Spring PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer工作原理
前言
Spring提供配置解析功能,就是這種:
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" 或者是這種:
@Value("${spring_only}")
private String springOnly;可以很方便的通過配置XML來實現對Classpath下的配置檔案的注入。
在Spring3.1版本之前是通過PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer實現的。
而3.1之後則是通過PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 實現的。
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 和 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 在使用上並無本質的區別。兩者的根本目標是將配置檔案生成KV對。 真正的注入工作並不由它們本身執行。
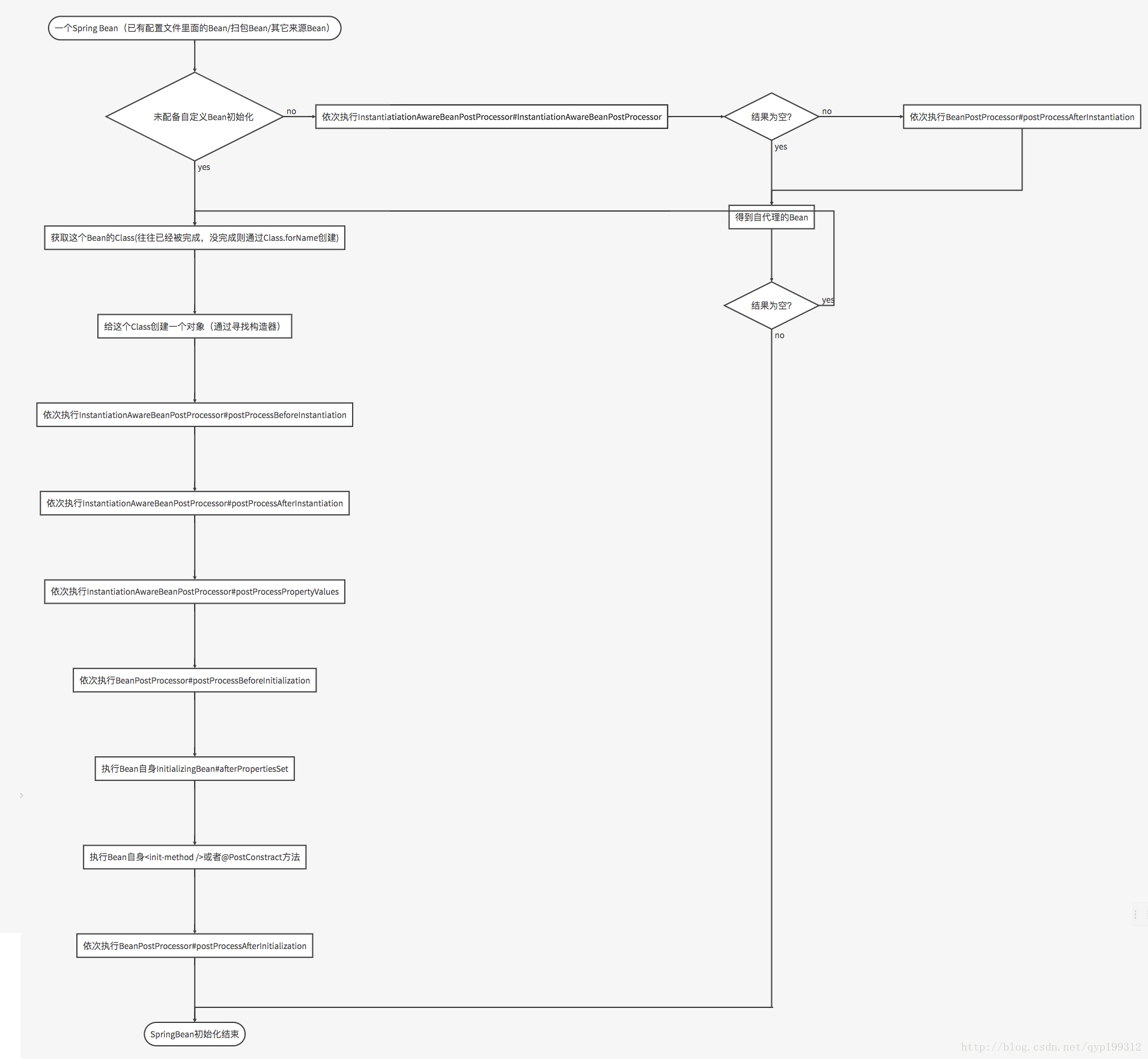
Spring生命週期
配置可以實現注入, 則必須得遵從Spring生命週期。Spring Bean的生命週期可以參考。
途中的
例項化指的是生成一個Java的物件。
元素注入時機
元素的注入依賴於 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessPropertyValues1。 通過解析了的PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 查詢得到元素值。 沒有則丟擲異常。如下原始碼:
原始碼摘自 DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency
// 獲取註解的 value() 值。被寫死為 Class<? extends Annotation> valueAnnotationType = Value.class;
// 見類 QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof String) {
// 通過PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer寫入的鍵值對元素獲取元素的值.
// 方法內註冊了多個StringValueResolver,迴圈查詢值。提供者為PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer,因此配置多個解析器的時候是以最後的配置為準的。
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ? getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}元素注入的序列圖如下:
在Spring初始化流程中,執行
AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitializatin方法。 該方法裡面發生的主要流程為Spring 業務 Bean初始化。 實際流程跟Spring Bean的初始化沒有任務區別。
通過對介面InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor實現類的方法進行執行。 僅此而已
可以看出
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer或者PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer僅僅是做了一個配置檔案的解析工作,真正的注入並不由它們完成,而是託付給了Spring 的Bean初始化流程。
之所以這麼做可以生效,是因為這兩個類實現了BeanFactoryPostProcessor介面,這個介面的優先順序高於後續的Spring Bean。
資料來源
配置Bean方式
單個配置檔案
<bean id="propertyConfigurer"class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location">
<value>conf/sqlmap/jdbc.properties</value>
</property>
<property name="fileEncoding">
<value>UTF-8</value>
</property>
</bean>多個配置檔案
<bean id="propertyConfigurer"class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>/WEB-INF/mail.properties</value>
<value>classpath: conf/sqlmap/jdbc.properties</value>//注意這兩種value值的寫法
</list>
</property>
</bean>其中PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer是Spring3.1之前使用的。
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer是Spring3.1之後使用的。
寫法都類似
Spring標籤方式
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:/WEB-INF/mail.properties" />這總方式的原理就是構造一個PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer, (3.1之前是PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer)
- ContextNamespaceHandler#init
- PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser#doParse
觸發點為:
AbstractApplicationContext#obtainFreshBeanFactory 。Spring初始化Context的時候讀取XML配置(基於XML), 這個流程優先於Spring 普通Bean初始化。配合掃包(<context:component-scan />)得到的Bean進而實現對XML裡面配置的Bean的載入。
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer本質上是一個BeanFactoryPostProcessor。解析XML的流程在BeanFactoryPostProcessor之前, 優先將配置檔案的路徑以及名字通過Setter傳入PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer。
如上BeanFactoryPostProcessor的優先順序又優於其餘的Bean。因此可以實現在bean初始化之前的注入。
引申mybatis資料來源配置
通常在配置mybatis的時候,配置 org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer需要使用<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactoryAccount" /> 引數實現SqlSessionFactory的注入。
這是由於MapperScannerConfigurer 本質上也是一個 BeanFactoryPostProcessor。 而SqlSessionFactory往往只是一個普通的Spring Bean, 它的優先順序是低於 MapperScannerConfigurer 的, 如果在初始化 MapperScannerConfigurer 的時候去尋找SqlSessionFactory, 肯定是會報依賴錯誤的, 因此之後在後續的流程中實現注入。
發生找不到配置的情況
在工作中我們會習慣性的使用多個Spring配置檔案, 例如spring.xml/spring-db.xml/spring-web.xml燈。 裡面就配置多個Spring標籤,或者多個 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 。但是時常會發生找不到配置的情況。
為什麼<context:property-placeholder />優先順序更高
因為基於XML配置的Spring, 不管是<context:property-placeholder />還是 <Bean />標籤都依賴於 NamespaceHandler去解析。 而<context:property-placeholder />在解析完畢之後就已經生成了 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer , <Bean />標籤還需要等待後續流程。
為什麼PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer唯一
這裡的”為什麼”, 指的不是它為什麼這麼設計,而是為什麼會有這麼樣的結果。
另外PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer並不唯一,只是在對外體現上後續的配置無法去到值,因此看起來是唯一的。
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer Bean的唯一是由Java web特性和Spring本身的設計決定的。
- Servlet的啟動,在web.xml中Listener序列單執行緒啟動。
- Spring內建的Bean模式為單例模式。
- Spring在初始化的時候會直接將需要的Bean給初始化成功。
- 啟動的先後順序依賴於它們在 xml 裡面配置的上下關係。
不管 <context:property-placeholder />或者PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer或者PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer方式配置的配置解析器,其本質就是得到一個 BeanFactoryPostProcessor, 並執行其 #postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory)方法。
其執行的根本目的在於 PlaceholderConfigurerSupport#doProcessProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, StringValueResolver )。
protected void doProcessProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,
StringValueResolver valueResolver) {
// ignore
....
// New in Spring 2.5: resolve placeholders in alias target names and aliases as well.
beanFactoryToProcess.resolveAliases(valueResolver);
// New in Spring 3.0: resolve placeholders in embedded values such as annotation attributes.
// 目的是為了新增解析器
beanFactoryToProcess.addEmbeddedValueResolver(valueResolver);
}這裡的 addEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver) 是為一個 LinkedList新增值。
在取用的時候是優先從連結串列頭開始取用的。 一旦發現無法找到值,直接就拋異常了。這個就對外體現出 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 的唯一性。 (然而Spring內部還是有多個PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer, 只不過除了排列在隊首的 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 之外全都被忽略掉了 )。
總結Spring Value注入流程
最後的總結:
配置Spring @Value("val2Inject") 方式獲取配置檔案的屬性,需要依賴於在Spring XML裡面配置<context:property-placeholder /> 或者PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurerBean來新增配置檔案的名稱。流程如下:
- Spring Context 的初始化開始
- 讀取到
context:property-placeholder標籤或者PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer - 解析並例項化一個
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer。同時向其中注入配置檔案路徑、名稱 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer自身生成多個StringValueResolver備用,Bean準備完畢- Spring在初始化非
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的Bean的時候,AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor負責找到Bean內有@Value註解的Field或者Method - 通過
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer尋找合適的StringValueResolver並解析得到val值。注入給@Value的Field或Method。(Method優先)2 - Spring的其他流程。