#基於SVM的人臉識別
#資料說明
LFW全稱為Labeled Faces in the Wild, 是一個應用於人臉識別問題的資料庫,更多內容檢視官方網站:http://vis-www.cs.umass.edu/lfw
LFW語料圖片,每張圖片都有人名Label標記。每個人可能有多張不同情況下情景下的圖片。如George W Bush 有530張圖片,而有一些人名對應的圖片可能只有一張或者幾張。我們將選取出現最多的人名作為人臉識別的類別,如本實驗中選取出現頻數超過70的人名為類別, 那麼共計1288張圖片。其中包括Ariel Sharon, Colin Powell, Donald Rumsfeld, George W Bush, Gerhard Schroeder, Hugo Chavez , Tony Blair等7個人名。
#問題描述
通過對7個人名的提取特徵和標記,進行新輸入的照片進行標記人名。這是一個多分類的問題,在本資料集合中類別數目為7. 這個問題的解決,不僅可以應用於像公司考勤一樣少量人員的識別,也可以應用到新資料的標註中。語料庫進一步標註,將進一步擴大訓練資料集合資料量,從而進一步提高人臉識別的精確度。因此,對於圖片的人名正確標註問題,或者這個多分類問題的研究和使用是有應用價值的。
#資料處理
訓練與測試資料中樣本數量為1288,對樣本圖片進行下采樣後特徵數為1850,所有人臉的Label數目為7。
首先將資料集劃分為訓練集合和測試集合,測試集合佔25%(一般應該10%或者20%),訓練資料進行訓練過程中,將分為訓練集合和驗證集合。通過驗證集合選擇最優模型,使用測試結合測試模型效能。
其次,通過對訓練集合PCA分解,提取特徵臉,提高訓練速度,防止過度擬合。圖片 1是關於不同的特徵所佔的總方差的比率關係,從中可以看出,關鍵特徵主要集中在前50個。圖片 2 是關於圖片 1的累計分佈圖。從曲線中可以看出,當特徵臉數目為50時,約佔85%的資料資訊,特徵臉資料為100時,約佔總資訊量的90%左右。經過測試,最佳分類結果時,特徵臉數目為80 .此時約佔88%的總體方差。
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import linear_model, decomposition, datasets
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
logistic = linear_model.LogisticRegression()
pca = decomposition.PCA()
pipe = Pipeline(steps=[('pca' 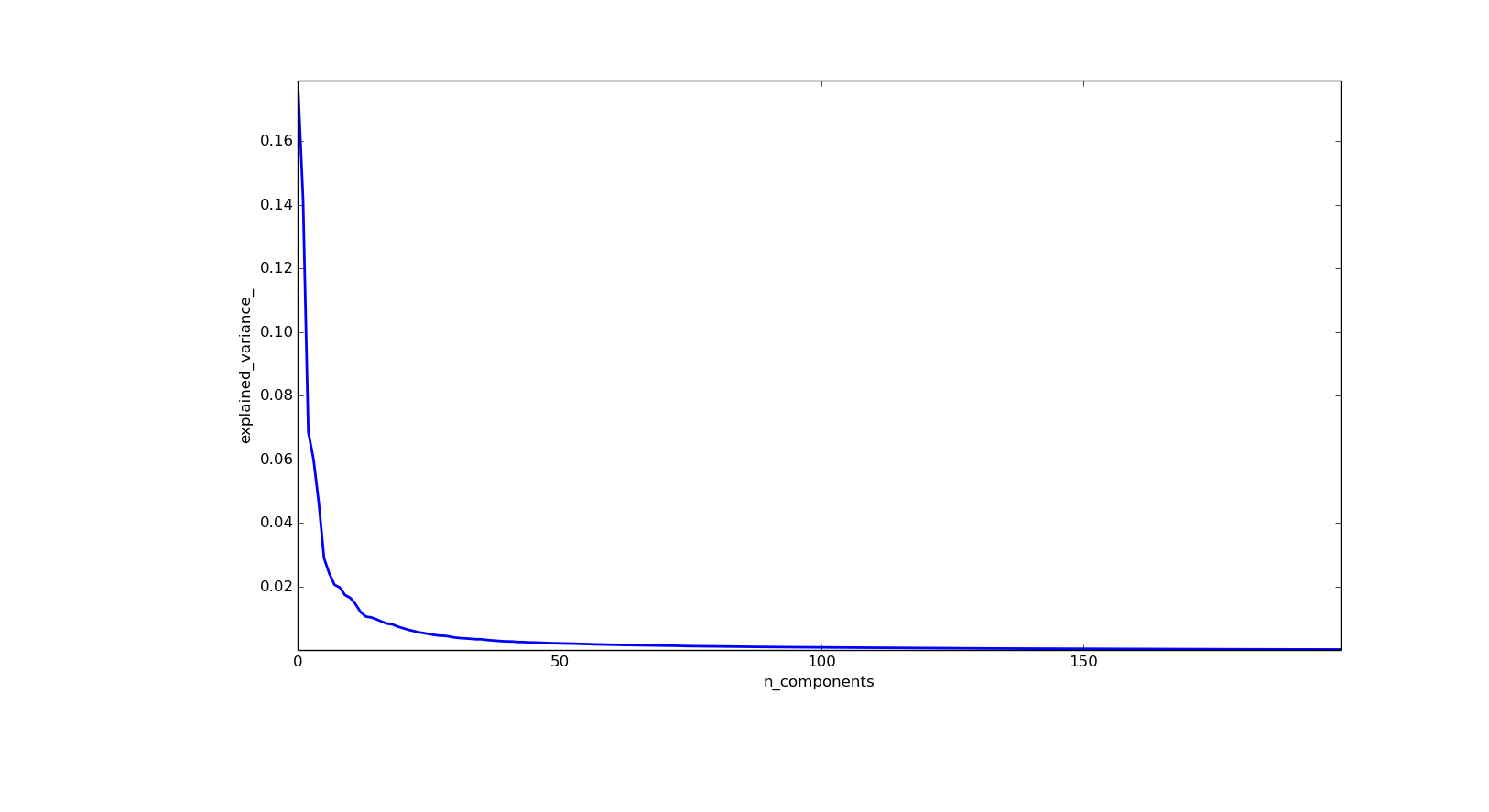
圖片1: 不同特徵選取數目的方差比率大小, 比率大小是按照從大到小的順序排列的,從曲線中可以看出,最大的一維約佔總體方差的18%
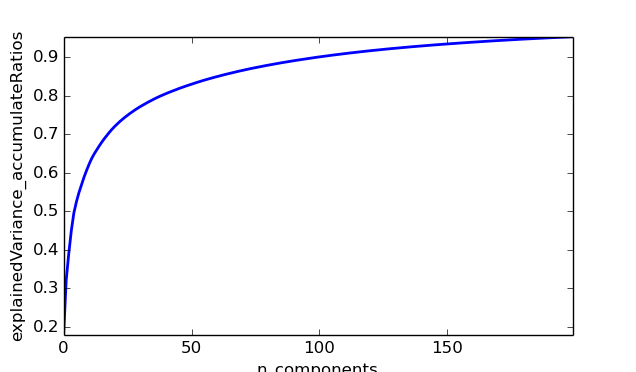
圖片 2: 不同特徵選取數目的方差累計比率曲線,從曲線中可以看出,當特徵臉數目為50時,約佔85%的資料資訊,特徵臉資料為100時,約佔總資訊量的90%左右經過測試,最佳分類結果時,特徵臉數目為80.此時約佔88%的總體方差。
因為不同的人有多個不同角度的照片,如果提取特徵臉過多,會導致過度擬合,從而測試結果不理想,如果使用特徵臉過少,則會導致人臉多類過程區分度不高而使得部分結果分類錯誤。而在LFW資料集合中,使用特徵臉數目為80時效果最佳是可以理解的。圖片 3 顯示了前16個特徵臉。
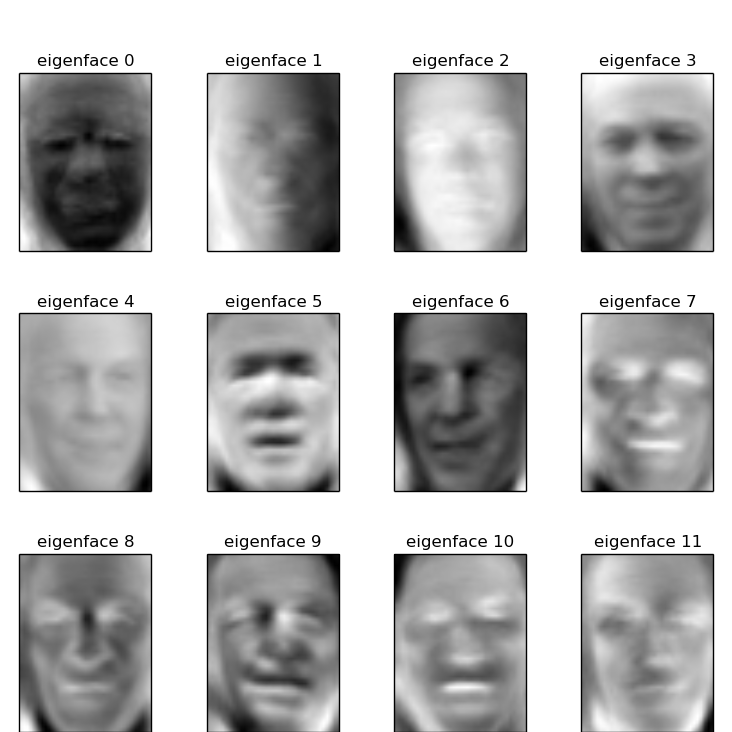

圖片 3:對PCA降維度結果中16個特徵臉先行呈現效果圖
當然,數字影象處理常用的特徵降維中NMF分解前幾年取得了很多成果,有機會可以使用NMF分級進行特徵提取和降維。
#模型訓練與結果
訓練程式碼
from __future__ import print_function
from time import time
import logging
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_lfw_people
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.decomposition import RandomizedPCA
from sklearn.svm import SVC
print(__doc__)
# Display progress logs on stdout
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s %(message)s')
###############################################################################
# Download the data, if not already on disk and load it as numpy arrays
lfw_people = fetch_lfw_people(min_faces_per_person=70, resize=0.4)
# introspect the images arrays to find the shapes (for plotting)
n_samples, h, w = lfw_people.images.shape
# for machine learning we use the 2 data directly (as relative pixel
# positions info is ignored by this model)
X = lfw_people.data
n_features = X.shape[1]
# the label to predict is the id of the person
y = lfw_people.target
target_names = lfw_people.target_names
n_classes = target_names.shape[0]
print("Total dataset size:")
print("n_samples: %d" % n_samples)
print("n_features: %d" % n_features)
print("n_classes: %d" % n_classes)
###############################################################################
# Split into a training set and a test set using a stratified k fold
# split into a training and testing set
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42)
###############################################################################
# Compute a PCA (eigenfaces) on the face dataset (treated as unlabeled
# dataset): unsupervised feature extraction / dimensionality reduction
n_components = 80
print("Extracting the top %d eigenfaces from %d faces"
% (n_components, X_train.shape[0]))
t0 = time()
pca = RandomizedPCA(n_components=n_components, whiten=True).fit(X_train)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
eigenfaces = pca.components_.reshape((n_components, h, w))
print("Projecting the input data on the eigenfaces orthonormal basis")
t0 = time()
X_train_pca = pca.transform(X_train)
X_test_pca = pca.transform(X_test)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
###############################################################################
# Train a SVM classification model
print("Fitting the classifier to the training set")
t0 = time()
param_grid = {'C': [1,10, 100, 500, 1e3, 5e3, 1e4, 5e4, 1e5],
'gamma': [0.0001, 0.0005, 0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.1], }
clf = GridSearchCV(SVC(kernel='rbf', class_weight='balanced'), param_grid)
clf = clf.fit(X_train_pca, y_train)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
print("Best estimator found by grid search:")
print(clf.best_estimator_)
print(clf.best_estimator_.n_support_)
###############################################################################
# Quantitative evaluation of the model quality on the test set
print("Predicting people's names on the test set")
t0 = time()
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test_pca)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred, target_names=target_names))
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred, labels=range(n_classes)))
###############################################################################
# Qualitative evaluation of the predictions using matplotlib
def plot_gallery(images, titles, h, w, n_row=3, n_col=4):
"""Helper function to plot a gallery of portraits"""
plt.figure(figsize=(1.8 * n_col, 2.4 * n_row))
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0, left=.01, right=.99, top=.90, hspace=.35)
for i in range(n_row * n_col):
plt.subplot(n_row, n_col, i + 1)
# Show the feature face
plt.imshow(images[i].reshape((h, w)), cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.title(titles[i], size=12)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
# plot the result of the prediction on a portion of the test set
def title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i):
pred_name = target_names[y_pred[i]].rsplit(' ', 1)[-1]
true_name = target_names[y_test[i]].rsplit(' ', 1)[-1]
return 'predicted: %s\ntrue: %s' % (pred_name, true_name)
prediction_titles = [title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i)
for i in range(y_pred.shape[0])]
plot_gallery(X_test, prediction_titles, h, w)
# plot the gallery of the most significative eigenfaces
eigenface_titles = ["eigenface %d" % i for i in range(eigenfaces.shape[0])]
plot_gallery(eigenfaces, eigenface_titles, h, w)
plt.show()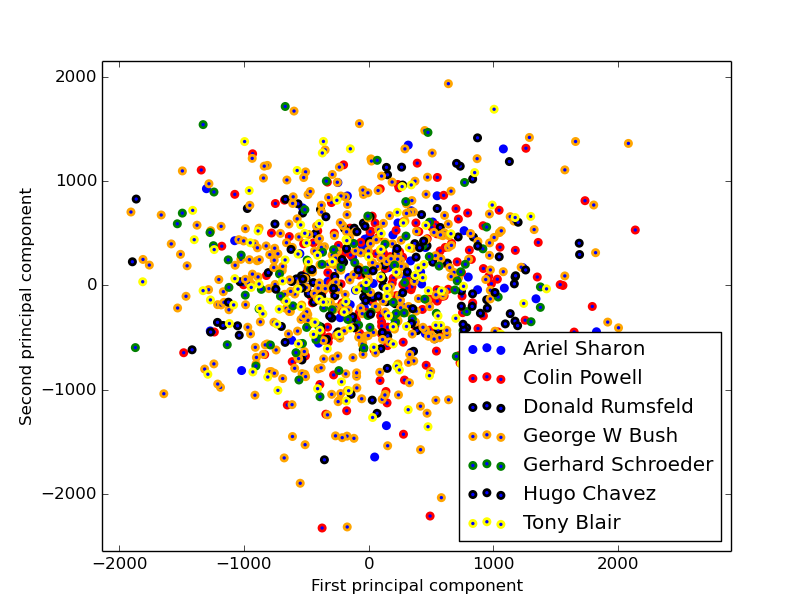
圖片 4 實驗資料在二維空間中分佈情況,可以看出該資料集如果使用線性模型進行分類,效果將很差;我們將從非線性模型帶核的SVM入手,解決該分類問題
分類模型將採用SVM分類器進行分類,其中核函式:
我們將對核函式中的 γ 進行引數評估優化,此外對不同特徵的權重進行優化,通過交叉驗證和網格搜尋方式,查詢到最佳模型為γ=0.01, C = 10時,平均正確率達到90%,如表格 1所示。
表格 1: 關於測試集合人名標記結果的正確率,召回率和F1
| # | Precision | Recall | F1 | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ariel Sharon | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 13 |
| Colin Powell | 0.86 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 60 |
| Donald Rumsfeld | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 27 |
| George W Bush | 0.91 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 146 |
| Gerhard Schroeder | 0.95 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 25 |
| Hugo Chavez | 1.00 | 0.60 | 0.75 | 15 |
| Tony Blair | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 36 |
| Avg/Total | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 322 |
這麼高的準確率,是由於我們僅僅選取了每個標識人名數目> 70的人名,但是大量的僅僅出現1次的人名存在。如果考慮這種資料稀疏性,將大大降低結果的準確率。但是,真實應用中,資料稀疏性問題是不得不考慮的問題。

圖片 5: 預測人名正確結果展示
#未來工作
本文中使用PCA實現特徵臉提取,也可以使用其他特徵提取方式進行降維。比如NMF實現矩陣分解在數字影象處理中的應用,實現NMF在人臉識別中的特徵分解。當前使用的訓練資料集使用的最小標記資料為70,當標記訓練資料比較稀疏的時候,能否利用未標記資料提供正確率。後面的研究中將注意這兩個方面的問題。