OpenCV之meanshift分割詳解
1. 原理
用meanshift做影象平滑和分割,其實是一回事。其本質是經過迭代,將收斂點的畫素值代替原來的畫素值,從而去除了區域性相似的紋理,同時保留了邊緣等差異較大的特徵。
OpenCV中自帶有基於meanshift的分割方法pyrMeanShiftFiltering()。由函式名pyrMeanShiftFiltering可知,這裡是將meanshift演算法和影象金字塔相結合用來分割的。
-
<span style="font-size:18px;">void PyrMeanShiftFiltering( const CvArr* srcarr, //輸入影象
- CvArr* dstarr, //輸出影象
- double sp, //顏色域半徑
- double sr, //空間域半徑
- int max_level, //金字塔最大層數
- CvTermCriteria termcrit ) //迭代終止條件</span>
要求輸入和輸出影象都是CV_8UC3型別,而且兩者尺寸一樣。實際上並不需要去先定義dstarr,因為程式裡會將srcarr的格式賦值給dstarr。
termcrit有三種情況,迭代次數、迭代精度和兩者同時滿足。預設為迭代次數為5同時迭代精度為1。termcrit是個結構體,其結構如下
- <span style="font-size:18px;">typedefstruct CvTermCriteria
- {
- int type; /*CV_TERMCRIT_ITER或CV_TERMCRIT_EPS 或二者都是*/
- int max_iter; /* 最大迭代次數 */
- double epsilon; /* 結果的精確性 */
- }
-
CvTermCriteria;</span>
在實際操作時,為了使分割的結果顯示得更明顯,經常用floodFill( )將不同連通域塗上不同的顏色。具體情況參看下 面的例項。
2. 程式例項
來看看opencv自帶的一個用meanshift進行分割的例子
原程式見 “ .\OpenCV249\sources\samples\cpp\meanshift_segmentation.cpp”
- <span style="font-size:18px;">#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
- #include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
- #include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
- #include <iostream>
- usingnamespace cv;
- usingnamespace std;
- staticvoid help(char** argv)
- {
- cout << "\nDemonstrate mean-shift based color segmentation in spatial pyramid.\n"
- << "Call:\n " << argv[0] << " image\n"
- << "This program allows you to set the spatial and color radius\n"
- << "of the mean shift window as well as the number of pyramid reduction levels explored\n"
- << endl;
- }
- //This colors the segmentations
- staticvoid floodFillPostprocess( Mat& img, const Scalar& colorDiff=Scalar::all(1) )
- {
- CV_Assert( !img.empty() );
- RNG rng = theRNG();
- Mat mask( img.rows+2, img.cols+2, CV_8UC1, Scalar::all(0) );
- for( int y = 0; y < img.rows; y++ )
- {
- for( int x = 0; x < img.cols; x++ )
- {
- if( mask.at<uchar>(y+1, x+1) == 0 )
- {
- Scalar newVal( rng(256), rng(256), rng(256) );
- floodFill( img, mask, Point(x,y), newVal, 0, colorDiff, colorDiff );
- }
- }
- }
- }
- string winName = "meanshift";
- int spatialRad, colorRad, maxPyrLevel;
- Mat img, res;
- staticvoid meanShiftSegmentation( int, void* )
- {
- cout << "spatialRad=" << spatialRad << "; "
- << "colorRad=" << colorRad << "; "
- << "maxPyrLevel=" << maxPyrLevel << endl;
- pyrMeanShiftFiltering( img, res, spatialRad, colorRad, maxPyrLevel );
- //Mat imgGray;
- //cvtColor(res,imgGray,CV_RGB2GRAY);
- //imshow("res",res);
- floodFillPostprocess( res, Scalar::all(2) );
- imshow( winName, res );
- }
- int main(int argc, char** argv)
- {
- img = imread("rubberwhale1.png");
- //img = imread("pic2.png");
- if( img.empty() )
- return -1;
- spatialRad = 10;
- colorRad = 10;
- maxPyrLevel = 1;
- namedWindow( winName, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
- //imshow("img",img);
- createTrackbar( "spatialRad", winName, &spatialRad, 80, meanShiftSegmentation );
- createTrackbar( "colorRad", winName, &colorRad, 60, meanShiftSegmentation );
- createTrackbar( "maxPyrLevel", winName, &maxPyrLevel, 5, meanShiftSegmentation );
- meanShiftSegmentation(0, 0);
- //floodFillPostprocess( img, Scalar::all(2) );
- //imshow("img2",img);
- waitKey();
- return 0;
- }</span>
int floodFill( InputOutputArray image, Point seedPoint, Scalar newVal, CV_OUT Rect* rect=0, Scalar loDiff=Scalar(), Scalar upDiff=Scalar(), int flags=4 );
int floodFill( InputOutputArray image, InputOutputArray mask, Point seedPoint, Scalar newVal, CV_OUT Rect* rect=0, Scalar loDiff=Scalar(), Scalar upDiff=Scalar(), int flags=4 );
InputOutputArray image 輸入輸出影象,要求格式為1通道或3通道,8位或浮點
InputOutputArray mask 掩膜,比image的寬和高各大兩畫素點
Point seedPoint 填充的起始點
Scalar newVal 畫素點被染色的值
CV_OUT Rect* rect=0 可選引數,設定floodFill()要重繪區域的最小邊界矩形區域
Scalar loDiff=Scalar() 定義當前畫素值與起始點畫素值的亮度或顏色負差的最大值
Scalar upDiff=Scalar() 定義當前畫素值與起始點畫素值的亮度或顏色正差的最大值
flags 操作標誌符
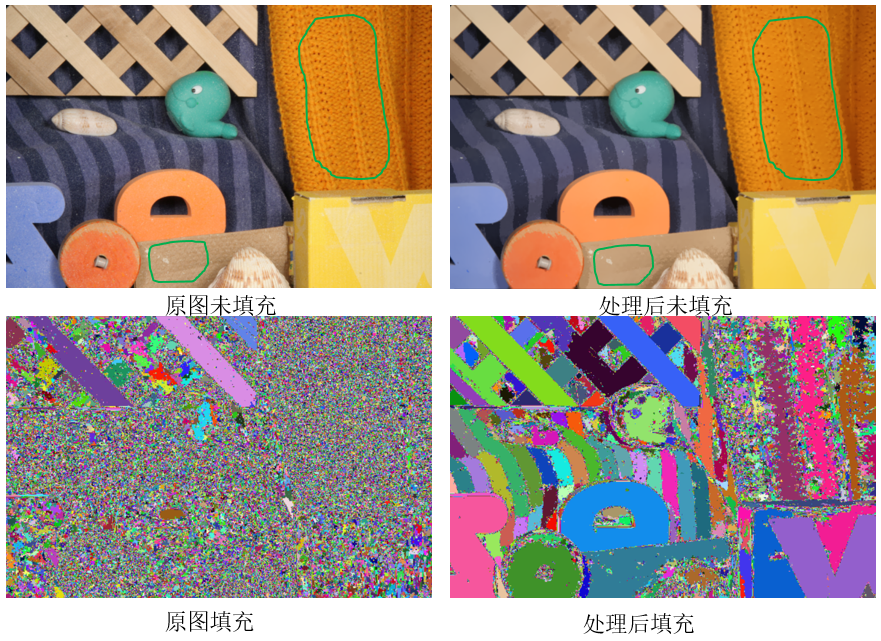
程式結果
處理後一些細小的紋理都平滑掉了,例如圖中綠色線條所指示的區域。未填充時,很多地方看得並不明顯,填充後就能明顯看出差別來了。填充後的圖很好地體現了meanshift聚類的思想!
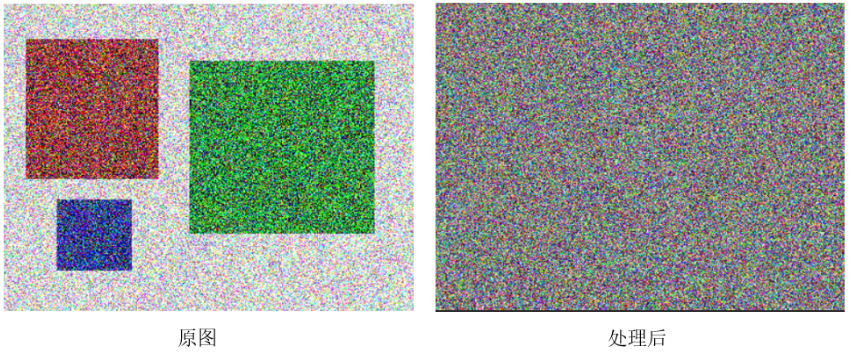
再來看一組更“誇張”的效果圖
使用meanshift方法進行處理後,原來的三個矩形區域消失了!平滑掉了!
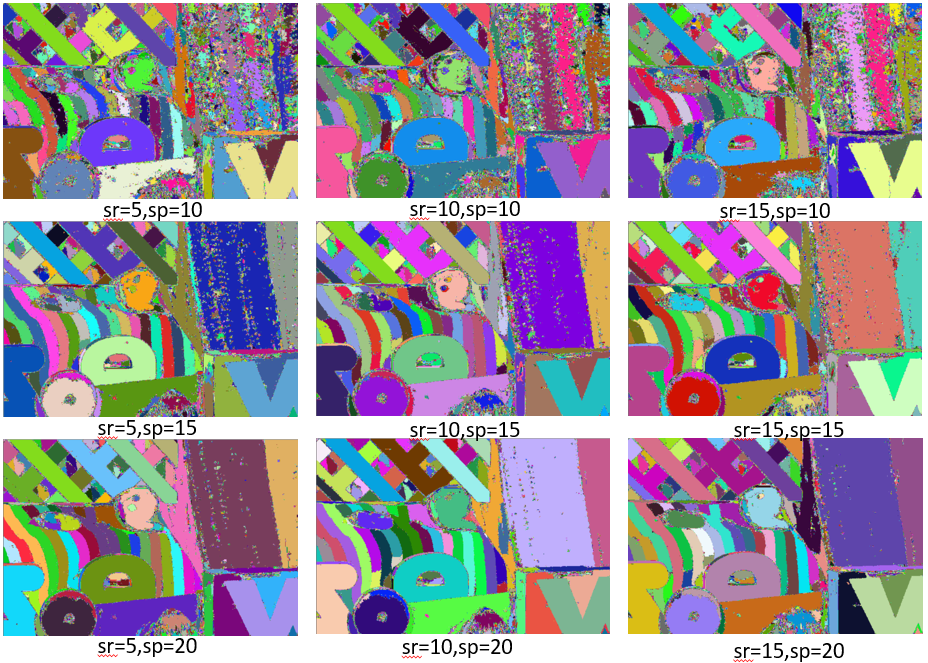
meanshift演算法的兩個關鍵引數是空間域半徑sr和顏色域半徑sp,別說max_level,那是構建影象金字塔的引數好吧。最後,我們來看看sr和sp對結果的影響。
顯然顏色域半徑sp對結果的影響比空間域半徑sr對結果的影響大。sp和sr越小,細節保留得越多,sp和sr越大,平滑力度越大。邊緣和顏色突變的區域的特徵保留的較好。因為meanshift要對每個畫素點進行操作,所以演算法的時間花銷很大。