JDK原始碼 -- Map篇
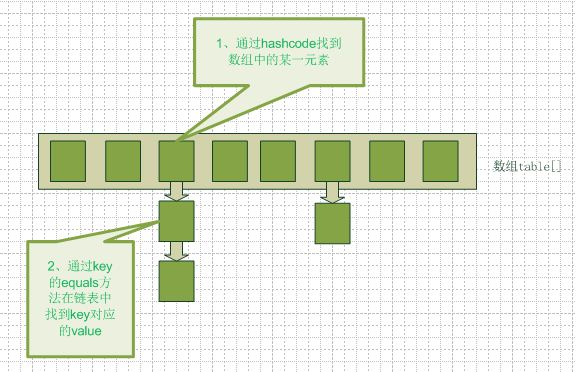
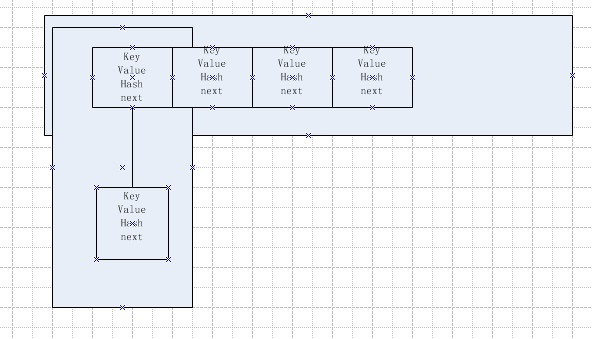
在java程式語言中,最基本的結構就是兩種,一個是陣列,另外一個是模擬指標(引用),所有的資料結構都可以用這兩個基本結構來構造的,hashmap也不例外。 Hashmap 實際上是一個數組和連結串列的結合體(在資料結構中,一般稱之為“連結串列雜湊“),請看下圖(橫排表示陣列,縱排表示陣列元素【實際上是一個連結串列】)。
HashMap是一個 Entry 鍵值對:
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
...
}
先看get() 方法:
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
// 首先 根據 key的 hashcode得到hash值(先不糾結演算法),再在 table中 找到該hash地址 對應的值; 如果該地址存在多個值,且以連結串列的形式存在,那麼根據for迴圈,直到取得對應的key的值。
---------------分割線 ---------------
put() 方法:
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
解析: 當我們將 新元素 往 map 中加的時候,首先 根據key值得到 hash值; 如果 在該hash值的位置上 已經有值了,那麼將元素以連結串列的形式存放,且最先放進來的元素 放在連結串列的最末尾; 如果 在該hash值的位置上沒有值,直接 將該位置留給 該 K-V鍵值對, table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
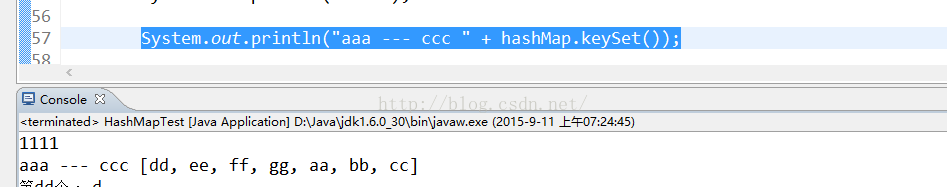
keySet():
返回此對映中包含的鍵的 set 檢視: 內部邏輯 包括迭代和匿名內部類: public Set<K> keySet() {if (keySet == null) {
keySet = new AbstractSet<K>() {
public Iterator<K> iterator() {
return new Iterator<K>() {
private Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
public boolean hasNext() {
return i.hasNext();
}
public K next() {
return i.next().getKey();
}
public void remove() {
i.remove();
}
};
}
public int size() {
return AbstractMap.this.size();
}
public boolean contains(Object k) {
return AbstractMap.this.containsKey(k);
}
};
}
return keySet;
}
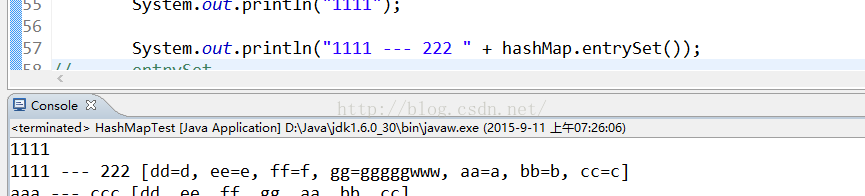
entrySet() 方法 :
此對映所包含的對映關係的 set 檢視。用到的 主要邏輯 還是 iterator 。