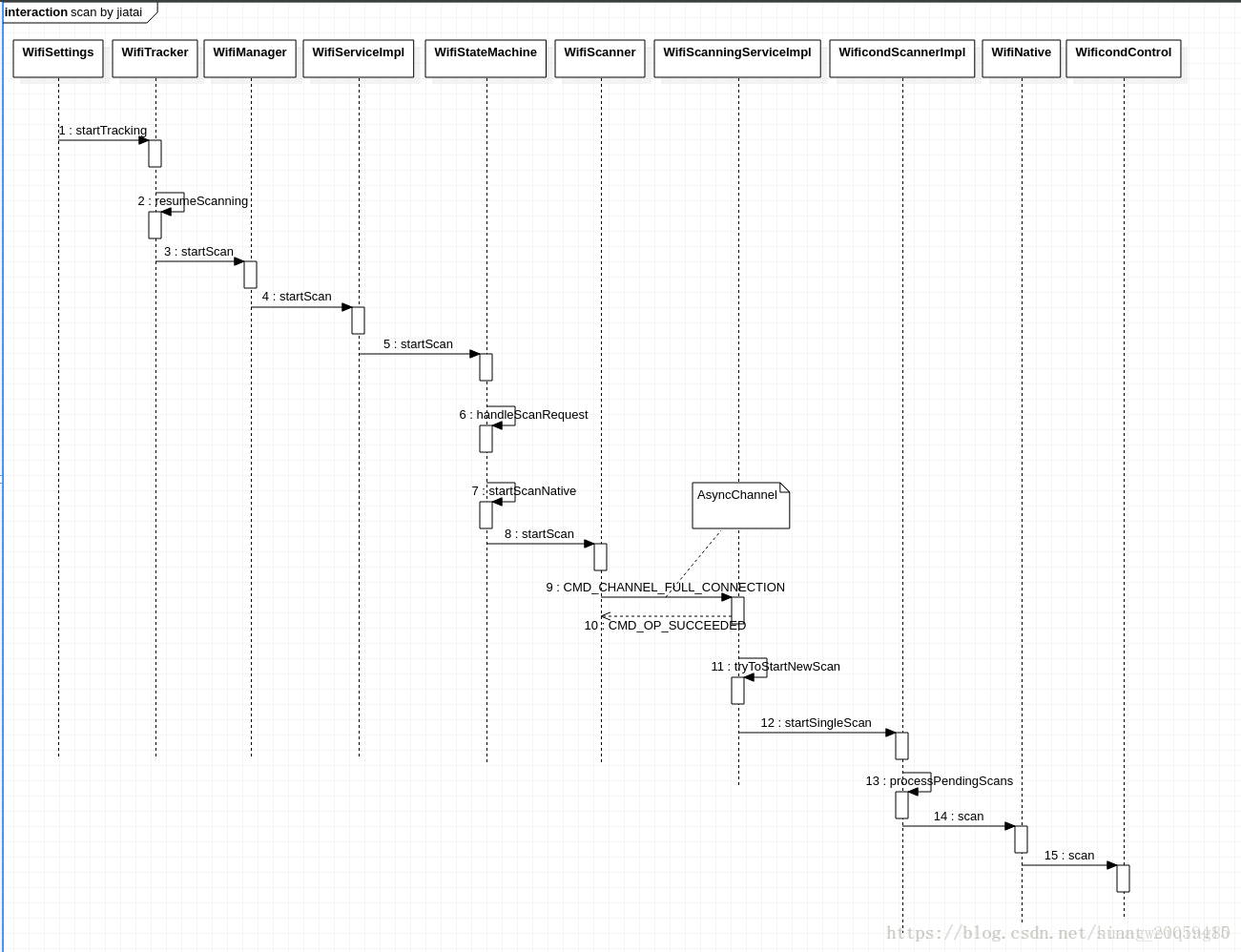
Android O WiFi的掃描流程
1.Android O的scan跟之前Android版本存在的差異
1) Android O開始scan的命令不是通過wpa_supplicant下發到kernel,而是直接由wificond傳送到kernel,而scan results的結果也是直接由kernel傳給wificond,再由wificond傳送給上層去顯示
2) 在framework層,現在scan改由scanner這個類去使用,之前從6.0開始慢慢用起來,現在到了8.0,可以說已經用了近95%了,剩下了目前google還在修改中,google的目標應該是想把scan整個完全獨立出來,不跟其他的扯太大,例如WifiStateMachine
3) 目前上層下發的scan,已經改由SettingsLib去定時下,不交給apk去做了。
在android 8.0之前的版本,scan的定時掃描都是在上層app做的,但從8.0開始,google把這個定時器改到了framework中的SettingsLib(frameworks/base/packages/SettingsLib)中去了
4) 之前的版本scan操作,當同一時間下兩次scan時,是直接交由wpa_supplicant去隔開的,現在由於直接把scan下發給kernel。所以,google已經把上層下的scan跟framework的自動scan也實現了分離,不讓這兩種flow打到,讓同一時間只下一次scan,後一次則做pending動作
2. 流程分析
2.1 Settings
WiFi Settings在Android 8.0程式碼同樣分為兩部分,packages/apps/Settings和framework/base/packages/SettingsLib。
/packages/apps/Settings/src/com/android/settings/wifi/WifiSettings.java
@Override
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
// On/off switch is hidden for Setup Wizard (returns null 這裡會呼叫到SettingsLib的WifiTracker,WifiTracker中包含了wifi掃描的操作。比較奇怪的是,這裡沒有走監聽wifi開啟訊息,待WiFi開啟後開始掃描,而是隻要在WiFi介面就開始掃描了。不用奇怪,因為後面會去做檢查只有wifi開啟之後,才會真正下發scan命令到底層,具體請看下面的分析。
2.2 SettingsLib
/frameworks/base/packages/SettingsLib/src/com/android/settingslib/wifi/WifiTracker.java
/**
* Start tracking wifi networks and scores.
*
* <p>Registers listeners and starts scanning for wifi networks. If this is not called
* then forceUpdate() must be called to populate getAccessPoints().
*/
@MainThread
public void startTracking() {
synchronized (mLock) {
registerScoreCache();
mNetworkScoringUiEnabled =
Settings.Global.getInt(
mContext.getContentResolver(),
Settings.Global.NETWORK_SCORING_UI_ENABLED, 0) == 1;
mMaxSpeedLabelScoreCacheAge =
Settings.Global.getLong(
mContext.getContentResolver(),
Settings.Global.SPEED_LABEL_CACHE_EVICTION_AGE_MILLIS,
DEFAULT_MAX_CACHED_SCORE_AGE_MILLIS);
resumeScanning();
if (!mRegistered) {
mContext.registerReceiver(mReceiver, mFilter);
// NetworkCallback objects cannot be reused. http://b/20701525 .
mNetworkCallback = new WifiTrackerNetworkCallback();
mConnectivityManager.registerNetworkCallback(mNetworkRequest, mNetworkCallback);
mRegistered = true;
}
}
}startTracking() –> resumeScanning();
/**
* Resume scanning for wifi networks after it has been paused.
*
* <p>The score cache should be registered before this method is invoked.
*/
public void resumeScanning() {
if (mScanner == null) {
mScanner = new Scanner();
}
mWorkHandler.sendEmptyMessage(WorkHandler.MSG_RESUME);
if (mWifiManager.isWifiEnabled()) {
mScanner.resume();
}
}這裡可以看到resumeScanning()會去判斷wifi有沒有開啟mWifiManager.isWifiEnabled(),如果沒有開啟就不繼續進行掃描流程了。只有打開了wifi才會呼叫mScanner.resume()繼續走下去
frameworks/base/packages/SettingsLib/src/com/android/settingslib/wifi/WifiTracker.java
@VisibleForTesting
class Scanner extends Handler {
static final int MSG_SCAN = 0;
private int mRetry = 0;
void resume() {
if (!hasMessages(MSG_SCAN)) {
sendEmptyMessage(MSG_SCAN);
}
}
void forceScan() {
removeMessages(MSG_SCAN);
sendEmptyMessage(MSG_SCAN);
}
void pause() {
mRetry = 0;
removeMessages(MSG_SCAN);
}
@VisibleForTesting
boolean isScanning() {
return hasMessages(MSG_SCAN);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message message) {
if (message.what != MSG_SCAN) return;
if (mWifiManager.startScan()) {
mRetry = 0;
} else if (++mRetry >= 3) {
mRetry = 0;
if (mContext != null) {
Toast.makeText(mContext, R.string.wifi_fail_to_scan, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
return;
}
sendEmptyMessageDelayed(MSG_SCAN, WIFI_RESCAN_INTERVAL_MS);
}
}class Scanner是WifiTracker中的一個內部類,整個類就這麼一點程式碼,那麼來分析一下這個Scanner類,前面呼叫的這個mScanner.resume()函式中就傳送了一條訊息sendEmptyMessage(MSG_SCAN);然後在類中的handleMessage中對這個訊息進行處理,這個類的handleMessage中也只處理這一個訊息,從handleMessage函式中可以看到if (message.what != MSG_SCAN) return;如果不是MSG_SCAN就退出函數了,如果是才會接著去進行掃描。
這裡可以看到如果掃描失敗3次就會導致掃描失敗的toast的提醒,如果掃描成功則會進行掃描間隔為10s的持續掃描。
// TODO: Allow control of this?
// Combo scans can take 5-6s to complete - set to 10s.
private static final int WIFI_RESCAN_INTERVAL_MS = 10 * 1000;從mWifiManager.startScan()可以知道,這裡掃描流程就走到WifiManager裡去了
2.3 WiFi framework
2.3.1 WifiManager
/framework/base/wifi/java/android/net/wifi/WifiManager.java
/**
* Request a scan for access points. Returns immediately. The availability
* of the results is made known later by means of an asynchronous event sent
* on completion of the scan.
* @return {@code true} if the operation succeeded, i.e., the scan was initiated
*/
public boolean startScan() {
return startScan(null);
} /** @hide */
@SystemApi
@RequiresPermission(android.Manifest.permission.UPDATE_DEVICE_STATS)
public boolean startScan(WorkSource workSource) {
try {
String packageName = mContext.getOpPackageName();
mService.startScan(null, workSource, packageName);
return true;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}從程式碼角度來看startScan要麼返回true要麼拋異常呀,false不可能。。。
之前分析過mService對應的服務端是WifiServiceImpl
2.3.2 WifiServiceImpl
framework/opt/net/wifi/service/java/com/android/server/wifi/WifiServiceImpl.java
/**
* see {@link android.net.wifi.WifiManager#startScan}
* and {@link android.net.wifi.WifiManager#startCustomizedScan}
*
* @param settings If null, use default parameter, i.e. full scan.
* @param workSource If null, all blame is given to the calling uid.
* @param packageName Package name of the app that requests wifi scan.
*/
@Override
public void startScan(ScanSettings settings, WorkSource workSource, String packageName) {
enforceChangePermission();
mLog.info("startScan uid=%").c(Binder.getCallingUid()).flush();
// Check and throttle background apps for wifi scan.
if (isRequestFromBackground(packageName)) {
long lastScanMs = mLastScanTimestamps.getOrDefault(packageName, 0L);
long elapsedRealtime = mClock.getElapsedSinceBootMillis();
if (lastScanMs != 0 && (elapsedRealtime - lastScanMs) < mBackgroundThrottleInterval) {
sendFailedScanBroadcast();
return;
}
// Proceed with the scan request and record the time.
mLastScanTimestamps.put(packageName, elapsedRealtime);
}
synchronized (this) {
if (mWifiScanner == null) {
mWifiScanner = mWifiInjector.getWifiScanner();
}
if (mInIdleMode) {
// Need to send an immediate scan result broadcast in case the
// caller is waiting for a result ..
// TODO: investigate if the logic to cancel scans when idle can move to
// WifiScanningServiceImpl. This will 1 - clean up WifiServiceImpl and 2 -
// avoid plumbing an awkward path to report a cancelled/failed scan. This will
// be sent directly until b/31398592 is fixed.
sendFailedScanBroadcast();
mScanPending = true;
return;
}
}
if (settings != null) {
settings = new ScanSettings(settings);
if (!settings.isValid()) {
Slog.e(TAG, "invalid scan setting");
return;
}
}
if (workSource != null) {
enforceWorkSourcePermission();
// WifiManager currently doesn't use names, so need to clear names out of the
// supplied WorkSource to allow future WorkSource combining.
workSource.clearNames();
}
if (workSource == null && Binder.getCallingUid() >= 0) {
workSource = new WorkSource(Binder.getCallingUid());
}
mWifiStateMachine.startScan(Binder.getCallingUid(), scanRequestCounter++,
settings, workSource);
}注意這個方法前兩個引數傳進來的都是null,這邊一開始會對wifi掃描的請求物件做個過濾,畢竟WiFi掃描是耗電的,不能誰都來請求一下。不在白名單的後臺應用的請求掃描時間間隔如果短於30min,則通報批評。下面是startScan函式中對此過濾的操作和分析
// Check and throttle background apps for wifi scan.
if (isRequestFromBackground(packageName)) {
long lastScanMs = mLastScanTimestamps.getOrDefault(packageName, 0L);
long elapsedRealtime = mClock.getElapsedSinceBootMillis();
if (lastScanMs != 0 && (elapsedRealtime - lastScanMs) < mBackgroundThrottleInterval) {
sendFailedScanBroadcast();
return;
}
// Proceed with the scan request and record the time.
mLastScanTimestamps.put(packageName, elapsedRealtime);
}isRequestFromBackground函式原始碼如下:
// Check if the request comes from background.
private boolean isRequestFromBackground(String packageName) {
// Requests from system or wifi are not background.
if (Binder.getCallingUid() == Process.SYSTEM_UID
|| Binder.getCallingUid() == Process.WIFI_UID) {
return false;
}
mAppOps.checkPackage(Binder.getCallingUid(), packageName);
if (mBackgroundThrottlePackageWhitelist.contains(packageName)) {
return false;
}
// getPackageImportance requires PACKAGE_USAGE_STATS permission, so clearing the incoming
// identify so the permission check can be done on system process where wifi runs in.
long callingIdentity = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
return mActivityManager.getPackageImportance(packageName)
> BACKGROUND_IMPORTANCE_CUTOFF;
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(callingIdentity);
}
}掃描間隔DEFAULT_SCAN_BACKGROUND_THROTTLE_INTERVAL_MS定義如下
private static final long DEFAULT_SCAN_BACKGROUND_THROTTLE_INTERVAL_MS = 30 * 60 * 1000;sendFailedScanBroadcast函式原始碼如下
// Send a failed scan broadcast to indicate the current scan request failed.
private void sendFailedScanBroadcast() {
// clear calling identity to send broadcast
long callingIdentity = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
Intent intent = new Intent(WifiManager.SCAN_RESULTS_AVAILABLE_ACTION);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY_BEFORE_BOOT);
intent.putExtra(WifiManager.EXTRA_RESULTS_UPDATED, false);
mContext.sendBroadcastAsUser(intent, UserHandle.ALL);
} finally {
// restore calling identity
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(callingIdentity);
}
}回到剛才的startScan函式。由於傳入的前兩個引數是null,則直接走到WifiStateMachine裡去了。
mWifiStateMachine.startScan(Binder.getCallingUid(), scanRequestCounter++,
settings, workSource);2.3.3 WifiStateMachine
framework/opt/net/wifi/service/java/com/android/server/wifi/WifiStateMachine.java
/**
* Initiate a wifi scan. If workSource is not null, blame is given to it, otherwise blame is
* given to callingUid.
*
* @param callingUid The uid initiating the wifi scan. Blame will be given here unless
* workSource is specified.
* @param workSource If not null, blame is given to workSource.
* @param settings Scan settings, see {@link ScanSettings}.
*/
public void startScan(int callingUid, int scanCounter,
ScanSettings settings, WorkSource workSource) {
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putParcelable(CUSTOMIZED_SCAN_SETTING, settings);
bundle.putParcelable(CUSTOMIZED_SCAN_WORKSOURCE, workSource);
bundle.putLong(SCAN_REQUEST_TIME, mClock.getWallClockMillis());
sendMessage(CMD_START_SCAN, callingUid, scanCounter, bundle);
}sendMessage(CMD_START_SCAN, callingUid, scanCounter, bundle);傳送一條訊息CMD_START_SCAN;
由於前面已經enable supplicant,所以到目前掃描階段,WifiStateMachine狀態機目前的狀態應該是SupplicantStartedState,下面來看看WifiStateMachine在SupplicantStartedState 怎麼處理這個訊息
class SupplicantStartedState extends State {
...
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
logStateAndMessage(message, this);
switch(message.what) {
...
case CMD_START_SCAN:
// TODO: remove scan request path (b/31445200)
handleScanRequest(message);
break;呼叫handleScanRequest(message);進行處理
private void handleScanRequest(Message message) {
ScanSettings settings = null;
WorkSource workSource = null;
// unbundle parameters
Bundle bundle = (Bundle) message.obj;
if (bundle != null) {
settings = bundle.getParcelable(CUSTOMIZED_SCAN_SETTING);
workSource = bundle.getParcelable(CUSTOMIZED_SCAN_WORKSOURCE);
}
Set<Integer> freqs = null;
if (settings != null && settings.channelSet != null) {
freqs = new HashSet<>();
for (WifiChannel channel : settings.channelSet) {
freqs.add(channel.freqMHz);
}
}
// Retrieve the list of hidden network SSIDs to scan for.
List<WifiScanner.ScanSettings.HiddenNetwork> hiddenNetworks =
mWifiConfigManager.retrieveHiddenNetworkList();
// call wifi native to start the scan
if (startScanNative(freqs, hiddenNetworks, workSource)) {
// a full scan covers everything, clearing scan request buffer
if (freqs == null)
mBufferedScanMsg.clear();
messageHandlingStatus = MESSAGE_HANDLING_STATUS_OK;
return;
}
// if reach here, scan request is rejected
if (!mIsScanOngoing) {
// if rejection is NOT due to ongoing scan (e.g. bad scan parameters),
// discard this request and pop up the next one
if (mBufferedScanMsg.size() > 0) {
sendMessage(mBufferedScanMsg.remove());
}
messageHandlingStatus = MESSAGE_HANDLING_STATUS_DISCARD;
} else if (!mIsFullScanOngoing) {
// if rejection is due to an ongoing scan, and the ongoing one is NOT a full scan,
// buffer the scan request to make sure specified channels will be scanned eventually
if (freqs == null)
mBufferedScanMsg.clear();
if (mBufferedScanMsg.size() < SCAN_REQUEST_BUFFER_MAX_SIZE) {
Message msg = obtainMessage(CMD_START_SCAN,
message.arg1, message.arg2, bundle);
mBufferedScanMsg.add(msg);
} else {
// if too many requests in buffer, combine them into a single full scan
bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putParcelable(CUSTOMIZED_SCAN_SETTING, null);
bundle.putParcelable(CUSTOMIZED_SCAN_WORKSOURCE, workSource);
Message msg = obtainMessage(CMD_START_SCAN, message.arg1, message.arg2, bundle);
mBufferedScanMsg.clear();
mBufferedScanMsg.add(msg);
}
messageHandlingStatus = MESSAGE_HANDLING_STATUS_LOOPED;
} else {
// mIsScanOngoing and mIsFullScanOngoing
messageHandlingStatus = MESSAGE_HANDLING_STATUS_FAIL;
}
}if (startScanNative(freqs, hiddenNetworks, workSource))
繼續呼叫startScanNative
// TODO this is a temporary measure to bridge between WifiScanner and WifiStateMachine until
// scan functionality is refactored out of WifiStateMachine.
/**
* return true iff scan request is accepted
*/
private boolean startScanNative(final Set<Integer> freqs,
List<WifiScanner.ScanSettings.HiddenNetwork> hiddenNetworkList,
WorkSource workSource) {
WifiScanner.ScanSettings settings = new WifiScanner.ScanSettings();
if (freqs == null) {
settings.band = WifiScanner.WIFI_BAND_BOTH_WITH_DFS;
} else {
settings.band = WifiScanner.WIFI_BAND_UNSPECIFIED;
int index = 0;
settings.channels = new WifiScanner.ChannelSpec[freqs.size()];
for (Integer freq : freqs) {
settings.channels[index++] = new WifiScanner.ChannelSpec(freq);
}
}
settings.reportEvents = WifiScanner.REPORT_EVENT_AFTER_EACH_SCAN
| WifiScanner.REPORT_EVENT_FULL_SCAN_RESULT;
settings.hiddenNetworks =
hiddenNetworkList.toArray(
new WifiScanner.ScanSettings.HiddenNetwork[hiddenNetworkList.size()]);
WifiScanner.ScanListener nativeScanListener = new WifiScanner.ScanListener() {
// ignore all events since WifiStateMachine is registered for the supplicant events
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
}
@Override
public void onFailure(int reason, String description) {
mIsScanOngoing = false;
mIsFullScanOngoing = false;
}
@Override
public void onResults(WifiScanner.ScanData[] results) {
}
@Override
public void onFullResult(ScanResult fullScanResult) {
}
@Override
public void onPeriodChanged(int periodInMs) {
}
};
mWifiScanner.startScan(settings, nativeScanListener, workSource);
mIsScanOngoing = true;
mIsFullScanOngoing = (freqs == null);
lastScanFreqs = freqs;
return true;
}由於freqs和workSource這兩個引數為null,走settings.band = WifiScanner.WIFI_BAND_BOTH_WITH_DFS;所以settings.band是7,即頻段為7
/** Both 2.4 GHz band and 5 GHz band; with DFS channels */
public static final int WIFI_BAND_BOTH_WITH_DFS = 7; /* both bands with DFS channels */這邊繼續呼叫WifiScanner的startScan,settings不是null了,已經在startScanNative函式中被預設初始化過了。另外
WifiScanner.ScanListener nativeScanListener = new WifiScanner.ScanListener()
這邊初始化了一個nativeScanListener委託給WifiScanner,從方法來看是有結果了會回撥這個Listner,使用了委託模式。
2.3.4 WifiScanner
framework/base/wifi/java/android/net/wifi/WifiScanner.java
/**
* starts a single scan and reports results asynchronously
* @param settings specifies various parameters for the scan; for more information look at
* {@link ScanSettings}
* @param listener specifies the object to report events to. This object is also treated as a
* key for this scan, and must also be specified to cancel the scan. Multiple
* scans should also not share this object.
*/
@RequiresPermission(android.Manifest.permission.LOCATION_HARDWARE)
public void startScan(ScanSettings settings, ScanListener listener) {
startScan(settings, listener, null);
}
/**
* starts a single scan and reports results asynchronously
* @param settings specifies various parameters for the scan; for more information look at
* {@link ScanSettings}
* @param workSource WorkSource to blame for power usage
* @param listener specifies the object to report events to. This object is also treated as a
* key for this scan, and must also be specified to cancel the scan. Multiple
* scans should also not share this object.
*/
@RequiresPermission(android.Manifest.permission.LOCATION_HARDWARE)
public void startScan(ScanSettings settings, ScanListener listener, WorkSource workSource) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(listener, "listener cannot be null");
int key = addListener(listener);
if (key == INVALID_KEY) return;
validateChannel();
Bundle scanParams = new Bundle();
scanParams.putParcelable(SCAN_PARAMS_SCAN_SETTINGS_KEY, settings);
scanParams.putParcelable(SCAN_PARAMS_WORK_SOURCE_KEY, workSource);
mAsyncChannel.sendMessage(CMD_START_SINGLE_SCAN, 0, key, scanParams);
}這裡用了AsyncChannel,和aidl一樣,也是IPC的一種方式。其實WifiScanner對應的服務端就是WifiScanningServiceImpl
下面來分析一下為什麼WifiScanner對應的服務端就是WifiScanningServiceImpl,看一WifiScanner的建構函式
/**
* Create a new WifiScanner instance.
* Applications will almost always want to use
* {@link android.content.Context#getSystemService Context.getSystemService()} to retrieve
* the standard {@link android.content.Context#WIFI_SERVICE Context.WIFI_SERVICE}.
* @param context the application context
* @param service the Binder interface
* @param looper the Looper used to deliver callbacks
* @hide
*/
public WifiScanner(Context context, IWifiScanner service, Looper looper) {
mContext = context;
mService = service;
Messenger messenger = null;
try {
messenger = mService.getMessenger();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
if (messenger == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("getMessenger() returned null! This is invalid.");
}
mAsyncChannel = new AsyncChannel();
mInternalHandler = new ServiceHandler(looper);
mAsyncChannel.connectSync(mContext, mInternalHandler, messenger);
// We cannot use fullyConnectSync because it sends the FULL_CONNECTION message
// synchronously, which causes WifiScanningService to receive the wrong replyTo value.
mAsyncChannel.sendMessage(AsyncChannel.CMD_CHANNEL_FULL_CONNECTION);
}從WifiScanner的構造方法裡可以看到InternalHandler/AsyncChannel/Messenger是完成IPC的橋樑。
另外WifiScanner的初始化是經由WifiStateMachine在WifiInjector裡完成的。
// We can't do this in the constructor because WifiStateMachine is created before the
// wifi scanning service is initialized
if (mWifiScanner == null) {
mWifiScanner = mWifiInjector.getWifiScanner();framework/opt/net/wifi/service/java/com/android/server/wifi/WifiInjector.java
/**
* Obtain an instance of WifiScanner.
* If it was not already created, then obtain an instance. Note, this must be done lazily since
* WifiScannerService is separate and created later.
*/
public synchronized WifiScanner getWifiScanner() {
if (mWifiScanner == null) {
mWifiScanner = new WifiScanner(mContext,
IWifiScanner.Stub.asInterface(ServiceManager.getService(
Context.WIFI_SCANNING_SERVICE)),
mWifiStateMachineHandlerThread.getLooper());
}
return mWifiScanner;
}先看下在SystemServer會啟動WifiScanningService服務
traceBeginAndSlog("StartWifiScanning");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(
"com.android.server.wifi.scanner.WifiScanningService");
traceEnd();再看下WifiScanningService這個服務
public class WifiScanningService extends SystemService {
static final String TAG = "WifiScanningService";
private final WifiScanningServiceImpl mImpl;
private final HandlerThread mHandlerThread;
public WifiScanningService(Context context) {
super(context);
Log.i(TAG, "Creating " + Context.WIFI_SCANNING_SERVICE);
mHandlerThread = new HandlerThread("WifiScanningService");
mHandlerThread.start();
mImpl = new WifiScanningServiceImpl(getContext(), mHandlerThread.getLooper(),
WifiScannerImpl.DEFAULT_FACTORY, BatteryStatsService.getService(),
WifiInjector.getInstance());
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
Log.i(TAG, "Publishing " + Context.WIFI_SCANNING_SERVICE);
publishBinderService(Context.WIFI_SCANNING_SERVICE, mImpl);
}
/**
* Publish the service so it is accessible to other services and apps.
*/
protected final void publishBinderService(String name, IBinder service) {
publishBinderService(name, service, false);
}
/**
* Publish the service so it is accessible to other services and apps.
*/
protected final void publishBinderService(String name, IBinder service,
boolean allowIsolated) {
ServiceManager.addService(name, service, allowIsolated);
}果不其然和WifiService一個套路,裡面會new WifiScanningServiceImpl,經由SystemService的publishBinderService將自己加入到ServiceManager管理的Service中去,那麼這裡WifiScanner對應的服務端就是WifiScanningServiceImpl了。
現在就從WifiScanner進入到WifiScanningServiceImpl了
2.3.5 WifiScanningServiceImpl
framework/opt/net/wifi/service/java/com/android/server/wifi/scanner/WifiScanningServiceImpl.java
繼而再看下getMessenger方法:
@Override
public Messenger getMessenger() {
if (mClientHandler != null) {
mLog.trace("getMessenger() uid=%").c(Binder.getCallingUid()).flush();
return new Messenger(mClientHandler);
}
loge("WifiScanningServiceImpl trying to get messenger w/o initialization");
return null;
}
這裡梳理出來WifiScanningServiceImpl的ClientHander是處理WifiScanner發出的CMD_START_SINGLE_SCAN訊息
framework/opt/net/wifi/service/java/com/android/server/wifi/scanner/WifiScanningServiceImpl.java
private class ClientHandler extends WifiHandler {
ClientHandler(String tag, Looper looper) {
super(tag, looper);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
...
case WifiScanner.CMD_START_SINGLE_SCAN:
case WifiScanner.CMD_STOP_SINGLE_SCAN:
mSingleScanStateMachine.sendMessage(Message.obtain(msg));
break; mSingleScanStateMachine = new WifiSingleScanStateMachine(mLooper);這裡又是狀態模式,其中有個DriverStartedState繼續處理,
framework/opt/net/wifi/service/java/com/android/server/wifi/scanner/WifiScanningServiceImpl.java
/**
* State representing when the driver is running. This state is not meant to be transitioned
* directly, but is instead indented as a parent state of ScanningState and IdleState
* to hold common functionality and handle cleaning up scans when the driver is shut down.
*/
class DriverStartedState extends State {
@Override
public void exit() {
// clear scan results when scan mode is not active
mCachedScanResults.clear();
mWifiMetrics.incrementScanReturnEntry(
WifiMetricsProto.WifiLog.SCAN_FAILURE_INTERRUPTED,
mPendingScans.size());
sendOpFailedToAllAndClear(mPendingScans, WifiScanner.REASON_UNSPECIFIED,
"Scan was interrupted");
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
ClientInfo ci = mClients.get(msg.replyTo);
switch (msg.what) {
case WifiScanner.CMD_START_SINGLE_SCAN:
mWifiMetrics.incrementOneshotScanCount();
int handler = msg.arg2;
Bundle scanParams = (Bundle) msg.obj;
if (scanParams == null) {
logCallback("singleScanInvalidRequest", ci, handler, "null params");
replyFailed(msg, WifiScanner.REASON_INVALID_REQUEST, "params null");
return HANDLED;
}
scanParams.setDefusable(true);
ScanSettings scanSettings =
scanParams.getParcelable(WifiScanner.SCAN_PARAMS_SCAN_SETTINGS_KEY);
WorkSource workSource =
scanParams.getParcelable(WifiScanner.SCAN_PARAMS_WORK_SOURCE_KEY);
if (validateScanRequest(ci, handler, scanSettings, workSource)) {
logScanRequest("addSingleScanRequest", ci, handler, workSource,
scanSettings, null);
replySucceeded(msg);
// If there is an active scan that will fulfill the scan request then
// mark this request as an active scan, otherwise mark it pending.
// If were not currently scanning then try to start a scan. Otherwise
// this scan will be scheduled when transitioning back to IdleState
// after finishing the current scan.
if (getCurrentState() == mScanningState) {
if (activeScanSatisfies(scanSettings)) {
mActiveScans.addRequest(ci, handler, workSource, scanSettings);
} else {
mPendingScans.addRequest(ci, handler, workSource, scanSettings);
}
} else {
mPendingScans.addRequest(ci, handler, workSource, scanSettings);
tryToStartNewScan();
}
} else {
logCallback("singleScanInvalidRequest", ci, handler, "bad request");
replyFailed(msg, WifiScanner.REASON_INVALID_REQUEST, "bad request");
mWifiMetrics.incrementScanReturnEntry(
WifiMetricsProto.WifiLog.SCAN_FAILURE_INVALID_CONFIGURATION, 1);
}
return HANDLED;這裡可以看到對上了,把我們千辛萬苦傳來的引數取了出來,雖然workSource就是個null,但是scanSettings的band是7
ScanSettings scanSettings =
scanParams.getParcelable(WifiScanner.SCAN_PARAMS_SCAN_SETTINGS_KEY);
WorkSource workSource =
scanParams.getParcelable(WifiScanner.SCAN_PARAMS_WORK_SOURCE_KEY);
之後返回一個操作成功的訊息replySucceeded(msg);但這並不是搜尋成功了,這裡還沒進行搜尋scan;返回訊息之後才會真正去進行搜尋,
void replySucceeded(Message msg) {
if (msg.replyTo != null) {
Message reply = Message.obtain();
reply.what = WifiScanner.CMD_OP_SUCCEEDED;
reply.arg2 = msg.arg2;
if (msg.obj != null) {
reply.obj = msg.obj;
}
try {
msg.replyTo.send(reply);
mLog.trace("replySucceeded recvdMessage=%").c(msg.what).flush();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// There's not much we can do if reply can't be sent!
}
} else {
// locally generated message; doesn't need a reply!
}
}這邊WifiScanner的ServiceHandler會收到並處理
frameworks/base/wifi/java/android/net/wifi/WifiScanner.java
private class ServiceHandler extends Handler {
ServiceHandler(Looper looper) {
super(looper);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case AsyncChannel.CMD_CHANNEL_FULLY_CONNECTED:
return;
case AsyncChannel.CMD_CHANNEL_DISCONNECTED:
Log.e(TAG, "Channel connection lost");
// This will cause all further async API calls on the WifiManager
// to fail and throw an exception
mAsyncChannel = null;
getLooper().quit();
return;
}
Object listener = getListener(msg.arg2);
if (listener == null) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "invalid listener key = " + msg.arg2);
return;
} else {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "listener key = " + msg.arg2);
}
switch (msg.what) {
/* ActionListeners grouped together */
case CMD_OP_SUCCEEDED :
((ActionListener) listener).onSuccess();
break;最後再呼叫到我們在WifiStateMachine裡初始化好的listener的success方法,但是這裡是空的
frameworks/opt/net/wifi/service/java/com/android/server/wifi/WifiStateMachine.java
WifiScanner.ScanListener nativeScanListener = new WifiScanner.ScanListener() {
// ignore all events since WifiStateMachine is registered for the supplicant events
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
}
@Override
public void onFailure(int reason, String description) {
mIsScanOngoing = false;
mIsFullScanOngoing = false;
}
@Override
public void onResults(WifiScanner.ScanData[] results) {
}
@Override
public void onFullResult(ScanResult fullScanResult) {
}
@Override
public void onPeriodChanged(int periodInMs) {
}
};接著前面的DriverStartedState進行分析返回操作成功訊息返回一個操作成功的訊息replySucceeded(msg);之後的程式碼如下
framework/opt/net/wifi/service/java/com/android/server/wifi/scanner/WifiScanningServiceImpl.java
replySucceeded(msg);
// If there is an active scan that will fulfill the scan request then
// mark this request as an active scan, otherwise mark it pending.
// If were not currently scanning then try to start a scan. Otherwise
// this scan will be scheduled when transitioning back to IdleState
// after finishing the current scan.
if (getCurrentState() == mScanningState) {
if (activeScanSatisfies(scanSettings)) {
mActiveScans.addRequest(ci, handler, workSource, scanSettings);
} else {
mPendingScans.addRequest(ci, handler, workSource, scanSettings);
}
} else {
mPendingScans.addRequest(ci, handler, workSource, scanSettings);
tryToStartNewScan();
}
} else {
logCallback("singleScanInvalidRequest", ci, handler, "bad request");
replyFailed(msg, WifiScanner.REASON_INVALID_REQUEST, "bad request");
mWifiMetrics.incrementScanReturnEntry(
WifiMetricsProto.WifiLog.SCAN_FAILURE_INVALID_CONFIGURATION, 1);
}
return HANDLED;這邊程式碼意思是如果正在搜尋那麼就不重新開始新的scan了,否則tryToStartNewScan()
然後看下tryToStartNewScan()
framework/opt/net/wifi/service/java/com/android/server/wifi/scanner/WifiScanningServiceImpl.java
void tryToStartNewScan() {
if (mPendingScans.size() == 0) { // no pending requests
return;
}
mChannelHelper.updateChannels();
// TODO move merging logic to a scheduler
WifiNative.ScanSettings settings = new WifiNative.ScanSettings();
settings.num_buckets = 1;
WifiNative.BucketSettings bucketSettings = new WifiNative.BucketSettings();
bucketSettings.bucket = 0;
bucketSettings.period_ms = 0;
bucketSettings.report_events = WifiScanner.REPORT_EVENT_AFTER_EACH_SCAN;
ChannelCollection channels = mChannelHelper.createChannelCollection();
List<WifiNative.HiddenNetwork> hiddenNetworkList = new ArrayList<>();
for (RequestInfo<ScanSettings> entry : mPendingScans) {
channels.addChannels(entry.settings);
if (entry.settings.hiddenNetworks != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < entry.settings.hiddenNetworks.length; i++) {
WifiNative.HiddenNetwork hiddenNetwork = new WifiNative.HiddenNetwork();
hiddenNetwork.ssid = entry.settings.hiddenNetworks[i].ssid;
hiddenNetworkList.add(hiddenNetwork);
}
}
if ((entry.settings.reportEvents & WifiScanner.REPORT_EVENT_FULL_SCAN_RESULT)
!= 0) {
bucketSettings.report_events |= WifiScanner.REPORT_EVENT_FULL_SCAN_RESULT;
}
}
if (hiddenNetworkList.size() > 0) {
settings.hiddenNetworks = new WifiNative.HiddenNetwork[hiddenNetworkList.size()];
int numHiddenNetworks = 0;
for (WifiNative.HiddenNetwork hiddenNetwork : hiddenNetworkList) {
settings.hiddenNetworks[numHiddenNetworks++] = hiddenNetwork;
}
}
channels.fillBucketSettings(bucketSettings, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
settings.buckets = new WifiNative.BucketSettings[] {bucketSettings};
if (mScannerImpl.startSingleScan(settings, this)) {
// store the active scan settings
mActiveScanSettings = settings;