兩種用於派生的Singleton模式(以TextureMgr為例)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-07
Singleton,顧名思義,從字面上來理解就是單例模式,這是C++程式中
常用到的一種設計模式,特別是像檔案管理器,紋理管理器這種整個軟體
中只需要唯一的例項來管理所有資源時,這種模式的價值便得以體現。
下面來介紹兩種用於派生管理的Singleton模式:
其中,第一種是Gof版本的Singleton, 其程式碼如下:
//【Singleton_Gof.h】 #pragma once template<typename T> class Singleton_Gof { protected: static T* ms_Singleton; Singleton_Gof(){assert(!ms_Singleton);} ~Singleton_Gof(){assert(ms_Singleton);ms_Singleton=NULL;} private: Singleton_Gof(const Singleton_Gof&); //防止建構函式的複製 Singleton_Gof& operator=(const Singleton_Gof&); public: static T* getSingletonPtr(){if (!ms_Singleton)ms_Singleton = new T();return ms_Singleton;} static T& getSingleton(){if (!ms_Singleton)ms_Singleton = new T();return (*ms_Singleton);} }; template<typename T>T* Singleton_Gof<T>::ms_Singleton = NULL;
其大致上的原理便是在需要初始化時,將靜態的Singleton例項指向派生類T物件,
類似的,還有第二種Singleton, 其程式碼如下:
Singleton()裡的程式碼在OGRE和《遊戲程式設計精粹》都出現過,這裡涉及VC編譯器的記憶體對齊,就不詳細講解了,//【Singleton.h】 #pragma once #include <cassert> template<typename T> class Singleton { private: Singleton(const Singleton<T>&); Singleton& operator=(const Singleton<T> &); protected: static T* ms_Singleton; Singleton(){ assert(!ms_Singleton); #if defined( _MSC_VER ) && _MSC_VER < 1200 int offset = (int)(T*)1 - (int)(Singleton <T>*)(T*)1; ms_Singleton = (T*)((int)this + offset); #else ms_Singleton = static_cast< T* >( this ); #endif }; ~Singleton(){assert(ms_Singleton); ms_Singleton = NULL;} public: static T& getSingleton(){if(!ms_Singleton)new T(); return (*ms_Singleton);} static T* getSingletonPtr(){if(!ms_Singleton)new T(); return ms_Singleton;} }; template<typename T>T* Singleton<T>::ms_Singleton = NULL;
然後我們便可以利用上面的Singleton()程式碼派生出一個紋理管理器來,我這裡粗略寫了下:
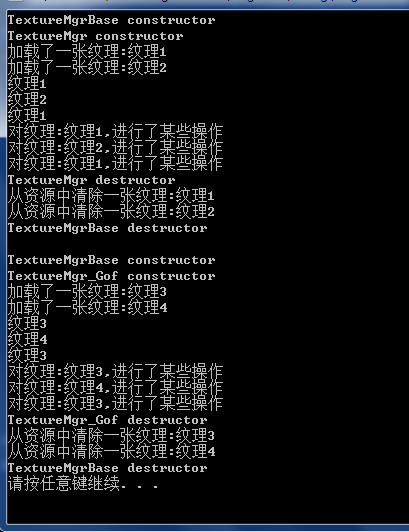
因為加了斷言保證只有一次呼叫,所以就能全域性唯一了,因此我們便可以如下來使用這紋理管理器(需要手動刪除)://【TextureMgr.h】 #include <string> #include <map> #include <iostream> #include "Singleton.h" #include "Singleton_Gof.h" using namespace std; //Texture class Texture { private: string m_Name; public: Texture(const string name):m_Name(name){load();}; ~Texture(){unload();} const string& getName()const {return m_Name;} bool load(){cout<<"載入了一張紋理:"+m_Name<<endl;return true;} bool unload(){cout<<"從資源中清除一張紋理:"+m_Name<<endl;return true;} void doSomeThing(){cout<<"對紋理:"+m_Name+",進行了某些操作"<<endl;} }; typedef std::map<string, Texture*> texMap; typedef texMap::iterator texMapIter; #define SAFE_DELETE(p) {if(p){delete p;p=NULL;}} //TextureMgrBase class TextureMgrBase { texMap m_TiMap; public: Texture* getTexture(const string name) { texMapIter iter = m_TiMap.find(name); if(iter == m_TiMap.end()) { Texture* tex = new Texture(name); m_TiMap.insert(std::make_pair(name, tex)); return tex; } else { return iter->second; } } TextureMgrBase(){cout<<"TextureMgrBase constructor"<<endl;} ~TextureMgrBase(){ for(texMapIter iter = m_TiMap.begin();iter!=m_TiMap.end();iter++) { SAFE_DELETE(iter->second); } cout<<"TextureMgrBase destructor"<<endl; } }; //TextureMgr class TextureMgr:public TextureMgrBase, public Singleton<TextureMgr>{ public: TextureMgr(){cout<<"TextureMgr constructor"<<endl;} ~TextureMgr(){cout<<"TextureMgr destructor"<<endl;} }; //TextureMgrGof class TextureMgr_Gof:public TextureMgrBase, public Singleton_Gof<TextureMgr_Gof>{ public: TextureMgr_Gof(){cout<<"TextureMgr_Gof constructor"<<endl;} ~TextureMgr_Gof(){cout<<"TextureMgr_Gof destructor"<<endl;} };
//【main.cpp】
#include "TextureMgr.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define g_TexMgr TextureMgr::getSingleton()
#define g_TexMgr_Gof TextureMgr_Gof::getSingleton()
int main(char argc, char* argv[])
{
//TextureMgr
Texture* tex1 = g_TexMgr.getTexture("紋理1");
Texture* tex2 = g_TexMgr.getTexture("紋理2");
Texture* _tex1 = g_TexMgr.getTexture("紋理1");
cout<<tex1->getName()<<endl;
cout<<tex2->getName()<<endl;
cout<<_tex1->getName()<<endl;
tex1->doSomeThing();
tex2->doSomeThing();
_tex1->doSomeThing();
delete &g_TexMgr;
cout<<endl;
//TextureMgr_Gof
Texture* tex3 = g_TexMgr_Gof.getTexture("紋理3");
Texture* tex4 = g_TexMgr_Gof.getTexture("紋理4");
Texture* _tex3 = g_TexMgr_Gof.getTexture("紋理3");
cout<<tex3->getName()<<endl;
cout<<tex4->getName()<<endl;
cout<<_tex3->getName()<<endl;
tex1->doSomeThing();
tex2->doSomeThing();
_tex3->doSomeThing();
delete &g_TexMgr_Gof;
system("pause");
return 0;
}