Java開發中用的比較多的資料結構
java 中幾種常用資料結構
2016年07月11日 09:11:27 閱讀數:83211 個人分類: 自行學習JAVA中常用的資料結構(java.util. 中)
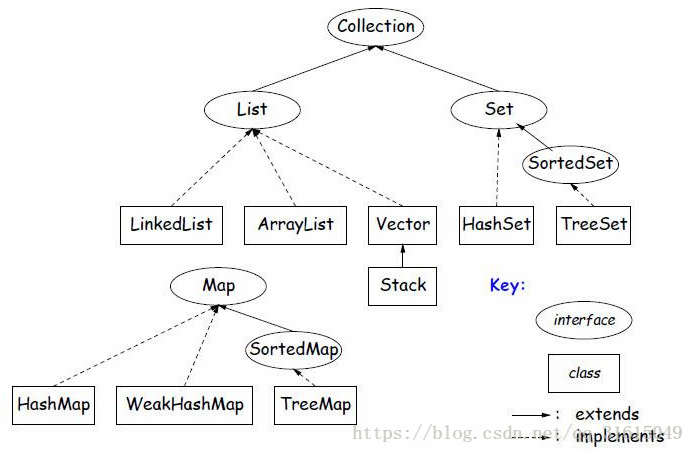
java中有幾種常用的資料結構,主要分為Collection和map兩個主要介面(介面只提供方法,並不提供實現),而程式中最終使用的資料結構是繼承自這些介面的資料結構類。其主要的關係(繼承關係)有: (----詳細參見java api文件!)
Collection---->Collections Map----->SortedMap------>TreeMap
Collection---->List----->(Vector \ ArryList \ LinkedList) Map------>HashMap
Collection---->Set------>(HashSet \ LinkedHashSet \ SortedSet)
--------------Collection----------------
1、Collections
API----This class consists exclusively of static methods that operate on or return collections. It contains polymorphic algorithms that operate on collections, "wrappers", which return a new collection backed by a specified collection, and a few other odds and ends.
The methods of this class all throw a NullPointerException if the collections or class objects provided to them are null.
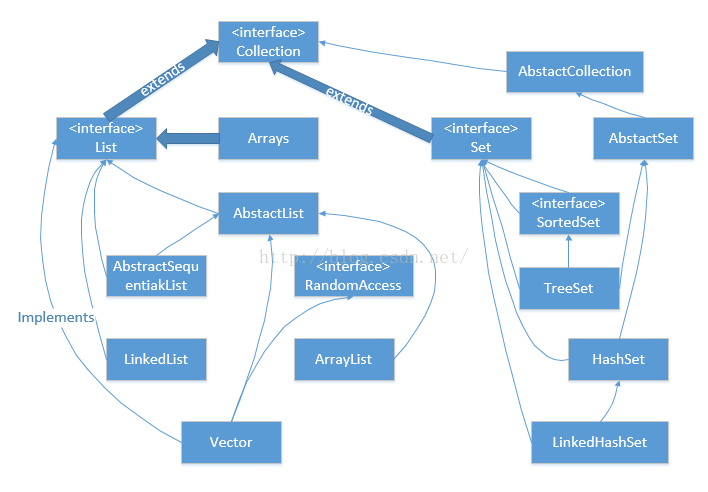
2、List
API----This class consists exclusively of static methods that operate on or return collections. It contains polymorphic algorithms that operate on collections, "wrappers", which return a new collection backed by a specified collection, and a few other odds and ends.The methods of this class all throw a NullPointerException if the collections or class objects provided to them are null.
List是有序的Collection,使用此介面能夠精確的控制每個元素插入的位置。使用者能夠使用索引(元素在List中的位置,類似於陣列下 >標)來訪問List中的元素,這類似於Java的陣列。
3、Vector
API----The Vector class implements a growable array of objects. Like an array, it contains components that can be accessed using an integer index. However, the size of aVector can grow or shrink as needed to accommodate adding and removing items after theVector has been created.
基於陣列(Array)的List,其實就是封裝了陣列所不具備的一些功能方便我們使用,所以它難易避免陣列的限制,同時效能也不可能超越陣列。所以,在可能的情況下,我們要多運用陣列。另外很重要的一點就是Vector是執行緒同步的(sychronized)的,這也是Vector和ArrayList 的一個的重要區別。
4、ArrayList
API----Resizable-array implementation of the List interface. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all elements, including null. In addition to implementing the List interface, this class provides methods to manipulate the size of the array that is used internally to store the list. (This class is roughly equivalent to Vector, except that it is unsynchronized.)
同Vector一樣是一個基於陣列上的連結串列,但是不同的是ArrayList不是同步的。所以在效能上要比Vector好一些,但是當執行到多執行緒環境中時,可需要自己在管理執行緒的同步問題。
5、LinkedList
API----Linked list implementation of the List interface. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all elements (including null). In addition to implementing the List interface, the LinkedList class provides uniformly named methods to get, remove and insert an element at the beginning and end of the list. These operations allow linked lists to be used as a stack, queue, or double-ended queue.
LinkedList不同於前面兩種List,它不是基於陣列的,所以不受陣列效能的限制。
它每一個節點(Node)都包含兩方面的內容:
1.節點本身的資料(data);
2.下一個節點的資訊(nextNode)。
所以當對LinkedList做新增,刪除動作的時候就不用像基於陣列的ArrayList一樣,必須進行大量的資料移動。只要更改nextNode的相關資訊就可以實現了,這是LinkedList的優勢。
List總結:
- 所有的List中只能容納單個不同型別的物件組成的表,而不是Key-Value鍵值對。例如:[ tom,1,c ]
- 所有的List中可以有相同的元素,例如Vector中可以有 [ tom,koo,too,koo ]
- 所有的List中可以有null元素,例如[ tom,null,1 ]
6、Set(介面)
API-----A collection that contains no duplicate elements. More formally, sets contain no pair of elementse1 and
e2 such that
e1.equals(e2), and at most one null element. As implied by its name, this interface models the mathematical
set abstraction.
Set是不包含重複元素的Collection
7、HashSet
API-----This class implements theSet interface, backed by a hash table (actually aHashMap instance). It makes no guarantees as to the iteration order of the set; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order will remain constant over time. This class permits thenull element.
雖然Set同List都實現了Collection介面,但是他們的實現方式卻大不一樣。List基本上都是以Array為基礎。但是Set則是在 HashMap的基礎上來實現的,這個就是Set和List的根本區別。HashSet的儲存方式是把HashMap中的Key作為Set的對應儲存項。看看 HashSet的add(Object obj)方法的實現就可以一目瞭然了。8、LinkedHashSet
API----Linked list implementation of the List interface. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all elements (including null). In addition to implementing the List interface, the LinkedList class provides uniformly named methods to get, remove and insert an element at the beginning and end of the list. These operations allow linked lists to be used as a stack, queue, or double-ended queue. HashSet的一個子類,一個連結串列。9、SortedSet
API---ASet that further provides atotal ordering on its elements. The elements are ordered using theirnatural ordering, or by aComparator typically provided at sorted set creation time. The set's iterator will traverse the set in ascending element order. Several additional operations are provided to take advantage of the ordering. (This interface is the set analogue ofSortedMap.)
有序的Set,通過SortedMap來實現的。
Set總結:
(1)Set實現的基礎是Map(HashMap)(2)Set中的元素是不能重複的,如果使用add(Object obj)方法新增已經存在的物件,則會覆蓋前面的物件
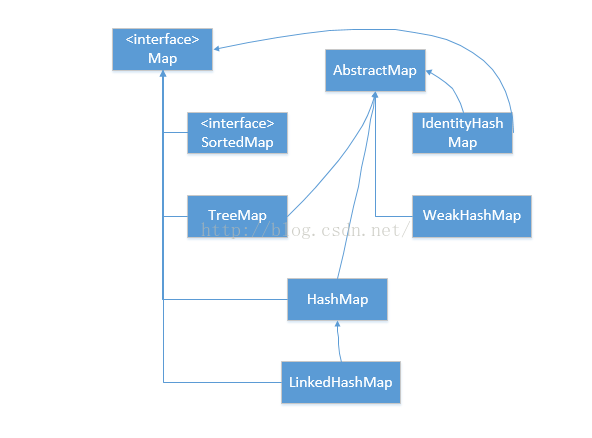
-------------Map-----------------
Map 是一種把鍵物件和值物件進行關聯的容器,而一個值物件又可以是一個Map,依次類推,這樣就可形成一個多級對映。對於鍵物件來說,像Set一樣,一個 Map容器中的鍵物件不允許重複,這是為了保持查詢結果的一致性;如果有兩個鍵物件一樣,那你想得到那個鍵物件所對應的值物件時就有問題了,可能你得到的並不是你想的那個值物件,結果會造成混亂,所以鍵的唯一性很重要,也是符合集合的性質的。當然在使用過程中,某個鍵所對應的值物件可能會發生變化,這時會按照最後一次修改的值物件與鍵對應。對於值物件則沒有唯一性的要求,你可以將任意多個鍵都對映到一個值物件上,這不會發生任何問題(不過對你的使用卻可能會造成不便,你不知道你得到的到底是那一個鍵所對應的值物件)。1、HashMap
API----Hash table based implementation of the Map interface. This implementation provides all of the optional map operations, and permits null values and the null key. (The HashMap class is roughly equivalent to Hashtable, except that it is unsynchronized and permits nulls.) This class makes no guarantees as to the order of the map; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order will remain constant over time.2、TreeMap
API----A Red-Black tree basedNavigableMap implementation. The map is sorted according to the
natural ordering of its keys, or by a
Comparator provided at map creation time, depending on which constructor is used.
TreeMap則是對鍵按序存放,因此它便有一些擴充套件的方法,比如firstKey(),lastKey()等,你還可以從TreeMap中指定一個範圍以取得其子Map。
鍵和值的關聯很簡單,用put(Object key,Object value)方法即可將一個鍵與一個值物件相關聯。用get(Object key)可得到與此key物件所對應的值物件。 ------------說明-----------
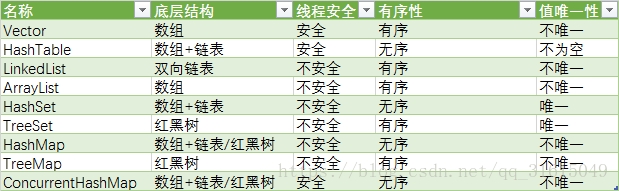
一、幾個常用類的區別
1.ArrayList: 元素單個,效率高,多用於查詢
2.Vector: 元素單個,執行緒安全,多用於查詢
3.LinkedList:元素單個,多用於插入和刪除
4.HashMap: 元素成對,元素可為空
5.HashTable: 元素成對,執行緒安全,元素不可為空
二、Vector、ArrayList和LinkedList
大多數情況下,從效能上來說ArrayList最好,但是當集合內的元素需要頻繁插入、刪除時LinkedList會有比較好的表現,但是它們三個效能都比不上陣列,另外Vector是執行緒同步的。所以:
如果能用陣列的時候(元素型別固定,陣列長度固定),請儘量使用陣列來代替List;
如果沒有頻繁的刪除插入操作,又不用考慮多執行緒問題,優先選擇ArrayList;
如果在多執行緒條件下使用,可以考慮Vector;
如果需要頻繁地刪除插入,LinkedList就有了用武之地;
如果你什麼都不知道,用ArrayList沒錯。
三、Collections和Arrays
在 Java集合類框架裡有兩個類叫做Collections(注意,不是Collection!)和Arrays,這是JCF裡面功能強大的工具,但初學者往往會忽視。按JCF文件的說法,這兩個類提供了封裝器實現(Wrapper Implementations)、資料結構演算法和陣列相關的應用。
想必大家不會忘記上面談到的“折半查詢”、“排序”等經典演算法吧,Collections類提供了豐富的靜態方法幫助我們輕鬆完成這些在資料結構課上煩人的工作:
binarySearch:折半查詢。
sort:排序,這裡是一種類似於快速排序的方法,效率仍然是O(n * log n),但卻是一種穩定的排序方法。
reverse:將線性表進行逆序操作,這個可是從前資料結構的經典考題哦!
rotate:以某個元素為軸心將線性表“旋轉”。
swap:交換一個線性表中兩個元素的位置。
……
Collections還有一個重要功能就是“封裝器”(Wrapper),它提供了一些方法可以把一個集合轉換成一個特殊的集合,如下:
unmodifiableXXX:轉換成只讀集合,這裡XXX代表六種基本集合介面:Collection、List、Map、Set、SortedMap和SortedSet。如果你對只讀集合進行插入刪除操作,將會丟擲UnsupportedOperationException異常。
synchronizedXXX:轉換成同步集合。
singleton:建立一個僅有一個元素的集合,這裡singleton生成的是單元素Set,
singletonList和singletonMap分別生成單元素的List和Map。
空集:由Collections的靜態屬性EMPTY_SET、EMPTY_LIST和EMPTY_MAP表示。
參考 https://blog.csdn.net/u010947402/article/details/51878166