【原】biginteger。大數乘法。大數運算。“無限大數字”乘法。大數乘法兩種方法對比
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-07
最近在看筆試題,得知大數運算是個經常考的題目。所以有興趣試了試。
一開始按照筆算方法自己寫了個,但是時間複雜度是o(n3)。
參考了網上的演算法之後,修改了自己的演算法,時間複雜度變成o(n2)。
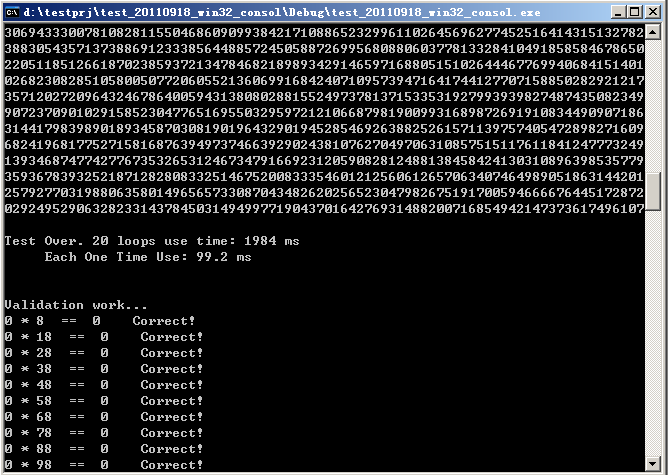
下面的測試結果中,兩個2000位的數字(阿拉伯數字的位數)相乘,耗時90多毫秒。
200位,1毫秒。可以看到,複雜度的確是N的平方級別。
自己寫的笨辦法,每次累加之後都要判斷是否有進位。但是安全。
網上有個高效的演算法,使用int儲存臨時結果,不用每次累加後都判斷一次進位。等
所有的累加都完成之後再判斷,所以時間複雜度降低了一個數量級。
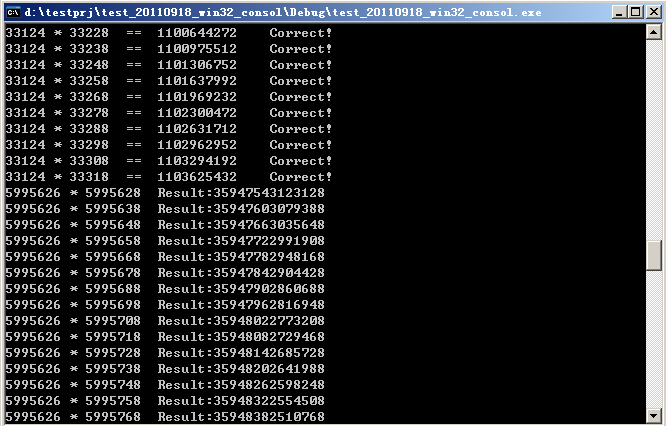
但是這樣也有個壞處,就是int早晚有溢位的時候,當整數的位數足夠多,
也就是達到了2的29、30、31、32次方位(當然這種情況基本沒可能發生),這種方法的運算結果就是錯誤的了。
下面是演算法對應的函式。
char* BigIntMultiply ( const char * const a, const char * const b , char* const lresult) { int i,j; int la = strlen(a); int lb = strlen(b); int rlen = la+lb; int* r = (int*)calloc( rlen, sizeof(int) ); for(i = 0;i < lb; i++) for(j = 0; j < la; j++) r[rlen - 1 - i - j] += (b[lb - i - 1] - '0') * (a[la - j - 1] - '0'); //then is there carry on current number for(j = rlen - 1; j >= 1; j--) if(r[j] > 9) { r[j-1] += r[j] / 10; r[j] %= 10; } //find first none_zero_index for(i = 0; 0 == r[i]; i++){} //mem cpy for(j=0; i< rlen; i++,j++) lresult[j] = r[i]+'0'; lresult[j]='\0'; free(r); return lresult; }
下面的程式碼在Visual Studio 2008裡面編譯執行,沒有問題。 Linux上沒有 SYSTEMTIME,
沒有atoi,itoa,GetLocalTime。所以要在Linux執行,得相應的修改一下。
#include <iostream> #include <assert.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> #include <windows.h> #include <malloc.h> using namespace std; const int MAX = 2001; char num1[MAX]; char num2[MAX]; char result[2*MAX]; void SafeGetNumFromStr ( char* num, char* str); char* BigIntMultiply ( const char * const a, const char * const b , char* const lresult); void multiply( const char *a, const char *b); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { //test speed cout<<"\n\nspeed test... Number of digits is : "<<MAX-1<<"\n"; int i; const int TEST_TIME = 20; srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); for(i = 0;i<MAX;i++) { num1[i] = 0; num2[i] = 0; } //create data with random for(i = 0; i< MAX - 1; i++) { num1[i] = rand()%10 + '0'; num2[i] = rand()%10 + '0'; } SYSTEMTIME wtm; GetLocalTime(&wtm); long long time_start = wtm.wMilliseconds + wtm.wSecond * 1000; cout<<num1<<endl; cout<<"*\n"; cout<<num2<<endl; for(i = 0; i<TEST_TIME; i++) { BigIntMultiply(num1,num2,result); } GetLocalTime(&wtm); cout<<"Result is:\n"; cout<<result<<endl; double tmv = (double)(wtm.wMilliseconds + wtm.wSecond * 1000 - time_start); cout<<"Test Over. "<<TEST_TIME<<" loops use time: "<<tmv<<" ms\n"; cout<<" Each One Time Use: "<<tmv/(double)TEST_TIME<<" ms\n\n\n"; //test validation cout<<"Validation work...\n"; long long testNum1; long long testNum2; int testI; for(testNum1 = 0;testNum1<1000000000000000;testNum1 = (testNum1+1)*181+1) for(testI= 0;testI<200; testI++) { char a[2*MAX]; char b[2*MAX]; testNum2 = (testNum1+testI)<0?0:testNum1+testI; for(i = 0;i<MAX;i++) { num1[i] = 0; num2[i] = 0; } itoa(testNum1,a,10); itoa(testNum2,b,10); SafeGetNumFromStr(num1,a); SafeGetNumFromStr(num2,b); BigIntMultiply(num1,num2,result); if(8 == testNum2%10) if(testNum1*testNum2 == atoi(result)) cout<<testNum1<<" * "<<testNum2<<" == "<<testNum1*testNum2<<" Correct!\n"; else cout<<testNum1<<" * "<<testNum2<<" Result:"<<result<<"\n"; } //free test cout<<"Now ..... Free Test!\n"; while(1) { char a[2*MAX]; char b[2*MAX]; cout<<"\n\ninput long integer for A"<<endl; cin>>a; cout<<"input long integer for B"<<endl; cin>>b; //get data SafeGetNumFromStr(num1,a); SafeGetNumFromStr(num2,b); cout<<endl<<endl; cout<<num1; cout<<" * "; cout<<num2; cout<<endl; BigIntMultiply(num1,num2,result); cout<<"Result is:"<<endl; cout<<result; } system("pause"); return 0; } void SafeGetNumFromStr( char* num, char* str) { memset(num,0,sizeof(num[0])*MAX); int i; int index = 0; for(i=0;i<2*MAX && index < MAX;i++) { if(str[i] <= '9' && str[i] >='0') num[index++] = str[i]; if('\0'==str[i]) break; } assert( 0 != index ); } char* BigIntMultiply ( const char * const a, const char * const b , char* const lresult) { int i,j; int la = strlen(a); int lb = strlen(b); int rlen = la+lb; int* r = (int*)calloc( rlen, sizeof(int) ); for(i = 0;i < lb; i++) for(j = 0; j < la; j++) r[rlen - 1 - i - j] += (b[lb - i - 1] - '0') * (a[la - j - 1] - '0'); //then is there carry on current number for(j = rlen - 1; j >= 1; j--) if(r[j] > 9) { r[j-1] += r[j] / 10; r[j] %= 10; } //find first none_zero_index for(i = 0; 0 == r[i]; i++){} //mem cpy for(j=0; i< rlen; i++,j++) lresult[j] = r[i]+'0'; lresult[j]='\0'; free(r); return lresult; }