Java直接記憶體和堆記憶體的效能比較
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-05
在JDK 1.4中新加入了NIO(New Input/Output)類,引入了一種基於通道(Channel)與緩衝區(Buffer)的I/O方式,
它可以使用Native函式庫直接分配堆外記憶體,然後通過一個儲存在Java堆裡面的DirectByteBuffer物件作為這塊記憶體的引用進行操作。
這樣能在一些場景中顯著提高效能,因為避免了在Java堆和Native堆中來回複製資料。
顯然,本機直接記憶體的分配不會受到Java堆大小的限制,
但是,既然是記憶體,則肯定還是會受到本機總記憶體(包括RAM及SWAP區或者分頁檔案)的大小及處理器定址空間的限制。
伺服器管理員配置虛擬機器引數時,一般會根據實際記憶體設定-Xmx等引數資訊,但經常會忽略掉直接記憶體,使得各個記憶體區域的總和大於實體記憶體限制(包括物理上的和
作業系統級的限制),從而導致動態擴充套件時出現OutOfMemoryError異常。上面這段話引用自該文章
程式碼實驗
注意到上面這段話中的黑體字:這樣能在一些場景中顯著提高效能,因為避免了在Java堆和Native堆中來回複製資料,然而這個“一些場景”具體指什麼呢?我們通過程式碼做個實驗看看。
- package com.winwill.jvm;
- import org.junit.Test;
- import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
- /**
- * @author qifuguang
- * @date 15-5-26 下午8:23
- */
- publicclass TestDirectMemory {
- /**
- * 測試DirectMemory和Heap讀寫速度。
- */
- @Test
- publicvoid testDirectMemoryWriteAndReadSpeed() {
- long tsStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
- ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(400);
- for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
- buffer.putInt(j);
- }
- buffer.flip();
- for (byte j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
- buffer.getInt();
- }
- buffer.clear();
- }
- System.out.println("DirectMemory讀寫耗用: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - tsStart) + " ms");
- tsStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
- buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(400);
- for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
- buffer.putInt(j);
- }
- buffer.flip();
- for (byte j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
- buffer.getInt();
- }
- buffer.clear();
- }
- System.out.println("Heap讀寫耗用: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - tsStart) + " ms");
- }
- /**
- * 測試DirectMemory和Heap記憶體申請速度。
- */
- @Test
- publicvoid testDirectMemoryAllocate() {
- long tsStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
- for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
- ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(400);
- }
- System.out.println("DirectMemory申請記憶體耗用: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - tsStart) + " ms");
- tsStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
- for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
- ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(400);
- }
- System.out.println("Heap申請記憶體耗用: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - tsStart) + " ms");
- }
- }
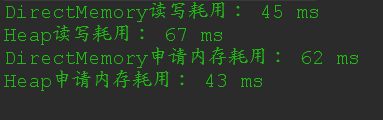
執行這段程式碼,得到的結果如下:
結論
從上面的實驗結果可以看出,直接記憶體在讀和寫的效能都優於堆內記憶體,但是記憶體申請速度卻不如堆內記憶體,所以可以歸納一下:
直接記憶體適用於不常申請,但是需要頻繁讀取的場景,
在需要頻繁申請的場景下不應該使用直接記憶體(DirectMemory),而應該使用堆內記憶體(HeapMemory)。