JDBC(Java Data Base Connectivity)基本用法
一、什麼是JDBC
JDBC(Java Database Connection)為java開發者使用資料庫提供了統一的程式設計介面,它由一組java類和介面組成.是java程式與資料庫系統通訊的標準APl。 JDBC API使得開發人員可以使用純 java 的方式來連線資料庫,並執行操作。
sun公司由於不知道各個主流商用資料庫的程式程式碼,因此無法自己寫程式碼連線各個資料庫。因此,sun公司決定自己提供一套api,凡是資料庫想與Java進行連線的,資料庫廠商自己必須實現JDBC這套介面。而資料庫廠商的JDBC實現,我們就叫它此資料庫的資料庫驅動。
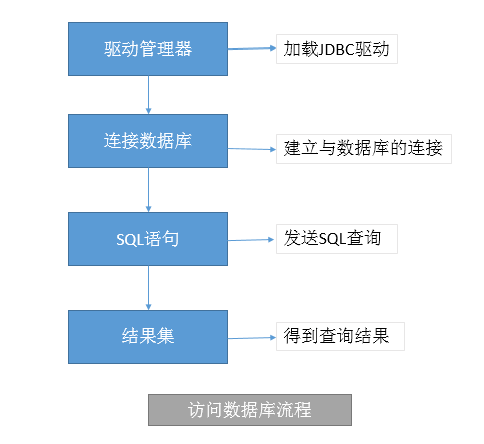
二、使用JDBC訪問資料庫流程
三、JDBC常用介面
1、Driver介面
Driver介面由資料庫廠家提供,對於java開發者而言,只需要使用Driver介面就可以了。
在程式設計中要連線資料庫,必須先裝載特定廠商的資料庫驅動程式。不同的資料庫有不同的裝載方法。
驅動就是各個資料庫廠商實現的sun公司提出的JDBC介面,即對Connection等介面的實現類的jar檔案。
裝載Mysql驅動
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
裝載Oracle驅動
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
2、DriverManage介面
一DriverManager是JDBC的管理層,作用於使用者和驅動程式之間。
一DriverManager跟蹤可用的驅動程式,並在資料庫和相應的驅動程式之間建立連線。
3、Connection介面
Connection與特定資料庫的連線(會話),在連線上下文中執行SQL語句並返回結果。
DriverManager的getConnection()方法建立在JDBC URL中定義的資料庫Connection連線上。
連線MYSQL資料庫:
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://host:port/database","user","password");
連線ORACLE資料庫:
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@host:port:database","user","password");
4、Statement介面
用於執行靜態SQL語句並返回它所生成結果的物件。
三種Statement類:
Statement:
由createStatement建立,用於傳送簡單的SQL語句。(不帶引數的)
PreparedStatement:**
繼承自Statement介面,由prepareStatement建立,用於傳送含有一個或多個輸入引數的sql語句。PreparedStatement物件,會進行預編譯,比Statement物件的效率更高,並且可以防止SQL注入。我們一般都使用PreparedStatement。
CallableStatement:
繼承自PreparedStatement,由方法prePareCall建立,用於呼叫儲存過程。
常用的Statement方法:
execute():執行語句,返回是否有結果集。
executeQuery():執行select語句,返回ResultSet結果集。
executeUpdate():執行insert/update/delete操作,返回更新的行數。
5、ResultSet介面
Statement執行SQL語句時,返回ResultSet結果集。
ResultSet提供的檢索不同型別欄位的方法,常用的有:
getString():獲得在資料庫裡varchar、char等資料型別的物件。
getFloat():獲得在資料庫裡Float型別的物件。
getDate():獲得在資料庫裡Date型別的資料。
getBoolean():獲得在資料庫裡面Boolean型別的資料。
依序關閉使用的物件及連線:
ResultSet–>Statement–>Connection
package com.lgd.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
//1、載入驅動類
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2、建立與資料庫的連線
//連線物件內部其實包含了Socket物件,是一個遠端的連線。比較耗時間,這是Connection物件管理的一個要點!
//真正開發中,為了提高效率,都會使用連線池來管理連線物件。
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testjdbc","root","liguodong");
System.out.println(connection);
//3、測試指定SQL語句以及SQL注入問題
//實際應用中比較少
//1.處理引數不方便
//2.容易發生SQL注入的危險
statement = connection.createStatement();
/*String sqlone = "insert into user(username,pwd,regTime) values ('蘇三',54423,NOW())";
statement.execute(sqlone);*/
/*String nameString = "宋八";
String sqltwo = "insert into user(username,pwd,regTime) values('"+nameString+"',54ds23,NOW())";
statement.execute(sqltwo);*/
//測試SQL注入
String idString = "5 or 1=1";
String sql1 = "delete from user where id="+idString;
statement.execute(sql1);//這樣會刪除所有元素
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
package com.lgd.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
//1、載入驅動類
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2、建立與資料庫的連線
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testjdbc","root","liguodong");
//3、測試PreparedStatement的基本用法
String sql1 = "insert into user(username,pwd,regTime) values (?,?,?)";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql1);
/*statement.setString(1, "周杰倫");//引數索引是從1開始計算,而不是0
statement.setString(2, "fdsf323");
statement.execute();*/
/*
//也可以使用setObject方法處理引數
statement.setObject(1, "詹姆斯");
statement.setObject(2, "fdf323");
statement.execute();*/
statement.setString(1, "德瑪西亞");
statement.setString(2, "fdsfds3");
statement.setDate(3, new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
statement.execute();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
package com.lgd.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet rs1 = null;
try {
//1、載入驅動類
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2、建立與資料庫的連線
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testjdbc","root","liguodong");
//3、測試PreparedStatement的基本用法 ?佔位符
String sql1 = "select * from user where id>?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql1);
statement.setObject(1, 2);//把大於2的記錄都取出來
rs1 = statement.executeQuery();
while(rs1.next()){
System.out.println(rs1.getInt(1)+"---"+rs1.getString(2)+"---"+rs1.getString(3));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//執行順序resultset-->statement-->connection這樣的關閉順序!一定要將三個try-catch塊分開寫!
if(rs1!=null){
try {
rs1.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}