執行緒特定資料(筆記)
概述:
執行緒特定資料,也稱為執行緒私有資料,是儲存和查詢某個特定資料相關資料的一種機制。
在單執行緒程式中,我們經常要用到“全域性變數”以實現多個函式間共享資料。
在多執行緒環境下,由於資料空間是共享的,因此全域性變數也為所有所有執行緒所共有。
但有時應用程式設計中有必要提供執行緒私有的全域性變數,僅在某個執行緒中有效,但卻可以跨多個函式訪問。
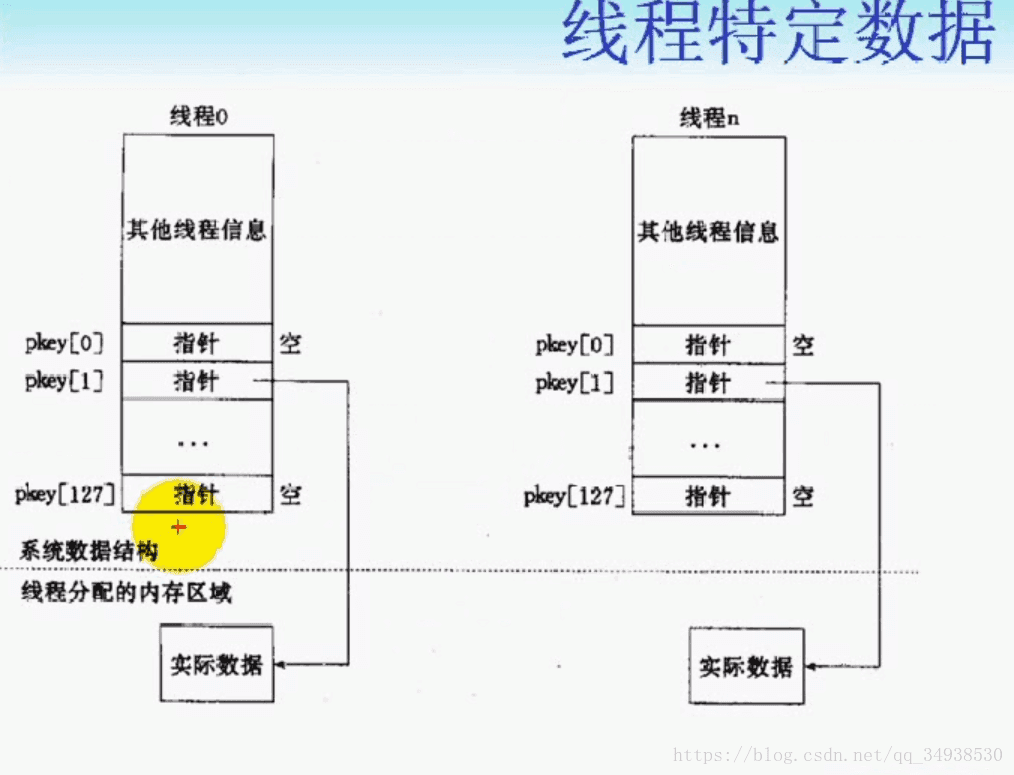
POSIX執行緒庫通過維護一定的資料結構來解決這個問題,這些資料被稱為執行緒特定資料(Thread-specific Data,或TSD)。
相關函式:
在分配執行緒特定資料之前,需要建立與該資料關聯的鍵。這個鍵將用於獲取對執行緒特定資料的訪問。使用pthread_key_create函式建立一個鍵。
int pthread_key_create(pthread_key_t *key, void (*destr_function) (void*));
建立的鍵儲存在pkey指向的記憶體單元中,這個鍵可以被程序中的所有執行緒使用,但每個執行緒與不同的執行緒特定資料地址相關聯。建立新鍵時,每個執行緒的資料地址設為空值。
除了建立鍵以外,pthread_key_create可以為該鍵關聯一個可選擇的解構函式。當這個執行緒退出時,如果資料地址已經被置為非空值,那麼解構函式就會被呼叫,它唯一的引數就是該資料地址。如果傳入的解構函式為空,就表明沒有解構函式與這個鍵關聯。
執行緒通常使用malloc為執行緒特定資料分配記憶體。解構函式通常釋放已分配的記憶體。
對所有的執行緒,我們都可以通過呼叫pthread_key_delete函式來取消鍵與執行緒特定資料值之間的聯絡。
int pthread_key_delete(pthread_key_t key);
有些執行緒可能看到一個鍵值,而其他的執行緒看到的可能是另一個不同的鍵值,這取決於系統是如何排程執行緒的,解決這種競爭的辦法是使用pthread_once函式 。
pthread_once_t once_control = PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT; int pthread_once(pthread_once_t *once_control, void (*init_routine) (void));
once_control必須是一個非本地變數(如全域性變數或靜態變數),而且必須初始化為PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT。如果每個執行緒都呼叫pthread_once,系統就能保證初始化once_control只被呼叫一次,即系統首次呼叫pthread_once時。
鍵一旦建立以後,就可以通過呼叫pthread_setspecific函式把鍵和執行緒特定資料關聯起來。可以通過pthread_getspecific獲得執行緒特定資料的地址。
int pthread_setspecific(pthread_key_t key, const void *pointer);
void * pthread_getspecific(pthread_key_t key);
如果沒有執行緒特定資料值與鍵關聯,pthread_getspecific將返回一個空指標,我們可以用這個空指標確定是否需要呼叫pthread_setspecific。
注:參考UNIX高階環境程式設計(第三版)
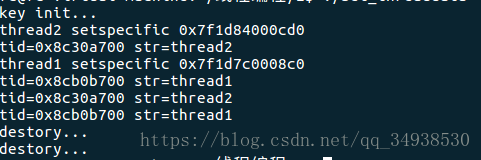
測試程式碼:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do \
{ \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
}while(0); \
//自定義執行緒資料
typedef struct tid
{
pthread_t tid;
char *str;
}tsd_t;
pthread_key_t key_tsd;
pthread_once_t once_control = PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;
void destory_routine(void *value)
{
printf("destory...\n");
free(value);
}
void once_routine(void)
{
pthread_key_create(&key_tsd, destory_routine);
printf("key init...\n");
}
void *thread_routine(void *arg)
{
pthread_once(&once_control,once_routine) ;
tsd_t *value = (tsd_t*)malloc(sizeof(tsd_t));
value->tid = pthread_self();
value->str = (char*)arg;
//設定執行緒特定資料
pthread_setspecific(key_tsd, value);
printf("%s setspecific %p\n",(char*)arg, value);
value = (tsd_t*)pthread_getspecific(key_tsd);
printf("tid=0x%x str=%s\n",(int)value->tid, value->str);
sleep(2);
value = (tsd_t*)pthread_getspecific(key_tsd);
printf("tid=0x%x str=%s\n",(int)value->tid, value->str);
sleep(2);
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
//pthread_key_create(&key_tsd, destory_routine);
pthread_t tid1;
pthread_t tid2;
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread_routine, "thread1");
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread_routine, "thread2");
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
return 0;
}