Android系統載入Apk檔案的時機和流程分析(1)--Android 4.4.4 r1的原始碼
Android系統在啟動時安裝應用程式的過程,這些應用程式安裝好之後,還需要有一個Home應用程式來負責把它們在桌面上展示出來,在Android系統中,這個預設的Home應用程式就是Launcher了。Android系統的Home應用程式Launcher是由ActivityManagerService啟動的,而ActivityManagerService和PackageManagerService一樣,都是在開機時由SystemServer元件啟動的,SystemServer元件首先是啟動PackageManagerServic,由它來負責安裝系統的應用程式,系統中的應用程式安裝好了以後,SystemServer元件接下來就要通過ActivityManagerService來啟動Home應用程式Launcher了,Launcher在啟動的時候便會通過PackageManagerServic把系統中已經安裝好的應用程式以快捷圖示的形式展示在桌面上,這樣使用者就可以使用這些應用程式了。
上面這段內容,摘自老羅部落格《Android系統預設Home應用程式(Launcher)的啟動過程原始碼分析》,有關點選Android系統的Home介面上的Android應用程式的圖示啟動Android應用的流程和原理,可以參考老羅的這篇部落格。
Android應用程式的啟動是一個非常複雜的流程,涉及到的Android系統的服務和底層的知識也不比較多,這裡只學習一下Android系統是在什麼時機載入Apk檔案的,簡單的瞭解一下Android系統載入Apk檔案的流程,後面我會研究一下Xposed多dex的Hook問題。
在建立Android應用程式的程序時,指定了該程序的入口是ActivityThread的main方法,此時便進入啟動Android應用程式的Activity的第4個階段:載入應用程式的Activity。Android系統載入Apk檔案,除錯模式等待除錯,Android應用程式的類Application例項的建立、attach方法和onCreate方法的被呼叫都是在這個階段。
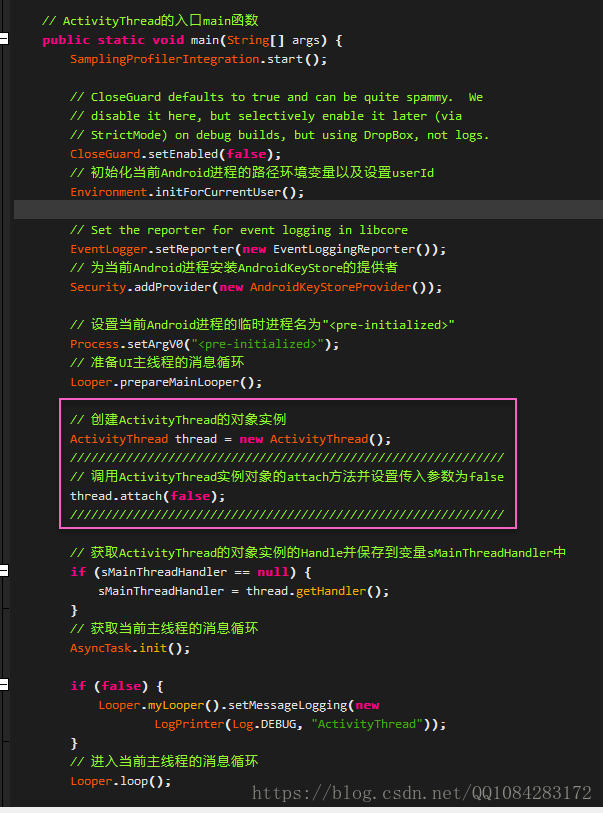
1.ActivityThread.main
載入Android應用程式Activity階段的第一步工作由ActivityThread.main完成,程式碼如下:
在ActivityThread.main方法中,首先設定臨時程序名為<pre-initialized>,準備UI主執行緒的訊息迴圈,然後建立應用程式的主執行緒ActivityThread,並呼叫其attach方法,設定傳入引數為false,最後進入主執行緒的訊息迴圈。
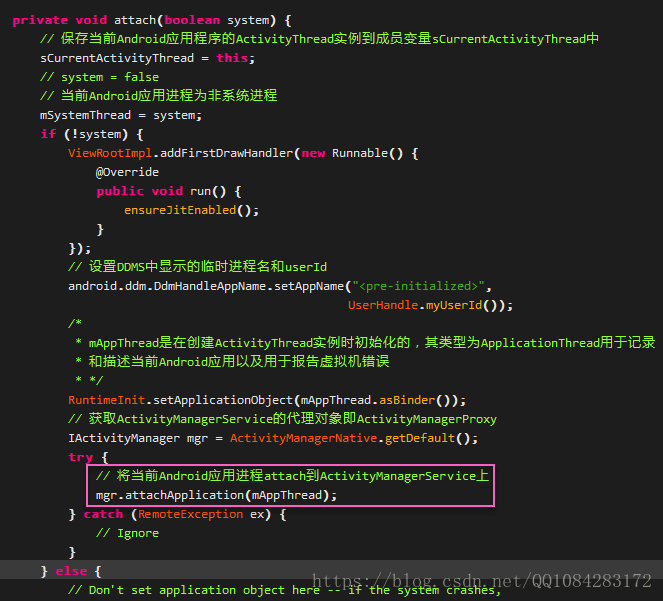
2.ActivityThread.attach
載入Android應用程式Activity階段的第二步工作由ActivityThread.attach完成,程式碼如下:
中間的無關程式碼省略......
在函式ActivityThread.attach中,當傳入引數為true時,對應Android系統的system程序的處理流程,此處傳入的引數false,對應普通Android應用程序的處理流程。函式ActivityThread.attach首先設定DDMS中顯示的臨時程序名<pre-initialized>和userId,然後呼叫ActivityManagerProxy.attachApplication方法,傳入該方法的引數mAppThread是在建立ActivityThread例項物件時,初始化為ApplicationThread例項物件的,該例項物件是一個Binder介面,ActivityManagerService便是通過ApplicationThread跨程序排程應用程式程序的。
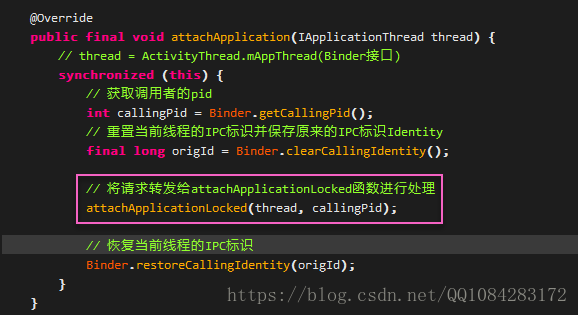
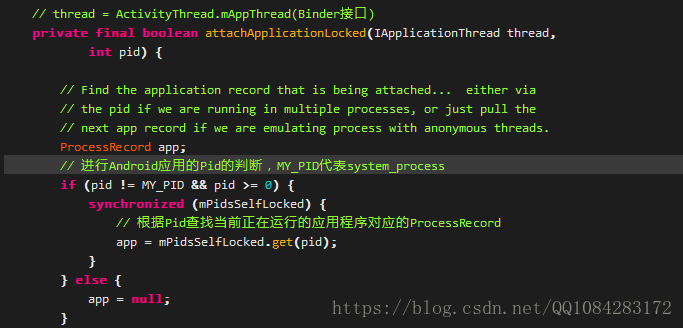
3.ActivityManagerService.attachApplication
載入Android應用程式Activity階段的第三步工作是由ActivityManagerProxy.attachApplication方法通過Binder通訊,進而呼叫ActivityManagerService的同名方法來完成attach操作的,這裡直接分析ActivityManagerService.attachApplication方法,程式碼如下:
在attachApplication中獲取到呼叫者的Pid後,將請求轉發給attachApplicationLocked方法進行處理,程式碼如下:
省略中間無關的程式碼......
省略中間無關的程式碼......
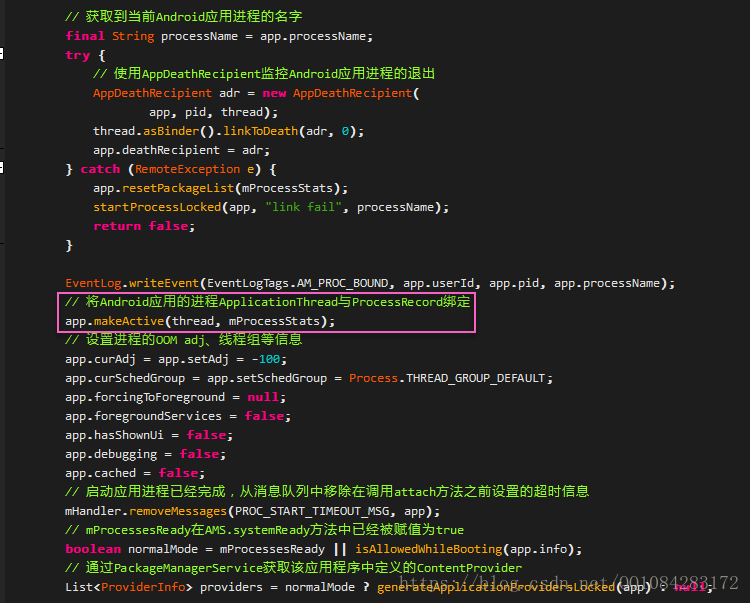
ActivityManagerService接收到Android應用程式程序的attach通知後,便會為將要啟動的應用程式程序執行以下操作:在mPidsSelfLocked中查詢到該Android應用程序的ProcessRecord資訊並進一步進行相關引數變數的賦值和設定,在ActivityManagerService訊息佇列中刪除啟動應用程式是新增的PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG訊息,然後緊接著呼叫類方法thread.bindApplication進入第四步操作,最終呼叫的是ApplicationThread.bindApplication方法。
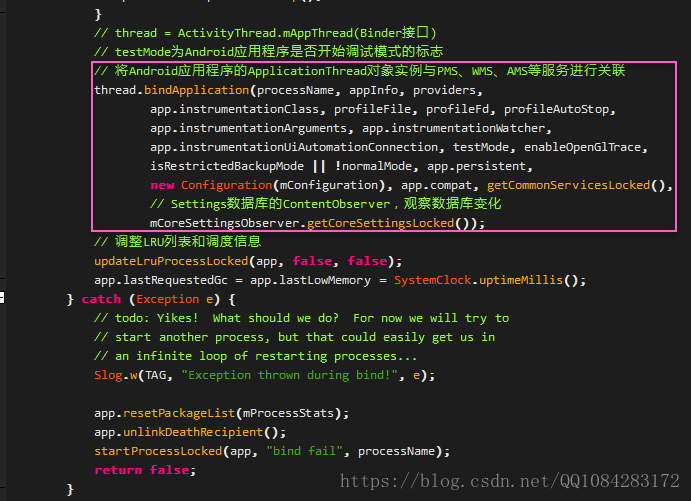
4.ApplicationThread.bindApplication
載入Android應用程式Activity階段的第四步工作是ApplicationThread.bindApplication完成的,程式碼如下:
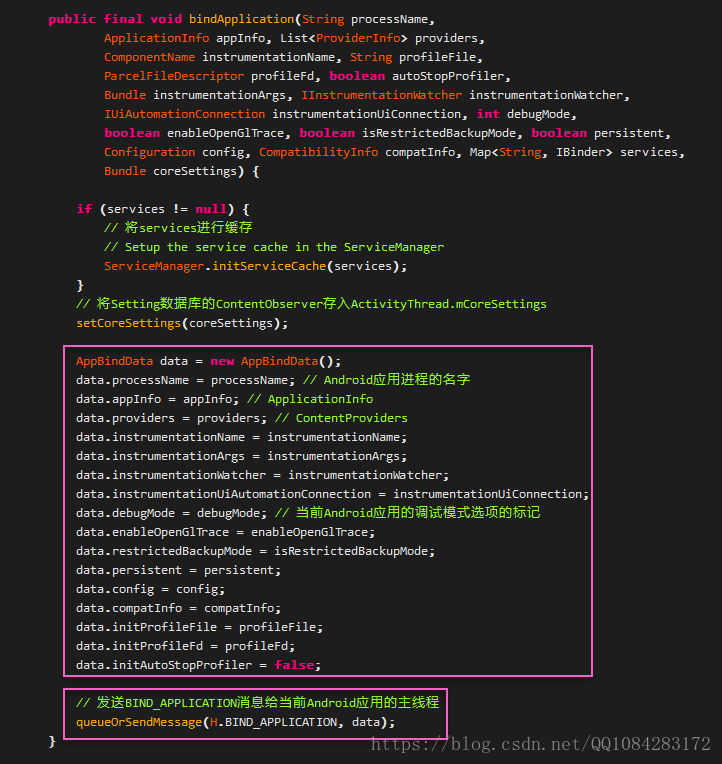
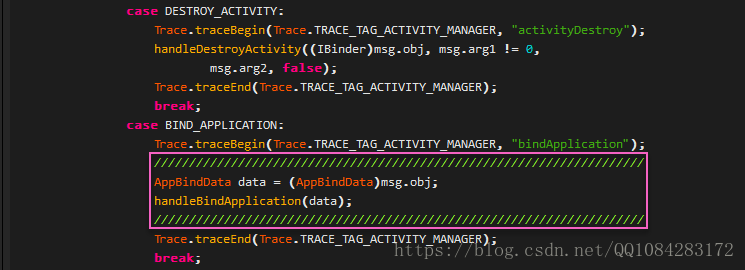
ApplicationThread.bindApplication將ActivityManagerService傳入的資料封裝到AppBindData中,然後將AppBindData資料通過BIND_APPLICATION訊息傳送給Android應用程式主執行緒的訊息迴圈中,由ActivityThread的 H.handleMessage 處理,程式碼如下:
H會根據傳入的訊息型別,匹配switch程式碼塊的BIND_APPLICATION訊息型別分支,獲取AppBindData資料,進而呼叫handleBindApplication方法。
5.ActivityThread.handleBindApplication
載入Android應用程式Activity階段的第五步工作是呼叫 ActivityThread.handleBindApplication 方法,程式碼如下:
省略中間的無關程式碼......
省略中間的無關程式碼......
省略中間的無關程式碼......
ActivityThread.handleBindApplication方法的主要工作如下:
1).為Android應用程式設定顯示的程序名稱。
2).為低記憶體裝置禁用硬體加速。
3).建立應用程式對應的Application,並設定該Android應用程序的初始Application。
4).安裝ContentProvider(可見ContentProvider的建立先於其他Android元件)。
5).執行Instrumentation的onCreate方法。
6).執行Application的onCreate方法。
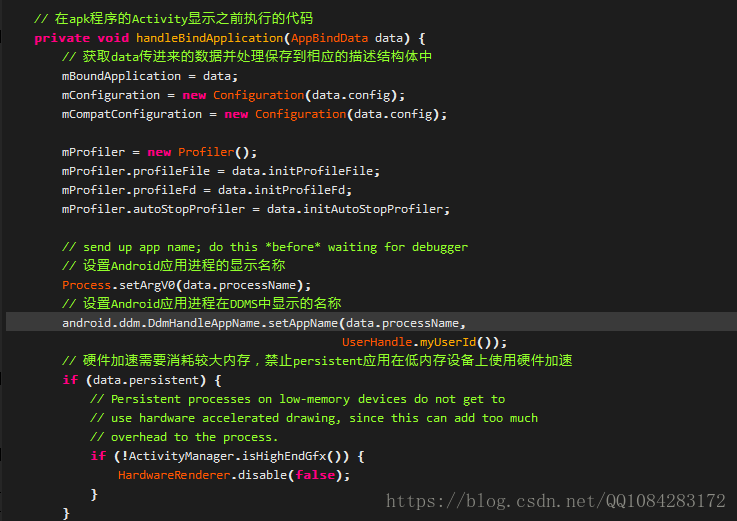
// 在apk程式的Activity顯示之前執行的程式碼
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
// 獲取data傳進來的資料並處理儲存到相應的描述結構體中
mBoundApplication = data;
mConfiguration = new Configuration(data.config);
mCompatConfiguration = new Configuration(data.config);
mProfiler = new Profiler();
mProfiler.profileFile = data.initProfileFile;
mProfiler.profileFd = data.initProfileFd;
mProfiler.autoStopProfiler = data.initAutoStopProfiler;
// send up app name; do this *before* waiting for debugger
// 設定Android應用程序的顯示名稱
Process.setArgV0(data.processName);
// 設定Android應用程序在DDMS中顯示的名稱
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName(data.processName,
UserHandle.myUserId());
// 硬體加速需要消耗較大記憶體,禁止persistent應用在低記憶體裝置上使用硬體加速
if (data.persistent) {
// Persistent processes on low-memory devices do not get to
// use hardware accelerated drawing, since this can add too much
// overhead to the process.
if (!ActivityManager.isHighEndGfx()) {
HardwareRenderer.disable(false);
}
}
if (mProfiler.profileFd != null) {
mProfiler.startProfiling();
}
// If the app is Honeycomb MR1 or earlier, switch its AsyncTask
// implementation to use the pool executor. Normally, we use the
// serialized executor as the default. This has to happen in the
// main thread so the main looper is set right.
if (data.appInfo.targetSdkVersion <= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB_MR1) {
AsyncTask.setDefaultExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR);
}
/*
* Before spawning a new process, reset the time zone to be the system time zone.
* This needs to be done because the system time zone could have changed after the
* the spawning of this process. Without doing this this process would have the incorrect
* system time zone.
*/
TimeZone.setDefault(null);
/*
* Initialize the default locale in this process for the reasons we set the time zone.
*/
Locale.setDefault(data.config.locale);
/*
* Update the system configuration since its preloaded and might not
* reflect configuration changes. The configuration object passed
* in AppBindData can be safely assumed to be up to date
*/
mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(data.config, data.compatInfo);
mCurDefaultDisplayDpi = data.config.densityDpi;
applyCompatConfiguration(mCurDefaultDisplayDpi);
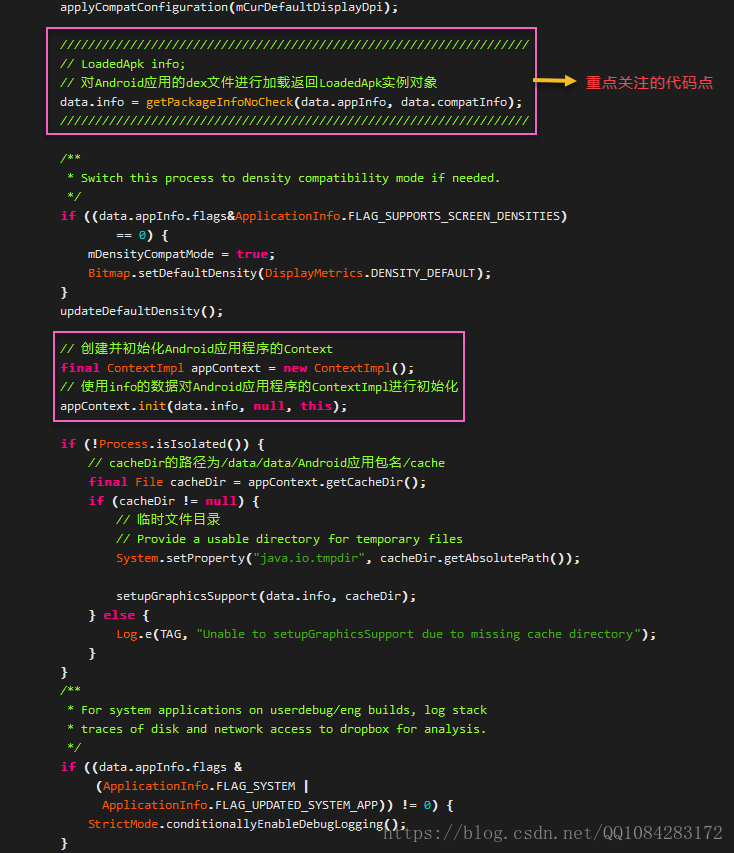
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// LoadedApk info;
// 對Android應用的dex檔案進行載入返回LoadedApk例項物件
data.info = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data.appInfo, data.compatInfo);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Switch this process to density compatibility mode if needed.
*/
if ((data.appInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SUPPORTS_SCREEN_DENSITIES)
== 0) {
mDensityCompatMode = true;
Bitmap.setDefaultDensity(DisplayMetrics.DENSITY_DEFAULT);
}
updateDefaultDensity();
// 建立並初始化Android應用程式的Context
final ContextImpl appContext = new ContextImpl();
// 使用info的資料對Android應用程式的ContextImpl進行初始化
appContext.init(data.info, null, this);
if (!Process.isIsolated()) {
// cacheDir的路徑為/data/data/Android應用包名/cache
final File cacheDir = appContext.getCacheDir();
if (cacheDir != null) {
// 臨時檔案目錄
// Provide a usable directory for temporary files
System.setProperty("java.io.tmpdir", cacheDir.getAbsolutePath());
setupGraphicsSupport(data.info, cacheDir);
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Unable to setupGraphicsSupport due to missing cache directory");
}
}
/**
* For system applications on userdebug/eng builds, log stack
* traces of disk and network access to dropbox for analysis.
*/
if ((data.appInfo.flags &
(ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM |
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_UPDATED_SYSTEM_APP)) != 0) {
StrictMode.conditionallyEnableDebugLogging();
}
/**
* For apps targetting SDK Honeycomb or later, we don't allow
* network usage on the main event loop / UI thread.
*
* Note to those grepping: this is what ultimately throws
* NetworkOnMainThreadException ...
*/
if (data.appInfo.targetSdkVersion > 9) {
StrictMode.enableDeathOnNetwork();
}
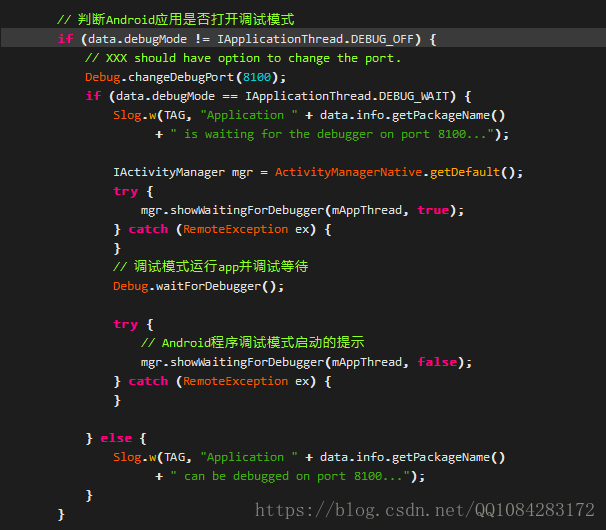
// 判斷Android應用是否開啟除錯模式
if (data.debugMode != IApplicationThread.DEBUG_OFF) {
// XXX should have option to change the port.
Debug.changeDebugPort(8100);
if (data.debugMode == IApplicationThread.DEBUG_WAIT) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Application " + data.info.getPackageName()
+ " is waiting for the debugger on port 8100...");
IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
mgr.showWaitingForDebugger(mAppThread, true);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
// 除錯模式執行app並除錯等待
Debug.waitForDebugger();
try {
// Android程式除錯模式啟動的提示
mgr.showWaitingForDebugger(mAppThread, false);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Application " + data.info.getPackageName()
+ " can be debugged on port 8100...");
}
}
// Enable OpenGL tracing if required
if (data.enableOpenGlTrace) {
GLUtils.setTracingLevel(1);
}
// Allow application-generated systrace messages if we're debuggable.
boolean appTracingAllowed = (data.appInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_DEBUGGABLE) != 0;
Trace.setAppTracingAllowed(appTracingAllowed);
/**
* Initialize the default http proxy in this process for the reasons we set the time zone.
*/
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
if (b != null) {
// In pre-boot mode (doing initial launch to collect password), not
// all system is up. This includes the connectivity service, so don't
// crash if we can't get it.
IConnectivityManager service = IConnectivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
try {
ProxyProperties proxyProperties = service.getProxy();
Proxy.setHttpProxySystemProperty(proxyProperties);
} catch (RemoteException e) {}
}
// 此處data.instrumentationName為null
// 對應AndroidManifest.xml的Instrumentation
if (data.instrumentationName != null) {
InstrumentationInfo ii = null;
try {
ii = appContext.getPackageManager().
getInstrumentationInfo(data.instrumentationName, 0);
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
}
if (ii == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to find instrumentation info for: "
+ data.instrumentationName);
}
mInstrumentationAppDir = ii.sourceDir;
mInstrumentationAppLibraryDir = ii.nativeLibraryDir;
mInstrumentationAppPackage = ii.packageName;
mInstrumentedAppDir = data.info.getAppDir();
mInstrumentedAppLibraryDir = data.info.getLibDir();
ApplicationInfo instrApp = new ApplicationInfo();
instrApp.packageName = ii.packageName;
instrApp.sourceDir = ii.sourceDir;
instrApp.publicSourceDir = ii.publicSourceDir;
instrApp.dataDir = ii.dataDir;
instrApp.nativeLibraryDir = ii.nativeLibraryDir;
// 得到Android應用dex檔案載入後的LoadedApk例項
LoadedApk pi = getPackageInfo(instrApp, data.compatInfo,
appContext.getClassLoader(), false, true);
ContextImpl instrContext = new ContextImpl();
instrContext.init(pi, null, this);
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = instrContext.getClassLoader();
mInstrumentation = (Instrumentation)
cl.loadClass(data.instrumentationName.getClassName()).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate instrumentation "
+ data.instrumentationName + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
mInstrumentation.init(this, instrContext, appContext,
new ComponentName(ii.packageName, ii.name), data.instrumentationWatcher,
data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection);
if (mProfiler.profileFile != null && !ii.handleProfiling
&& mProfiler.profileFd == null) {
mProfiler.handlingProfiling = true;
File file = new File(mProfiler.profileFile);
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
Debug.startMethodTracing(file.toString(), 8 * 1024 * 1024);
}
} else {
// AndroidManifest.xml未指定構建Instrumentation,建立預設值
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
}
if ((data.appInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_LARGE_HEAP) != 0) {
dalvik.system.VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
}
// Allow disk access during application and provider setup. This could
// block processing ordered broadcasts, but later processing would
// probably end up doing the same disk access.
final StrictMode.ThreadPolicy savedPolicy = StrictMode.allowThreadDiskWrites();
try {
// If the app is being launched for full backup or restore, bring it up in
// a restricted environment with the base application class.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
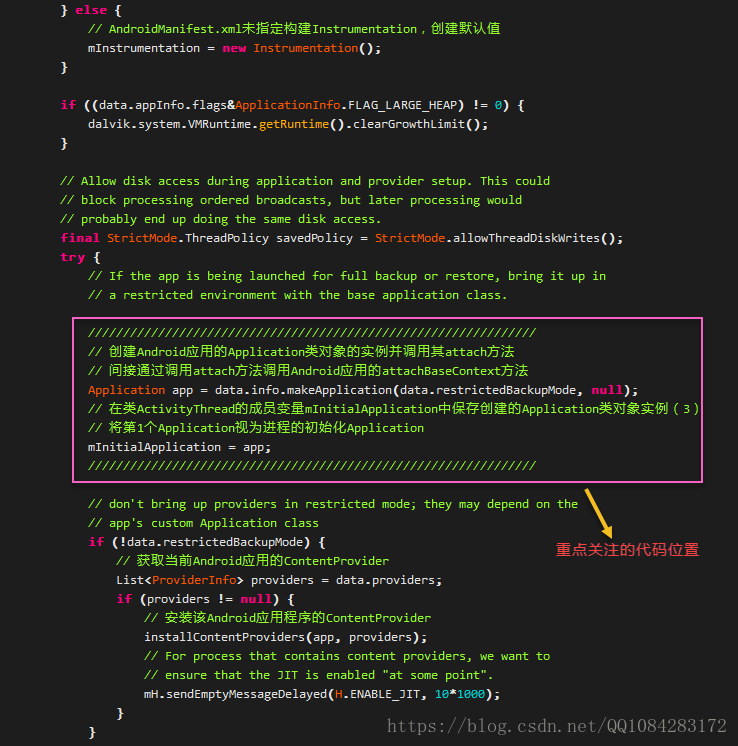
// 建立Android應用的Application類物件的例項並呼叫其attach方法
// 間接通過呼叫attach方法呼叫Android應用的attachBaseContext方法
Application app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
// 在類ActivityThread的成員變數mInitialApplication中儲存建立的Application類物件例項(3)
// 將第1個Application視為程序的初始化Application
mInitialApplication = app;
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// don't bring up providers in restricted mode; they may depend on the
// app's custom Application class
if (!data.restrictedBackupMode) {
// 獲取當前Android應用的ContentProvider
List<ProviderInfo> providers = data.providers;
if (providers != null) {
// 安裝該Android應用程式的ContentProvider
installContentProviders(app, providers);
// For process that contains content providers, we want to
// ensure that the JIT is enabled "at some point".
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.ENABLE_JIT, 10*1000);
}
}
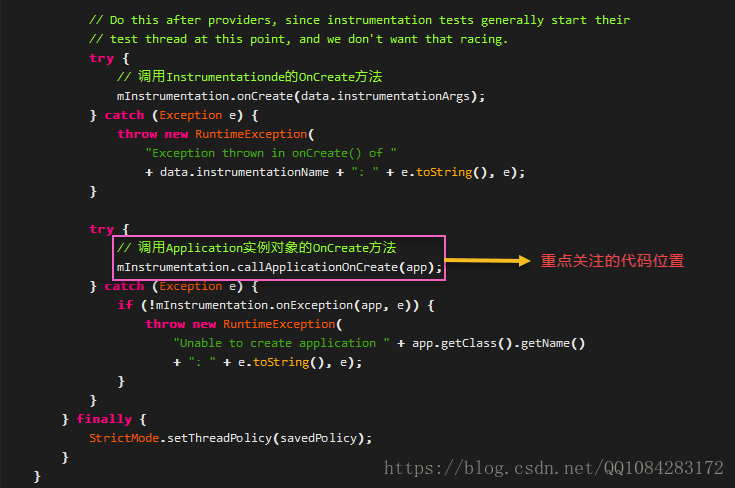
// Do this after providers, since instrumentation tests generally start their
// test thread at this point, and we don't want that racing.
try {
// 呼叫Instrumentationde的OnCreate方法
mInstrumentation.onCreate(data.instrumentationArgs);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Exception thrown in onCreate() of "
+ data.instrumentationName + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
try {
// 呼叫Application例項物件的OnCreate方法
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
} finally {
StrictMode.setThreadPolicy(savedPolicy);
}
}以上步驟執行完畢標誌著啟動Android應用程式載入Activity的階段結束,後面的步驟就是進行Activity的顯示,暫時不討論,有必要再研究。我在這裡只關注上面標註的3個程式碼點的位置。上面的程式碼分析很多參考了《Android的設計與實現 卷I》(作者楊雲君)這本書,雖然這本書的作者寫的內容對學習Android逆向的同學來說很有幫助,但是感覺作者很多地方分析的不是很詳細,要是能說的更明白一點就好了,老羅的部落格相對來說就講的細緻和明白一些。
未完待續,後面再寫篇部落格詳細分析這3個重要程式碼點的位置,因為這3個位置的程式碼涉及到Android的加固原理、Android的多dex載入原理以及Xposed Hook的多dex問題的理解~