面向物件2--原型
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-05
一、原型和原型物件
函式的原型prototype:函式才有prototype,prototype是一個物件,指向了當前建構函式的引用地址。
所有物件都有__proto__屬性, 所有的__proto 指向改物件的原型物件(注意:proto前面是兩個)
關係示意圖:
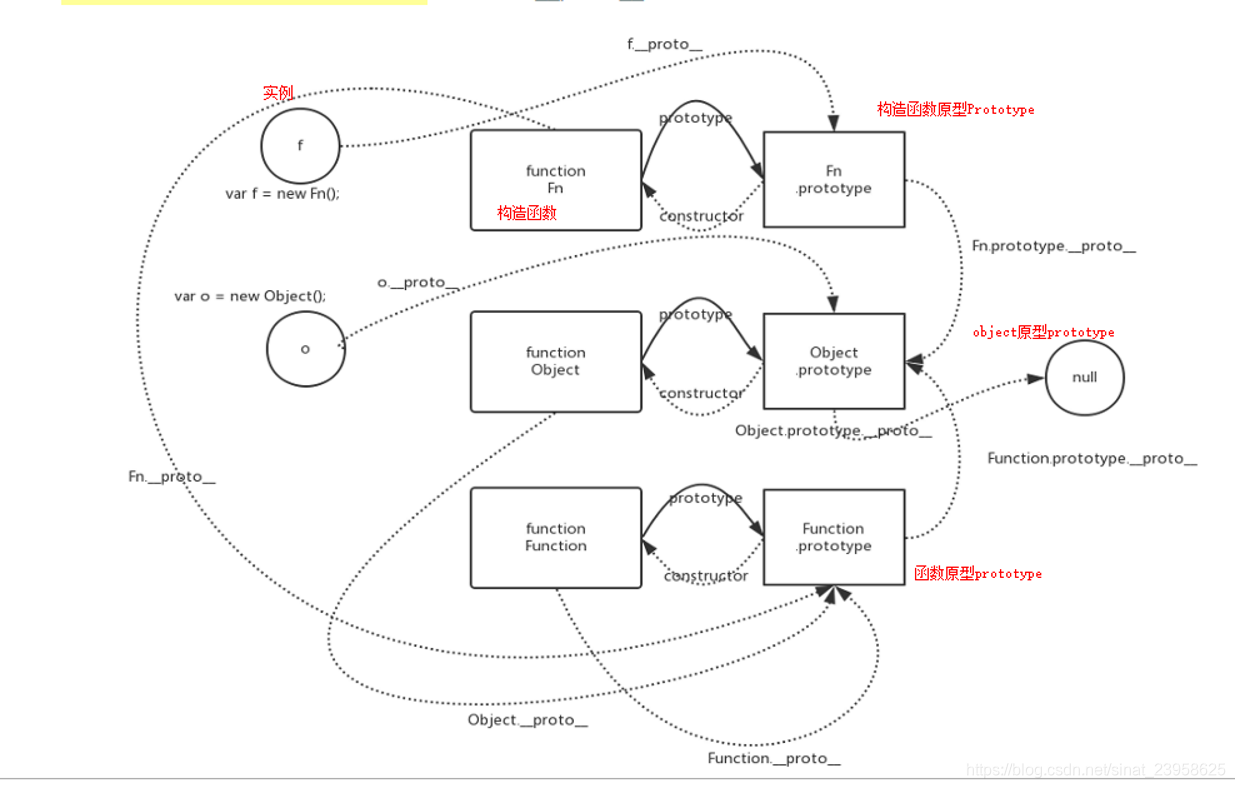
虛線代表:指標
實線:prototype原型物件
例項
function A() { this.a = 1; } var a = new A(); var obj = {}; console.log(a.constructor == A); //例項中無constructor屬性,在原型中存在,因為指標連結到a.__proto,輸出原型的constructor屬性A console.log(a.__proto__ === A.prototype); //ture 例項的__proto__指向建構函式的原型prototype console.log(A.__proto__ === Function.prototype);//true 建構函式的__proto__指向 Function的原型prototype console.log(A.prototype.constructor === A); //true 建構函式原型prototype的constructor屬性,指向建構函式 console.log(A.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype); //所有的prototype都是Object的例項 console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__ === null); //Object.prototype.__proto__ 是原型鏈的唯一出口 console.log(typeof null); //"object" null是一個空物件指標
二、原型的建立方式
2.1 單獨新增屬性方法
function Person(){ } Person.prototype.name = "Nicholas"; Person.prototype.age = 29; Person.prototype.job = "Software Engineer"; Person.prototype.sayName = function(){ console.log(this.name); }; var person1 = new Person(); person1.sayName(); //"Nicholas" var person2 = new Person(); person2.sayName(); //"Nicholas" //true 訪問的都是建構函式原型prototype的方法 console.log(person1.sayName == person2.sayName);

2.2 物件字面量方法
a. 採用{}方式
function Person(name, age, job) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.job = job; this.friends = ["Shelby", "Court"]; //引用型別屬性放在建構函式中 } Person.prototype = { constructor: Person, sayName: function () { alert(this.name); } }; var person1 = new Person("Nicholas", 29, "Software Engineer"); var person2 = new Person("Greg", 27, "Doctor"); person1.friends.push("Van"); alert(person1.friends); //"Shelby,Court,Van" alert(person2.friends); //"Shelby,Court" alert(person1.friends === person2.friends); //false alert(person1.sayName === person2.sayName); //true
b. 建構函式和原型結合
建構函式定義屬性,原型模式定義方法和共享的屬性
function Person(name, age, job){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.job = job;
this.friends = ["Shelby", "Court"]; //引用型別屬性放在建構函式中
}
Person.prototype = {
constructor: Person,
sayName : function () {
alert(this.name);
}
};
var person1 = new Person("Nicholas", 29, "Software Engineer");
var person2 = new Person("Greg", 27, "Doctor");
person1.friends.push("Van");
alert(person1.friends); //"Shelby,Court,Van"
alert(person2.friends); //"Shelby,Court"
alert(person1.friends === person2.friends); //false
alert(person1.sayName === person2.sayName); //true
2.3 class類
class A {
constructor(name) {
//建構函式
this.name = name; //給新的物件新增一個name屬性
}
// sayName相當於 A.prototype.sayName = function(){return this.name}
sayName() {
return this.name;
}
}
var a = new A('zhangsan');
console.log(a);
三、 原型物件屬性為引用型別
function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {
constructor: Person,
name: "Nicholas",
age: 29,
job: "Software Engineer",
friends: ["Shelby", "Court"],
sayName: function () {
console.log(this.name);
}
};
var person1 = new Person();
var person2 = new Person();
person1.friends.push("Van");
console.log(person1.friends); //"Shelby,Court,Van"
console.log(person2.friends); //"Shelby,Court,Van"
console.log(person1.friends === person2.friends); //true