Android 流式佈局FlowLayout 實現關鍵字標籤
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-07
1.介紹
流式佈局的應用還是很廣泛的,比如搜尋熱詞、關鍵詞標籤等,GitHub上已經有很多這樣的佈局了,但是還是想著自己實現一下,最近一直在學自定義控制元件,也鞏固一下所學的知識。
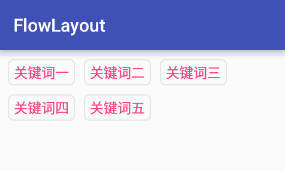
本文實現的效果如下圖所示:
2.思路
- 繼承自RelativeLayout,可以直接使用RelativeLayout中的相關屬性,本文也可以修改為繼承ViewGroup,並不會有什麼影響。
- 在onMeasure方法中計算出所有childView的寬和高,然後根據childView的寬和高計算出佈局自身的寬和高。
- 在onLayout方法中計算出所有childView的位置並進行佈局。
- 封裝Line物件,管理每行上的View物件
3.實現
初始化一些屬性
public class FlowLayout extends RelativeLayout {
// 水平間距,單位為dp
private int horizontalSpacing = dp2px(10);
// 豎直間距,單位為dp
private int verticalSpacing = dp2px(10);
// 行的集合
private List<Line> lines = new ArrayList<Line>();
// 當前的行
private Line line;
// 當前行使用的空間 onMeasure
首先獲取父容器傳入的寬高值與測量模式,計算出實際使用的寬和高,遍歷所有的childView,對childView進行測量,根據當前行已用的寬度判斷是否需要換行,然後累計所有高度,設定佈局自身尺寸。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 實際可以用的寬和高
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec) - getPaddingBottom() - getPaddingTop();
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// Line初始化
restoreLine();
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 測量所有的childView
int childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(width,
widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? MeasureSpec.AT_MOST : widthMode);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height,
heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? MeasureSpec.AT_MOST : heightMode);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if (line == null) {
// 建立新一行
line = new Line();
}
// 計算當前行已使用的寬度
int measuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
lineSize += measuredWidth;
// 如果使用的寬度小於可用的寬度,這時候childView能夠新增到當前的行上
if (lineSize <= width) {
line.addChild(child);
lineSize += horizontalSpacing;
} else {
// 換行
newLine();
line.addChild(child);
lineSize += child.getMeasuredWidth();
lineSize += horizontalSpacing;
}
}
// 把最後一行記錄到集合中
if (line != null && !lines.contains(line)) {
lines.add(line);
}
int totalHeight = 0;
// 把所有行的高度加上
for (int i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++) {
totalHeight += lines.get(i).getHeight();
}
// 加上行的豎直間距
totalHeight += verticalSpacing * (lines.size() - 1);
// 加上上下padding
totalHeight += getPaddingBottom();
totalHeight += getPaddingTop();
// 設定自身尺寸
// 設定佈局的寬高,寬度直接採用父view傳遞過來的最大寬度,而不用考慮子view是否填滿寬度
// 因為該佈局的特性就是填滿一行後,再換行
// 高度根據設定的模式來決定採用所有子View的高度之和還是採用父view傳遞過來的高度
setMeasuredDimension(MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec),
resolveSize(totalHeight, heightMeasureSpec));
}附上restoreLine與newLine方法
private void restoreLine() {
lines.clear();
line = new Line();
lineSize = 0;
}
private void newLine() {
// 把之前的行記錄下來
if (line != null) {
lines.add(line);
}
// 建立新的一行
line = new Line();
lineSize = 0;
}Line
封裝了每行上的View物件,提供新增與繪製childView的方法。
/**
* 管理每行上的View物件
*/
class Line {
// 子控制元件集合
private List<View> children = new ArrayList<View>();
// 行高
int height;
/**
* 新增childView
*
* @param childView 子控制元件
*/
public void addChild(View childView) {
children.add(childView);
// 讓當前的行高是最高的一個childView的高度
if (height < childView.getMeasuredHeight()) {
height = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
}
}
/**
* 設定childView的繪製區域
*
* @param left 左上角x軸座標
* @param top 左上角y軸座標
*/
public void layout(int left, int top) {
int totalWidth = getMeasuredWidth() - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
// 當前childView的左上角x軸座標
int currentLeft = left;
for (int i = 0; i < children.size(); i++) {
View view = children.get(i);
// 設定childView的繪製區域
view.layout(currentLeft, top, currentLeft + view.getMeasuredWidth(),
top + view.getMeasuredHeight());
// 計算下一個childView的位置
currentLeft = currentLeft + view.getMeasuredWidth() + horizontalSpacing;
}
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public int getChildCount() {
return children.size();
}
}onLayout
指定所有childView的位置,呼叫Line物件中的layout方法。
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
int left = getPaddingLeft();
int top = getPaddingTop();
for (int i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++) {
Line line = lines.get(i);
line.layout(left, top);
// 計算下一行的起點y軸座標
top = top + line.getHeight() + verticalSpacing;
}
}setFlowLayout
用於設定FlowLayout中的內容,並提供點選事件處理。
public void setFlowLayout(List<String> list, final OnItemClickListener onItemClickListener) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
final TextView tv = new TextView(getContext());
// 設定TextView屬性
tv.setText(list.get(i));
tv.setTextSize(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_PX, textSize);
tv.setTextColor(textColor);
tv.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
tv.setPadding(textPaddingH, textPaddingV, textPaddingH, textPaddingV);
tv.setClickable(true);
tv.setBackgroundResource(backgroundResource);
this.addView(tv, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
tv.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
onItemClickListener.onItemClick(tv.getText().toString());
}
});
}
}
public interface OnItemClickListener {
void onItemClick(String content);
}使用方法
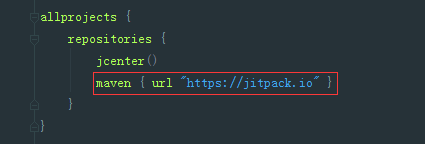
- 在專案根目錄的build.gradle檔案中加入如下程式碼
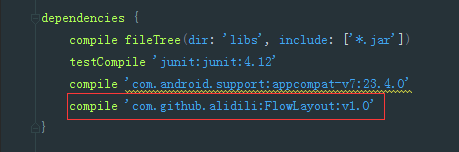
maven { url "https://jitpack.io" }- 在app根目錄的buil.gradle檔案中加入依賴
compile 'com.github.alidili:FlowLayout:v1.0'- 在Activity中使用,設定點選事件
相關屬性(字型大小、顏色、間距等)可以在佈局檔案中設定,也可以通過set方法設定。
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private FlowLayout flKeyword;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
flKeyword = (FlowLayout) findViewById(R.id.fl_keyword);
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("關鍵詞一");
list.add("關鍵詞二");
list.add("關鍵詞三");
list.add("關鍵詞四");
list.add("關鍵詞五");
flKeyword.setFlowLayout(list, new FlowLayout.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(String content) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, content, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}- 佈局檔案
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<com.yang.flowlayoutlibrary.FlowLayout
android:id="@+id/fl_keyword"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
app:itemColor="@color/colorAccent"
app:itemSize="15sp" />
</RelativeLayout>4.寫在最後
原始碼已託管到GitHub上,歡迎Fork,覺得還不錯就Start一下吧!
歡迎同學們吐槽評論,如果你覺得本篇部落格對你有用,那麼就留個言或者頂一下吧(^-^)