unix/linux who命令的實現
Understanding Unix/Linux Programming(Unix/Linux程式設計實踐教程)
學習模式:
(1)它能做什麼?
(2)它是如何實現的?
(3)能不能自己編寫一個?
(實驗環境:gcc version 5.4.0 20160609 (Ubuntu 5.4.0-6ubuntu1~16.04.4) )
who命令的學習
(1) who命令能做什麼?
(2)如何實現的?
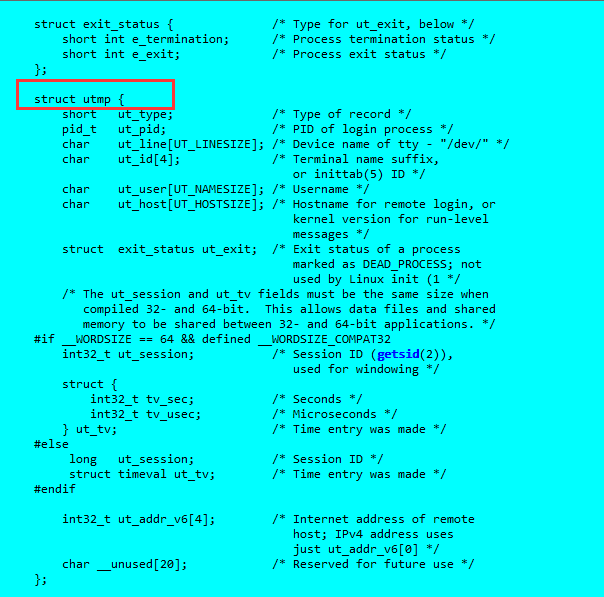
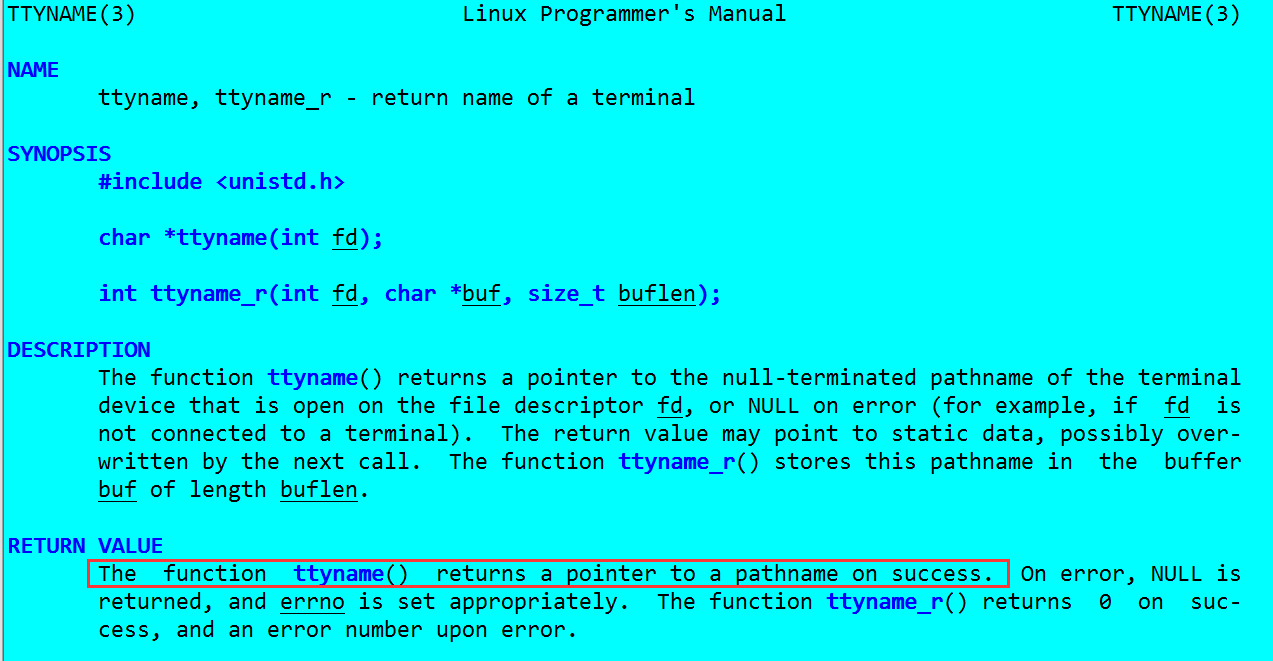
聯機幫助告訴我們,who命令通過讀取utmp這個檔案以實現對應的功能。utmp這個結構包含了我們需要的who所需要的全部資訊,除此之外還提供了其他資訊。
命令輸入: man 5 utmp
輸入命令:cat /usr/include/utmp.h
可知道_UTMP_FILE儲存了使用者登入的資訊。
(3)編碼實現
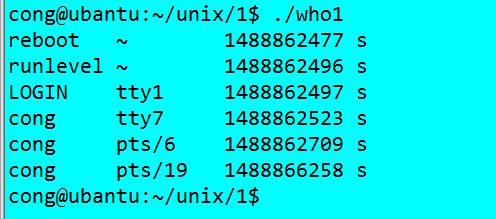
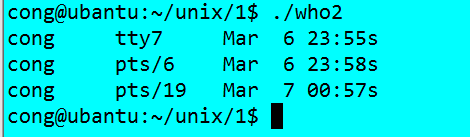
執行結果:可知跟我們shell提供的命令列印不太一樣。#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<utmp.h> #include<fcntl.h> #include<unistd.h> #define SHOWHOST /*include remote machine on output*/ void show_info(struct utmp* utbufp) { printf("%-8.8s ",utbufp->ut_name); /*thie logname */ printf("%-8.8s ",utbufp->ut_line); /*the logtty*/ printf("%10ld ",utbufp->ut_time); /*the logtime*/ #ifdef SHOWHOST printf("s",utbufp->ut_host); /*the host*/ #endif printf("\n"); } int main() { struct utmp current_record; /*read info into here*/ int utmpfd; /*read from the descriptor*/ int reclen = sizeof(current_record); //if((utmpfd = open("UTMP_FILE",O_RDONLY)) == -1) if((utmpfd = open(UTMP_FILE,O_RDONLY)) == -1) { perror(UTMP_FILE); /* UTMP_FILE is in utmp.h , #define UTMP_FILE _PATH_UTMP /*#define _PATH_UTMP "/var/run/utmp"*/ exit(1); } while(read(utmpfd,¤t_record,reclen) == reclen) show_info(¤t_record); close(utmpfd); return 0; }
完善:
(1) 清除空白記錄(通過判斷使用者是否線上即可)
同樣可通過命令:man 5 utmp
(2)時間格式化列印(使用系統呼叫將long int轉為ASCII 列印輸出)
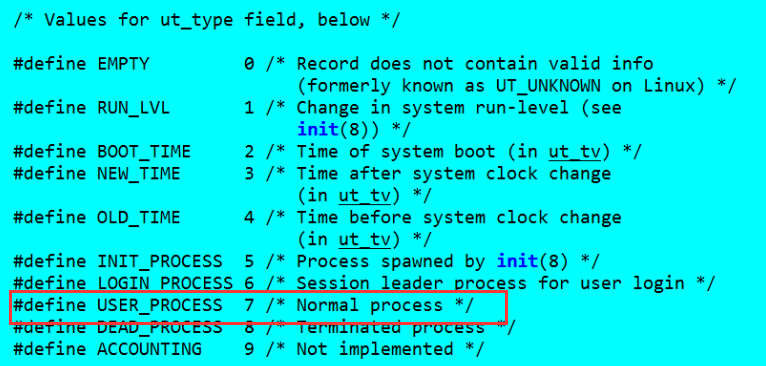
通過聯機查詢步驟:
1.man -k time | grep transform
2.man 3 ctime
程式碼完善實現如下:
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<utmp.h> #include<fcntl.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<time.h> #define SHOWHOST /*include remote machine on output*/ void showtime(long timeval) { char* cp; cp = ctime(&timeval); printf("%12.12s",cp+4); } void show_info(struct utmp* utbufp) { /*USER_PROCESS indicate the user is active or not*/ if(utbufp->ut_type!= USER_PROCESS) return ; printf("%-8.8s ",utbufp->ut_name); /*thie logname */ printf("%-8.8s ",utbufp->ut_line); /*the logtty*/ showtime(utbufp->ut_time); #ifdef SHOWHOST if(utbufp->ut_host[0] != '\0') printf("s",utbufp->ut_host); /*the host*/ #endif printf("\n"); } int main() { struct utmp current_record; /*read info into here*/ int utmpfd; /*read from the descriptor*/ int reclen = sizeof(current_record); //if((utmpfd = open("UTMP_FILE",O_RDONLY)) == -1) if((utmpfd = open(UTMP_FILE,O_RDONLY)) == -1) { perror(UTMP_FILE); /* UTMP_FILE is in utmp.h , #define UTMP_FILE _PATH_UTMP /*#define _PATH_UTMP "/var/run/utmp"*/ exit(1); } while(read(utmpfd,¤t_record,reclen) == reclen) show_info(¤t_record); close(utmpfd); return 0; }
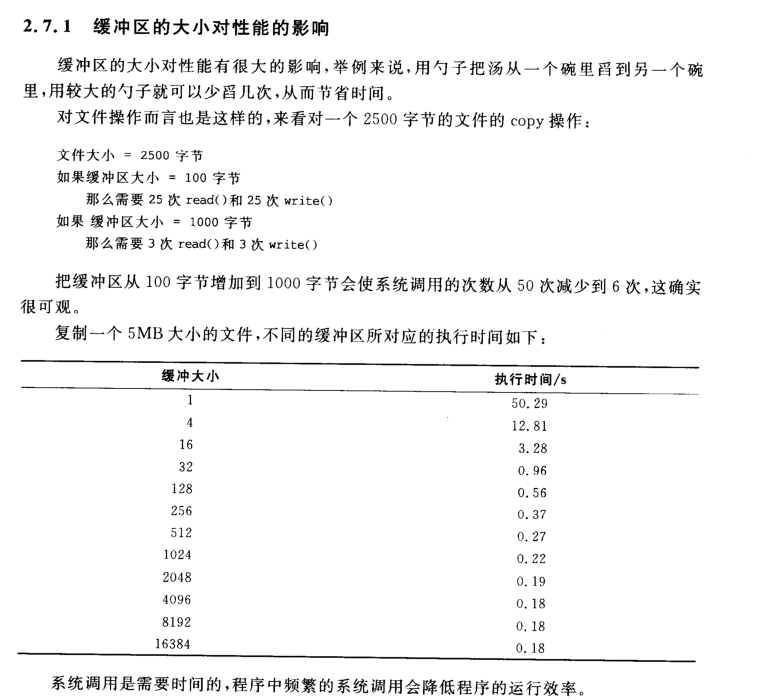
還記得前面那三個問題嗎?這裡增加一個問題,如何使程式的執行更加高效呢?
程式碼實現:
utmplib.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<utmp.h>
#define NRECS 16
#define NULLUT ((struct utmp*) NULL)
#define UTSIZE (sizeof(struct utmp))
static char utmpbuf[NRECS* UTSIZE]; /*storage*/
static int num_recs; /*num stored*/
static int cur_rec; /*next to go */
static int fd_utmp = -1; /*read from*/
int utmp_open(char* filename)
{
fd_utmp = open(filename,O_RDONLY);
cur_rec = num_recs = 0;
return fd_utmp;
}
int utmp_reload()
/*read next bunch of records into buffer*/
{
int amt_read;
amt_read = read(fd_utmp,utmpbuf,NRECS*UTSIZE);
num_recs = amt_read/UTSIZE;
cur_rec = 0;
return num_recs;
}
struct utmp* utmp_next()
{
struct utmp* recp;
if(fd_utmp == -1)
return NULLUT;
if(cur_rec == num_recs && utmp_reload() == 0)
return NULLUT;
recp = (struct utmp* )&utmpbuf[cur_rec * UTSIZE];
cur_rec ++;
return recp;
}
void utmp_close()
{
if(fd_utmp!=-1)
close(fd_utmp);
}
who3.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<utmp.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<time.h>
#include"utmplib.h"
#define SHOWHOST /*include remote machine on output*/
void showtime(long timeval)
{
char* cp;
cp = ctime(&timeval);
printf("%12.12s",cp+4);
}
void show_info(struct utmp* utbufp)
{
/*USER_PROCESS indicate the user is active or not*/
if(utbufp->ut_type!= USER_PROCESS)
return ;
printf("%-8.8s ",utbufp->ut_name); /*this logname */
printf("%-8.8s ",utbufp->ut_line); /*the logtty*/
showtime(utbufp->ut_time);
#ifdef SHOWHOST
if(utbufp->ut_host[0] != '\0')
printf("s",utbufp->ut_host); /*the host*/
#endif
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
struct utmp *utbufp; /*read info into here*/
int utmpfd; /*read from the descriptor*/
if(utmp_open(UTMP_FILE) == -1)
{
perror(UTMP_FILE);
exit(1);
}
while((utbufp =utmp_next()) != ((struct utmp*)NULL))
{
show_info(utbufp);
}
utmp_close();
return 0;
}(1)who am i 能做什麼?
使用者當前使用的相關終端裝置。
(2)如何實現?
我們可以在who2的基礎上進行篩選出使用者名稱相關終端裝置的資訊。
問題在於如何獲取使用者名稱相關的當前終端裝置??
(3)程式碼實現
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<utmp.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
void showtime(long);
void show_info(struct utmp*);
char* whats_my_line(int);
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
if(argc!=3)
{
printf("argument need : who am i");
exit(1);
}
struct utmp utbuf; //read info into here
int utmpfd; // read from this descriptor
char* myline = NULL;
myline = whats_my_line(0);// get the device name of tty
if((utmpfd = open(UTMP_FILE,O_RDONLY)) == -1)
{
perror(UTMP_FILE);
exit(1);
}
while(read(utmpfd,&utbuf,sizeof(utbuf)) == sizeof(utbuf))
{
if(myline == NULL || strcmp(utbuf.ut_line,myline) == 0)
show_info(&utbuf);
}
close(utmpfd);
return 0;
}
char* whats_my_line(int fd)
{
char *rv;
rv = ttyname(fd);
//puts(rv); //debug print: dev/pts/6
if(rv)
if(strncmp(rv,"/dev/",5) == 0)
return rv+5;
return rv;
// return pts/6
}
void showtime(long timeval)
{
char* cp;
cp = ctime(&timeval);
printf("%12.12s",cp + 4);
}
void show_info(struct utmp* utbufp)
{
if(utbufp->ut_type != USER_PROCESS) //online
return ;
printf("%-8.8s ",utbufp->ut_name);
printf("%-8.8s ",utbufp->ut_line);
showtime(utbufp->ut_time);
#ifdef SHOWHOST
if(utbufp->host[0] != '\0')
printf(" (%s) ",utbuf->ut_host);
#endif
printf("\n");
}
可知列印當前使用者名稱。
(2)如何實現的??
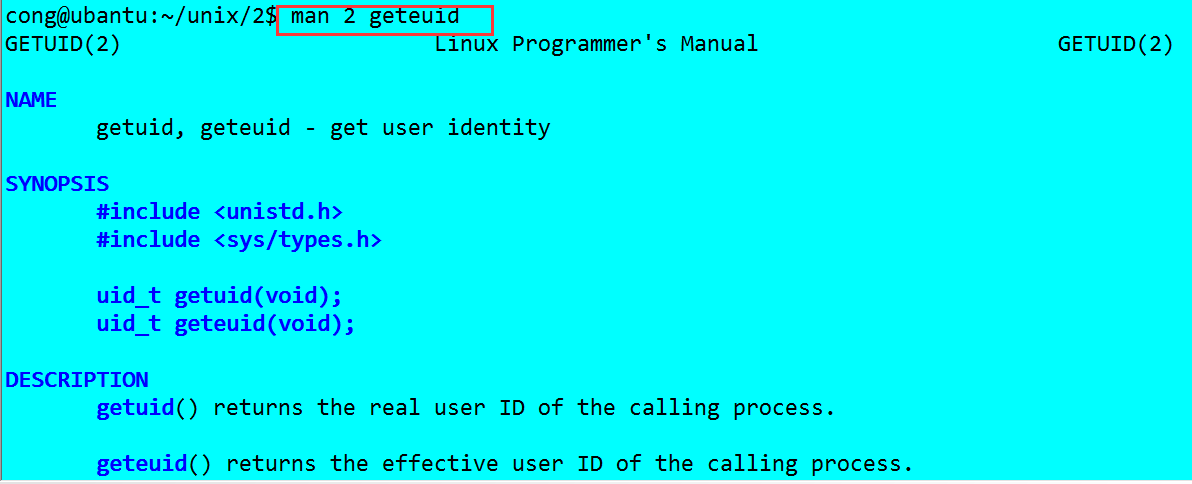
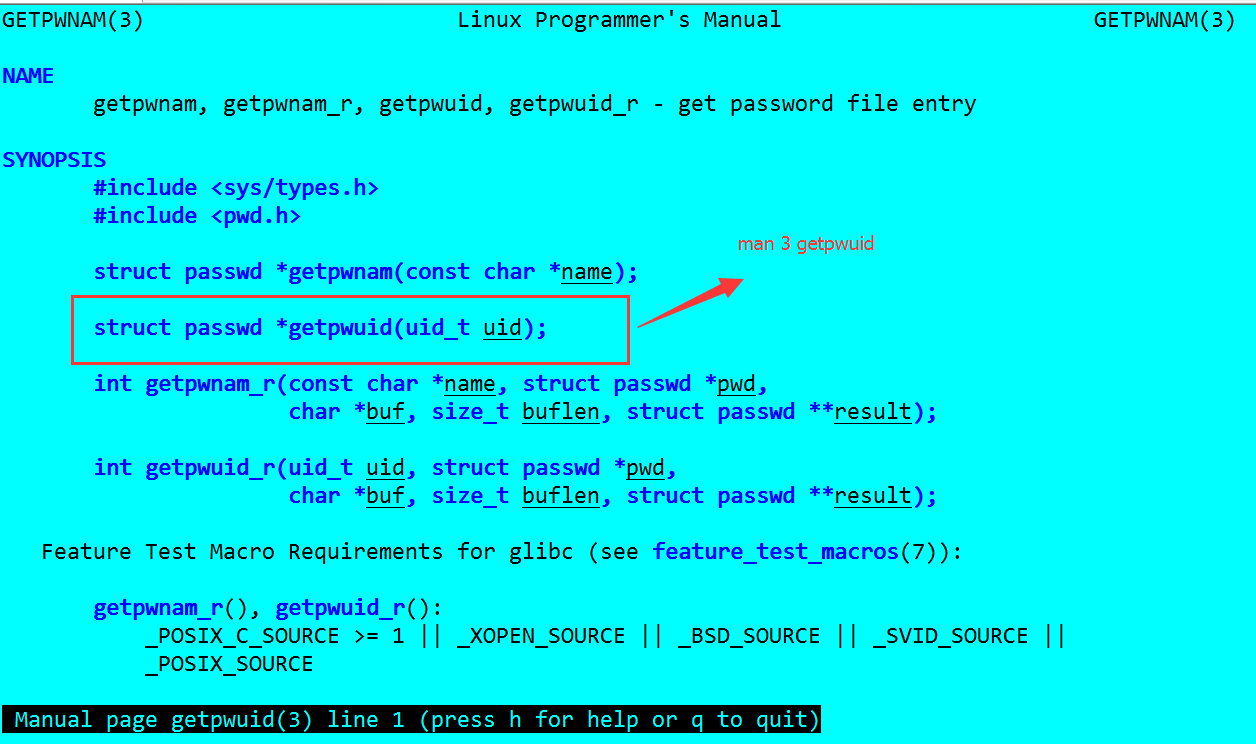
通過聯機幫助:man 2 geteuid, 可以通過獲取當前使用者id,通過使用getpwuid函式對應id找到使用者所對應的資訊,這些資訊包括使用者名稱。
cat /usr/include/pwd.h
(3)程式碼實現
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<pwd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
int main()
{
uid_t id; //effective user id of process
struct passwd* p; // will hold pwd data for user
id = geteuid(); //manpage says geteuid always succeeds
p = getpwuid(id);
if(p == NULL)
printf("I don't know thow you are \n");
else
printf("%s\n",p->pw_name);
return 0;
}