Android okhttp3 利用socket進行read/write的底層實現跟蹤
在okhttp3.internal.io.RealConnection#connectSocket中初始化了socket並進行了connect,此時tcp的三次握手已經搞定,接下來它通過okio庫與遠端socket建立I/O連線,如下程式碼所示:
/** Does all the work necessary to build a full HTTP or HTTPS connection on a raw socket. */
private void connectSocket(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout,
ConnectionSpecSelector connectionSpecSelector) throws Okio庫是一個由square公司開發的,它補充了Java.io和java.nio的不足,以便能夠更加方便,快速的訪問、儲存和處理你的資料。而OkHttp的底層也使用該庫作為支援。
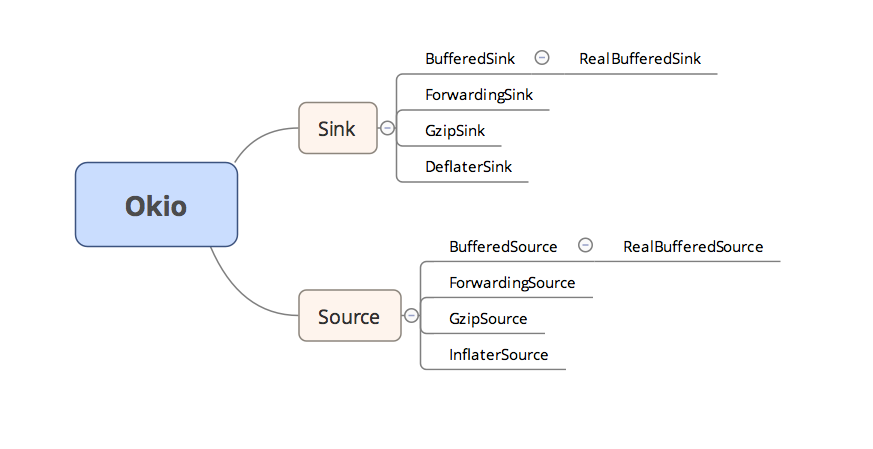
Okio中有兩個關鍵的介面,Sink和Source,這兩個介面都繼承了Closeable介面;而Sink可以簡單的看做OutputStream,Source可以簡單的看做InputStream。而這兩個介面都是支援讀寫超時設定的。它們各自有一個支援緩衝區的子類介面,BufferedSink和BufferedSource,而BufferedSink有一個實現類RealBufferedSink,BufferedSource有一個實現類RealBufferedSource;此外,Sink和Source它門還各自有一個支援gzip壓縮的實現類GzipSink和GzipSource;一個具有委託功能的抽象類ForwardingSink和ForwardingSource;還有一個實現類便是InflaterSource和DeflaterSink,這兩個類主要用於壓縮,為GzipSink和GzipSource服務;整體的結構圖如下
接下來以read為例,追蹤底層實現(write的邏輯是類似的)。
1.okhttp3.internal.io.RealConnection#connectSocket
source = Okio.buffer(Okio.source(rawSocket));2.okio#source
public static Source source(Socket socket) throws IOException {
if (socket == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("socket == null");
AsyncTimeout timeout = timeout(socket);
Source source = source(socket.getInputStream(), timeout);
return timeout.source(source);
}在這裡從socket拿InputStream
3./libcore/luni/src/main/java/java/net/Socket.java
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
checkOpenAndCreate(false);
if (isInputShutdown()) {
throw new SocketException("Socket input is shutdown");
}
return impl.getInputStream();
}4./libcore/luni/src/main/java/java/net/PlainSocketImpl.java
@Override protected synchronized InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
checkNotClosed();
return new PlainSocketInputStream(this);
}5./libcore/luni/src/main/java/java/net/PlainSocketImpl.java
private static class PlainSocketInputStream extends InputStream {
private final PlainSocketImpl socketImpl;
public PlainSocketInputStream(PlainSocketImpl socketImpl) {
this.socketImpl = socketImpl;
}
@Override public int available() throws IOException {
return socketImpl.available();
}
@Override public void close() throws IOException {
socketImpl.close();
}
@Override public int read() throws IOException {
return Streams.readSingleByte(this);
}
@Override public int read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int byteCount) throws IOException {
return socketImpl.read(buffer, offset, byteCount);
}
}接下來以read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int byteCount)為例。
6./libcore/luni/src/main/java/java/net/PlainSocketImpl.java
private int read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int byteCount) throws IOException {
if (byteCount == 0) {
return 0;
}
Arrays.checkOffsetAndCount(buffer.length, offset, byteCount);
if (shutdownInput) {
return -1;
}
int readCount = IoBridge.recvfrom(true, fd, buffer, offset, byteCount, 0, null, false);
// Return of zero bytes for a blocking socket means a timeout occurred
if (readCount == 0) {
throw new SocketTimeoutException();
}
// Return of -1 indicates the peer was closed
if (readCount == -1) {
shutdownInput = true;
}
return readCount;
}IoBridge.recvfrom(true, fd, buffer, offset, byteCount, 0, null, false)再次開始去調jni
7./libcore/luni/src/main/java/libcore/io/IoBridge.java
public static int recvfrom(boolean isRead, FileDescriptor fd, ByteBuffer buffer, int flags, DatagramPacket packet, boolean isConnected) throws IOException {
int result;
try {
InetSocketAddress srcAddress = (packet != null && !isConnected) ? new InetSocketAddress() : null;
result = Libcore.os.recvfrom(fd, buffer, flags, srcAddress);
result = postRecvfrom(isRead, packet, isConnected, srcAddress, result);
} catch (ErrnoException errnoException) {
result = maybeThrowAfterRecvfrom(isRead, isConnected, errnoException);
}
return result;
}
private static int postRecvfrom(boolean isRead, DatagramPacket packet, boolean isConnected, InetSocketAddress srcAddress, int byteCount) {
if (isRead && byteCount == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (packet != null) {
packet.setReceivedLength(byteCount);
if (!isConnected) {
packet.setAddress(srcAddress.getAddress());
packet.setPort(srcAddress.getPort());
}
}
return byteCount;
}==>Libcore.os.recvfrom
8.
/libcore/luni/src/main/java/libcore/io/BlockGuardOs.java
@Override public int recvfrom(FileDescriptor fd, ByteBuffer buffer, int flags, InetSocketAddress srcAddress) throws ErrnoException, SocketException {
BlockGuard.getThreadPolicy().onNetwork();
return os.recvfrom(fd, buffer, flags, srcAddress);
}/libcore/luni/src/main/java/libcore/io/ForwardingOs.java
public int recvfrom(FileDescriptor fd, ByteBuffer buffer, int flags, InetSocketAddress srcAddress) throws ErrnoException, SocketException {
return os.recvfrom(fd, buffer, flags, srcAddress);
}9./libcore/luni/src/main/java/libcore/io/Posix.java
public int recvfrom(FileDescriptor fd, ByteBuffer buffer, int flags, InetSocketAddress srcAddress) throws ErrnoException, SocketException {
if (buffer.isDirect()) {
return recvfromBytes(fd, buffer, buffer.position(), buffer.remaining(), flags, srcAddress);
} else {
return recvfromBytes(fd, NioUtils.unsafeArray(buffer), NioUtils.unsafeArrayOffset(buffer) + buffer.position(), buffer.remaining(), flags, srcAddress);
}
}
private native int recvfromBytes(FileDescriptor fd, Object buffer, int byteOffset, int byteCount, int flags, InetSocketAddress srcAddress) throws ErrnoException, SocketException;終於看到了jni的宣告
10./libcore/luni/src/main/native/libcore_io_Posix.cpp
static jint Posix_recvfromBytes(JNIEnv* env, jobject, jobject javaFd, jobject javaBytes, jint byteOffset, jint byteCount, jint flags, jobject javaInetSocketAddress) {
ScopedBytesRW bytes(env, javaBytes);
if (bytes.get() == NULL) {
return -1;
}
sockaddr_storage ss;
socklen_t sl = sizeof(ss);
memset(&ss, 0, sizeof(ss));
sockaddr* from = (javaInetSocketAddress != NULL) ? reinterpret_cast<sockaddr*>(&ss) : NULL;
socklen_t* fromLength = (javaInetSocketAddress != NULL) ? &sl : 0;
jint recvCount = NET_FAILURE_RETRY(env, ssize_t, recvfrom, javaFd, bytes.get() + byteOffset, byteCount, flags, from, fromLength);
fillInetSocketAddress(env, recvCount, javaInetSocketAddress, ss);
return recvCount;
}
#define NET_FAILURE_RETRY(jni_env, return_type, syscall_name, java_fd, ...) ({ \
return_type _rc = -1; \
do { \
{ \
int _fd = jniGetFDFromFileDescriptor(jni_env, java_fd); \
AsynchronousSocketCloseMonitor _monitor(_fd); \
_rc = syscall_name(_fd, __VA_ARGS__); \
} \
if (_rc == -1) { \
if (jniGetFDFromFileDescriptor(jni_env, java_fd) == -1) { \
jniThrowException(jni_env, "java/net/SocketException", "Socket closed"); \
break; \
} else if (errno != EINTR) { \
/* TODO: with a format string we could show the arguments too, like strace(1). */ \
throwErrnoException(jni_env, # syscall_name); \
break; \
} \
} \
} while (_rc == -1); \
_rc; })這邊是jni的實現
11./bionic/libc/arch-arm/syscalls/recvfrom.S
ENTRY(recvfrom)
mov ip, sp
.save {r4, r5, r6, r7}
stmfd sp!, {r4, r5, r6, r7}
ldmfd ip, {r4, r5, r6}
ldr r7, =__NR_recvfrom
swi #0
ldmfd sp!, {r4, r5, r6, r7}
cmn r0, #(MAX_ERRNO + 1)
bxls lr
neg r0, r0
b __set_errno
END(recvfrom)最終recvfrom是用匯編實現的,使用swi進行了系統呼叫