方法,返回一個自定義的ViewHolder
@Override
public MyViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.list_item,parent, false);
MyViewHolder holder= new MyViewHolder(view);
return holder;
}
class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
TextView tv_time;
TextView tv_content;
public MyViewHolder(View view) {
super(view);
tv_time=(TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.time);
tv_content=(TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.content);
}
}
public interface OnItemClickListener{
void onClick(int position);
}
public void setOnItemClickListener(OnItemClickListener onItemClickListener ){
this. mOnItemClickListener=onItemClickListener;
}
}
這裡用到了cursor來適配這個DBHelper,後面講SQLite的時候也會詳細講,這裡只需要將它理解成指標就好了,然後從表裡面取值的時候,用cursor.moveToPosition(int position);移動到那一行;然後cursor.getString(int x));移動到那一列,列的順序就是atabase.execSQL(“create table ” + TABLE_NAME + “(_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,date TEXT,content TEXT)”);引號裡面自己定義的順序。從0開始。
接下來就是我們的MainActivity了。
package com.example.notes_2;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton;
import android.support.design.widget.Snackbar;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.support.v7.widget.DefaultItemAnimator;
import android.support.v7.widget.GridLayoutManager;
import android.support.v7.widget.LinearLayoutManager;
import android.support.v7.widget.OrientationHelper;
import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;
import android.support.v7.widget.StaggeredGridLayoutManager;
import android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ListView listView;
private Cursor cursor;
private DBHelper dbHelper;
private RecyclerView recyclerView;
private MyRecyclerAdapter adapter;
private int _id=0;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.revycle_new);
dbHelper=new DBHelper(this);
cursor=dbHelper.select();
recyclerView=(RecyclerView)findViewById(R.id.recycle);
adapter=new MyRecyclerAdapter(this,cursor,dbHelper);
LinearLayoutManager layoutManager = new LinearLayoutManager(this);
GridLayoutManager gridLayoutManager=new GridLayoutManager(this,2);
StaggeredGridLayoutManager staggeredGridLayoutManager= new StaggeredGridLayoutManager(2, StaggeredGridLayoutManager.VERTICAL);
//設定佈局管理器
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(staggeredGridLayoutManager);
//設定為垂直佈局,這也是預設的
layoutManager.setOrientation(OrientationHelper.VERTICAL);
//設定Adapter
recyclerView.setAdapter(adapter);
Log.e("0","getcount:"+adapter.getItemCount());
//設定增加或刪除條目的動畫
recyclerView.setItemAnimator(new DefaultItemAnimator());
adapter.setOnItemClickListener(new MyRecyclerAdapter.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(int position) {
cursor.moveToPosition(cursor.getCount()-1-position);
_id=cursor.getInt(0);
Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this,Modify.class);
intent.putExtra("id",_id);
intent.putExtra("data",cursor.getString(2));//getString(1)顯示cursor該列的內容
Log.e("0","MainActivity to modify_contetn:"+cursor.getString(2));
Log.e("0","id:"+_id);
startActivity(intent);
finish();
}
});
Toolbar toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.toolbar);
setSupportActionBar(toolbar);
FloatingActionButton fab = (FloatingActionButton) findViewById(R.id.fab);
fab.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,Content.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
if (id == R.id.action_settings) {
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
邏輯很清晰就不用細講了。還有就是點選增加便籤的Activity還有點進便籤的Activity下面把程式碼貼出來。
content.java
package com.example.notes_2;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.KeyEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.sql.Time;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Created by my on 2016/10/23.
*/
public class Content extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener {
private Button okButton,cancleButton;
private EditText contentWrite;
private DBHelper dbHelper;
private Cursor cursor;
private int _id=0;
private Time time;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.content);
init();
}
private void init(){
dbHelper=new DBHelper(this);
cursor=dbHelper.select();
okButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_ok);
cancleButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_cancle);
contentWrite = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_content);
okButton.setOnClickListener(this);
cancleButton.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_ok:
addData() ;
Intent intent = new Intent(this,MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
finish();
break;
case R.id.btn_cancle:
Intent intent1 = new Intent(this,MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent1);
finish();
break;
}
}
private void addData(){
if (contentWrite.getText().toString().equals("")){
Toast.makeText(Content.this,"內容不能為空",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}else{
dbHelper.insert(contentWrite.getText().toString());
cursor.requery();
contentWrite.setText("");
_id=0;
}
}
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keycode,KeyEvent event){
if (keycode==KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK){
Intent intent = new Intent(this,MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
finish();return true;}else{
return super.onKeyDown(keycode,event);
}
}
}
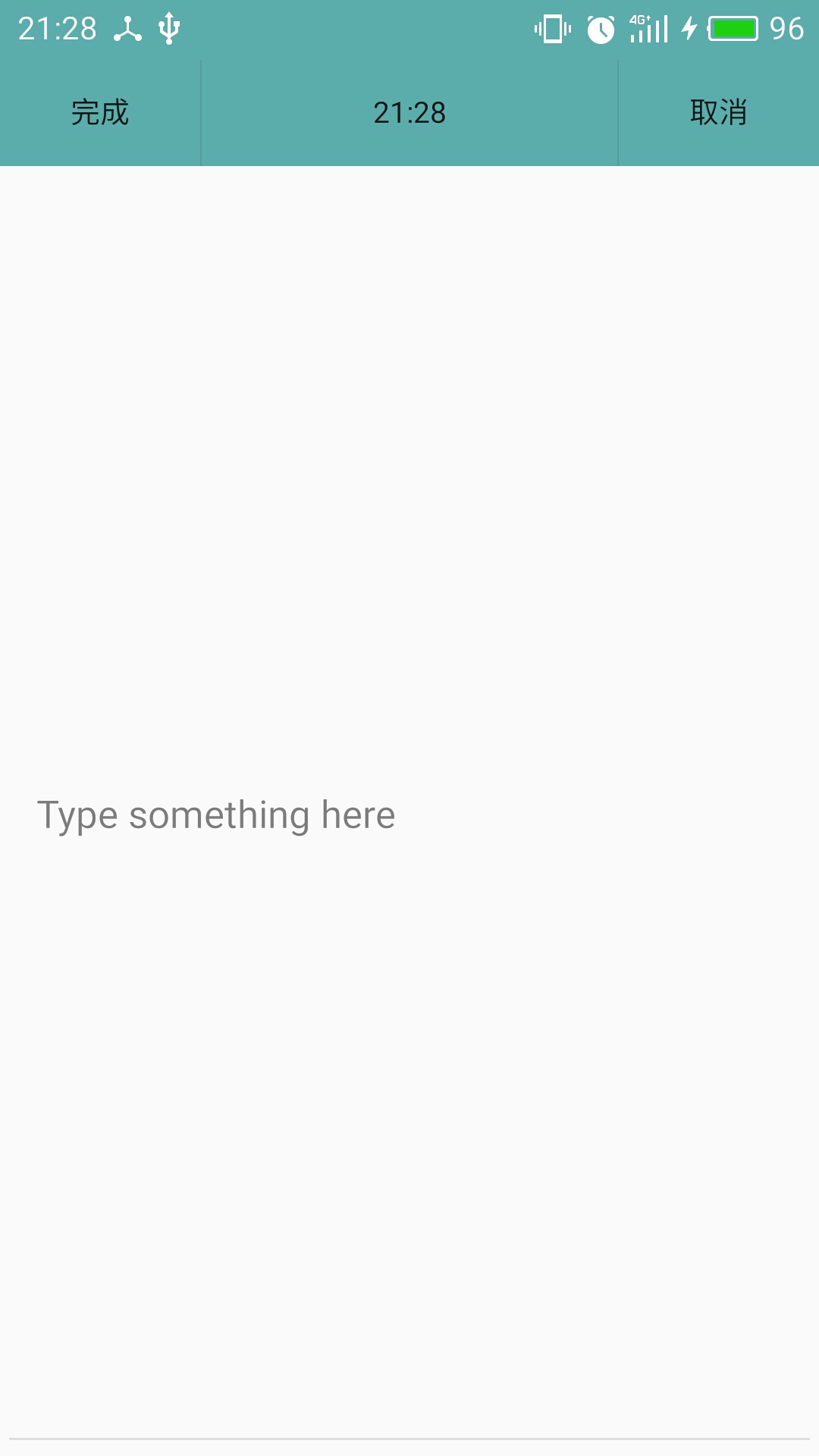
效果圖
modify.java
package com.example.notes_2;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.KeyEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
* Created by my on 2016/10/23.
*/
public class Modify extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener {
private EditText et_show;
private Button updateButton, deleteButton, backButton;
private DBHelper dbHelper;
private Cursor cursor;
private int id;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle s) {
super.onCreate(s);
setContentView(R.layout.modify);
init();
}
private void init() {
et_show = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_modify);
Intent intent = getIntent();
String data = intent.getStringExtra("data");
id = intent.getIntExtra("id", id);
et_show.setText(data);
dbHelper = new DBHelper(this);
cursor = dbHelper.select();
updateButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_update);
deleteButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_delete);
backButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_back);
updateButton.setOnClickListener(this);
deleteButton.setOnClickListener(this);
backButton.setOnClickListener(this);
}
public void updateData() {
if (id == 0) {
Toast.makeText(Modify.this, "內容不能為空", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} else {
dbHelper.update(id, et_show.getText().toString());
cursor.requery();
id = 0;
}
}
public void deleteData(){
if (id==0){
Toast.makeText(Modify.this, "內容不能為空", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}else{
dbHelper.delete(id);
cursor.requery();
id=0;
}
}
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
switch (arg0.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_update:
updateData();
Intent intent1 = new Intent(this,MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent1);
finish();
break;
case R.id.btn_delete:
deleteData();
Intent intent = new Intent(this,MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
finish();
break;
case R.id.btn_back:
Intent intent2 = new Intent(this,MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent2);
finish();
break;
}
}
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keycode,KeyEvent event){
if (keycode==KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK){
Intent intent = new Intent(this,MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
finish();return true;}else{
return super.onKeyDown(keycode,event);
}
}
}

還有這兩個activity的xml。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_ok"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="完成"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
/>
<TextClock
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:format12Hour="yyyy年dd月MM日 HH:mm"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_cancle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="取消"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:hint="Type something here"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<RelativeLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
android:id="@+id/xx"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_back"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="返回"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary" />
<TextClock
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:format12Hour="yy/dd/MM-HH:mm"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_delete"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="刪除"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary" />
</RelativeLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_update"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="儲存"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_modify"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_below="@+id/xx"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
這樣就實現了一個簡易的便籤了。 與大家分享。