Hadoop中RPC小結
- 概述
- Hadoop RPC
- Hadoop Client
- Hadoop Server
- Hadoop RPC的使用
- Yarn RPC
- 參考
概述
RPC(Remote Procedure Call)遠端過程呼叫,它是一種通過網路從遠端計算機程式上請求服務,而不需要了解底層網路技術的協議。RPC協議假定某些傳輸協議的存在,如TCP或UDP,為通訊程式之間攜帶資訊資料。在OSI網路通訊模型中,RPC跨越了傳輸層和應用層。RPC使得開發包括網路分散式多程式在內的應用程式更加容易。.
RPC內部的結構一般如下圖所示:
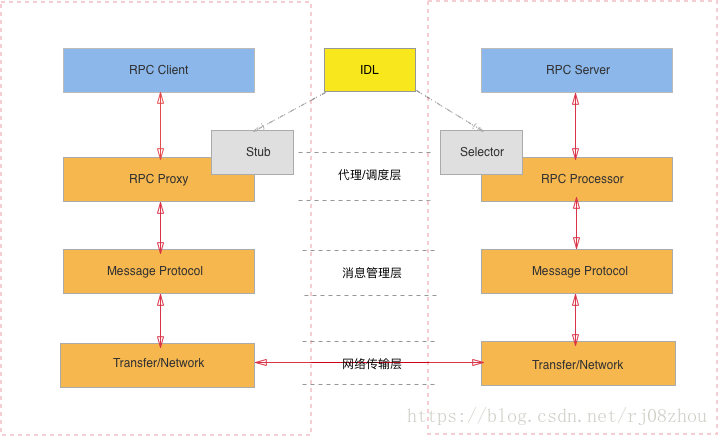
- RPC Client: RPC協議的呼叫方。
- RPC Server: 遠端方法的提供方。
- RPC Proxy/Stub: 存在於客戶端,因為RPC協議的”透明性”,需要存在一個Stub層封裝RPC遠端呼叫的過程實現,讓客戶端覺得是在本地呼叫方法一樣。
- RPC Processor/Selector: 存在於服務端,由於伺服器端某一個RPC介面的實現的特性(它並不知道自己是一個將要被RPC提供給第三方系統呼叫的服務),所以在RPC框架中應該有一種“負責執行RPC介面實現”的角色。它負責了包括:管理RPC介面的註冊、判斷客戶端的請求許可權、控制介面實現類的執行在內的各種工作。
- MessageProtocol: 由於一次互動都有服務端和客戶端兩端都能識別的,共同約定的格式。訊息管理層負責對訊息的編碼和解碼。同時要保證訊息序列化的高效性。
- Transfer/Network: 負責管理RPC框架所使用的網路協議、網路IO模型。
- IDL: 介面定義語言,為跨語言的特性設計的通用的訊息格式。
Hadoop RPC
Haddoop中的RPC有兩種,一種是hadoop-common下的ipc.RPC類,還有一種是hadoop-yarn-common下的ipc.YarnRPC類。
RPC類中是對底層客戶機-伺服器網路模型的封裝,以便為程式設計師提供一套簡潔的介面,是Hadoop的底層核心元件。在Hadoop HDFS,MapReduce和HBase中有著廣泛的使用。YarnRPC類是Yarn中使用的RPC類,其封裝了hadoop-common下的RPC,並預設使用了protobuf作為序列化工具,在Yarn的協議中使用。
下面分析hadoop-common下的RPC.java類。首先展示這個類的Outline:
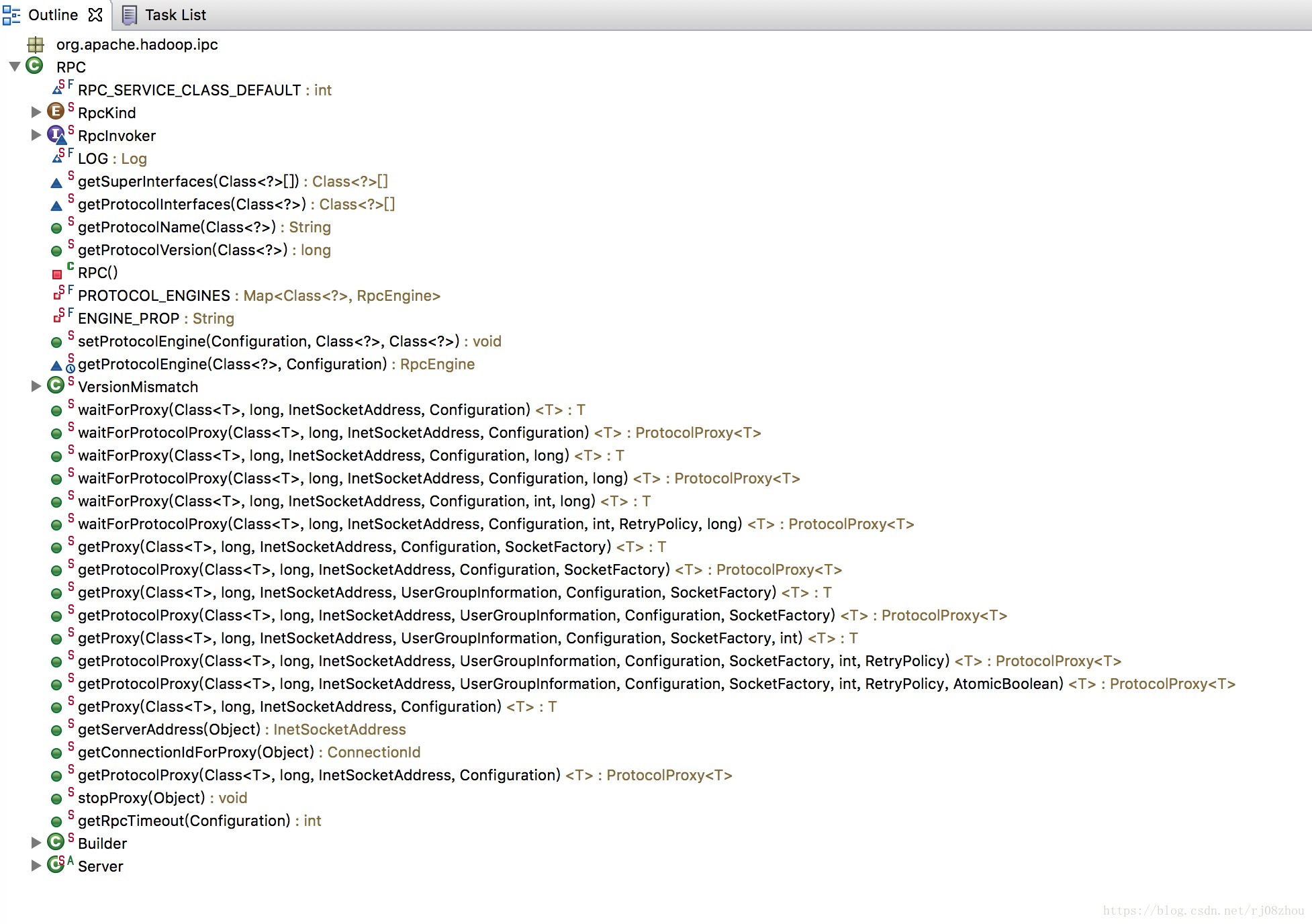
從outline中看到
- RpcKind: 內部列舉,展示了RPC框架將使用哪種Rpc引擎,其中包含了WritableRpcEngine和ProtobufRpcEngine,分別對應了不同序列化方式的RPC實現。
- RpcInvoker: 內部介面,官方註釋為: Process a client call on the server side,即表示這是一個在服務端處理客戶端請求的介面。
- getSuperInterfaces(Class
/**
* Get a protocol proxy that contains a proxy connection to a remote server
* and a set of methods that are supported by the server
*
* @param protocol protocol
* @param clientVersion client's version
* @param addr server address
* @param ticket security ticket
* @param conf configuration
* @param factory socket factory
* @param rpcTimeout max time for each rpc; 0 means no timeout
* @param connectionRetryPolicy retry policy
* @param fallbackToSimpleAuth set to true or false during calls to indicate if
* a secure client falls back to simple auth
* @return the proxy
* @throws IOException if any error occurs
*/
public static <T> ProtocolProxy<T> getProtocolProxy(Class<T> protocol,
long clientVersion,
InetSocketAddress addr,
UserGroupInformation ticket,
Configuration conf,
SocketFactory factory,
int rpcTimeout,
RetryPolicy connectionRetryPolicy,
AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth)
throws IOException {
if (UserGroupInformation.isSecurityEnabled()) {//安全
SaslRpcServer.init(conf);
}
return getProtocolEngine(protocol, conf).getProxy(protocol, clientVersion,
addr, ticket, conf, factory, rpcTimeout, connectionRetryPolicy,
fallbackToSimpleAuth);
}
可以看刀這個方法是獲取一個遠端服務的代理,中間包含了連線和server的方法的代理。其中通過getProtocolEngine獲取一個特定序列化協議的RpcEngine。
// return the RpcEngine configured to handle a protocol
static synchronized RpcEngine getProtocolEngine(Class<?> protocol,
Configuration conf) {
//從RpcEngine快取中獲取,如果不存在的話則讀取配置檔案通過反射機制建立一個rpcEngine
//預設是WritableRpcEngine
RpcEngine engine = PROTOCOL_ENGINES.get(protocol);
if (engine == null) {
Class<?> impl = conf.getClass(ENGINE_PROP+"."+protocol.getName(),
WritableRpcEngine.class);
engine = (RpcEngine)ReflectionUtils.newInstance(impl, conf);
PROTOCOL_ENGINES.put(protocol, engine);
}
return engine;
}
由於現在hadoop基本上都是用protobuf來序列化,下面從ProtobufRpcEngine中來分析getProxy這個方法。
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> ProtocolProxy<T> getProxy(Class<T> protocol, long clientVersion,
InetSocketAddress addr, UserGroupInformation ticket, Configuration conf,
SocketFactory factory, int rpcTimeout, RetryPolicy connectionRetryPolicy,
AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth) throws IOException {
final Invoker invoker = new Invoker(protocol, addr, ticket, conf, factory,
rpcTimeout, connectionRetryPolicy, fallbackToSimpleAuth);
return new ProtocolProxy<T>(protocol, (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
protocol.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{protocol}, invoker), false);
}
//InvocationHandler
private static class Invoker implements RpcInvocationHandler {
//中間程式碼省略...
/**
* This constructor takes a connectionId, instead of creating a new one.
*/
private Invoker(Class<?> protocol, Client.ConnectionId connId,
Configuration conf, SocketFactory factory) {
this.remoteId = connId;
this.client = CLIENTS.getClient(conf, factory, RpcResponseWrapper.class);
this.protocolName = RPC.getProtocolName(protocol);
this.clientProtocolVersion = RPC.getProtocolVersion(protocol);
}
//中間程式碼省略...
//invoke()
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws ServiceException {
//中間程式碼省略...
RequestHeaderProto rpcRequestHeader = constructRpcRequestHeader(method);
//中間程式碼省略...
try {
val = (RpcResponseWrapper) client.call(RPC.RpcKind.RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER,
new RpcRequestWrapper(rpcRequestHeader, theRequest), remoteId,
fallbackToSimpleAuth);
} catch (Throwable e) {...}
}
}
總體上來說,getProxy中使用的是java中的動態代理。首先建立一個叫invoker的invocationHandler,裡面包含了本次連線的id,客戶端client等,以及重寫了invoke()方法,在invoke()中將呼叫的method方法封裝在rpcRequestHeader中,同時通過client.call()傳送到服務端。建立好了invocationHandler後,再通過Proxy.newProxyInstance()建立代理類例項,根據生成的代理類例項,即可呼叫對應的方法。
- Builder
這個是RPC Server的一個構造者物件,可以通過RPC.Builder.build()方法構建一個伺服器物件。類似程式碼如下:
Server server = new RPC.Builder(config).setProtocol(protocol).
setInstance(instance).setBindAddress(address).setPort(port).
setNumHandlers(default).setnumReaders(defaultReaders).
setQueueSizePerHandler(1).setVerbose(true).build() ;
server.start();- Server
這個Server是RPC類對Hadoop Server的一個封裝,通過Builder中的build()方法呼叫生成org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server物件。
Hadoop Client
Client類的主要功能就是sendRequest和receiveResponse。首先來看看這個類的outline:
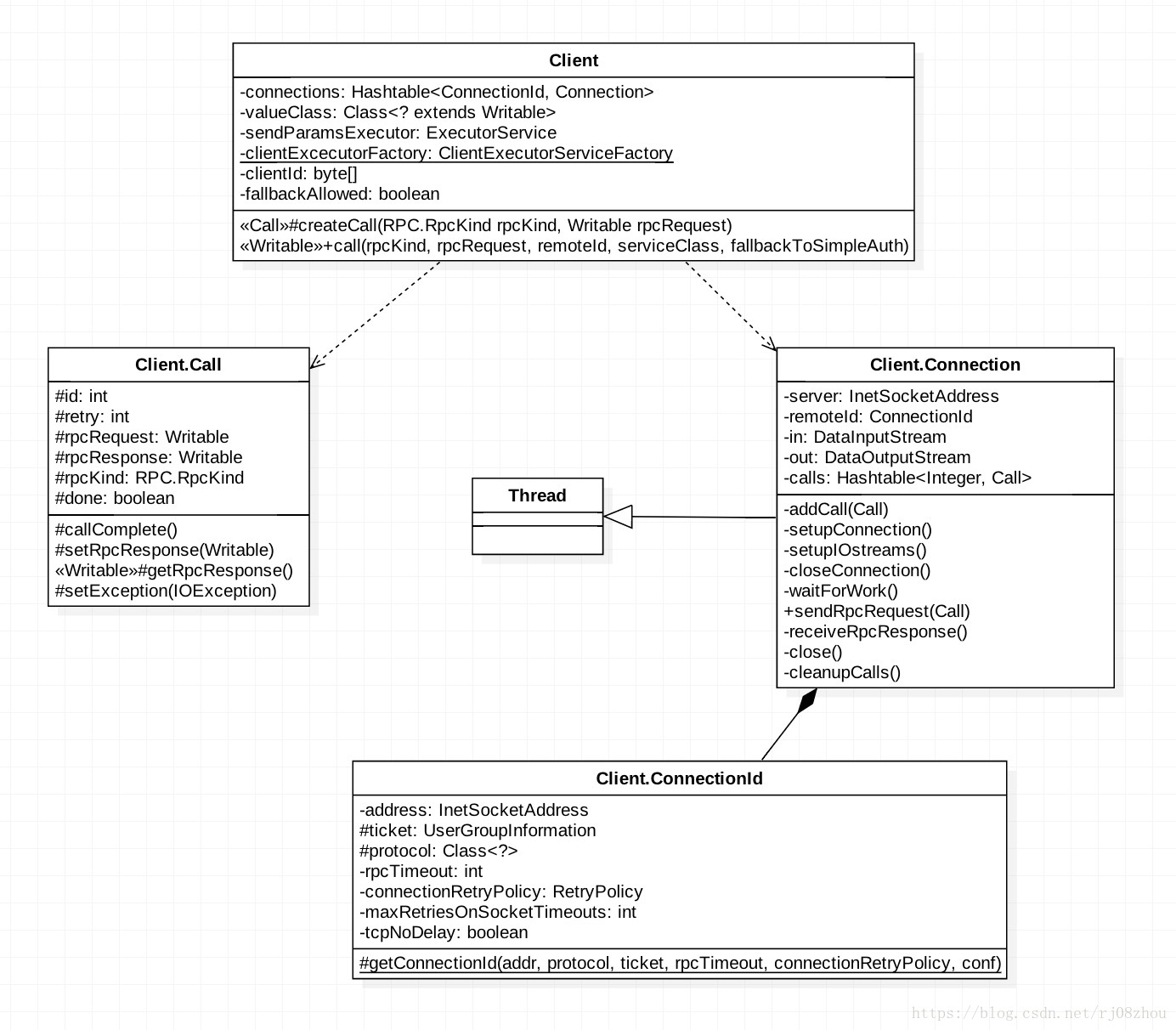
從outline中可以看到Client中主要有這麼幾個內部類:
- ClientExecutorServiceFactory 這個類主要是客戶端為了傳送rpc請求建立執行緒池的單例類,當建立客戶端時,會建立這樣一個執行緒池單例.
private final static ClientExecutorServiceFactory clientExcecutorFactory =
new ClientExecutorServiceFactory();
private static class ClientExecutorServiceFactory {
private int executorRefCount = 0;
private ExecutorService clientExecutor = null;
/**
* Get Executor on which IPC calls' parameters are sent.
* If the internal reference counter is zero, this method
* creates the instance of Executor. If not, this method
* just returns the reference of clientExecutor.
*
* @return An ExecutorService instance
*/
synchronized ExecutorService refAndGetInstance() {
if (executorRefCount == 0) {
clientExecutor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setDaemon(true)
.setNameFormat("IPC Parameter Sending Thread #%d")
.build());
}
executorRefCount++;
return clientExecutor;
}
...省略部分程式碼...
}- Call 這個類封裝了一個RPC請求,其中包含了唯一的id,重複次數retry,傳送請求rpcRequest,收到的結果rpcResponse,以及傳送的狀態error,done等。由於hadoop傳送請求是非同步的,所以需要id來確定不同的呼叫。
Connection 這個類封裝了Client和Server之間連線的基本資訊以及一些基本操作,如sendRpcRequest,receiveRpcRequest等。
- Connection類中維護了一個型別為Hashtable
public Writable call(RPC.RpcKind rpcKind, Writable rpcRequest,
ConnectionId remoteId, int serviceClass,
AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth) throws IOException {
final Call call = createCall(rpcKind, rpcRequest);
Connection connection = getConnection(remoteId, call, serviceClass,
fallbackToSimpleAuth);
try {
connection.sendRpcRequest(call); // send the rpc request
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
throw new IOException("connection has been closed", e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
LOG.warn("interrupted waiting to send rpc request to server", e);
throw new IOException(e);
}
boolean interrupted = false;
synchronized (call) {
while (!call.done) {
try {
call.wait(); // wait for the result
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
// save the fact that we were interrupted
interrupted = true;
}
}
if (interrupted) {
// set the interrupt flag now that we are done waiting
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
if (call.error != null) {
if (call.error instanceof RemoteException) {
call.error.fillInStackTrace();
throw call.error;
} else { // local exception
InetSocketAddress address = connection.getRemoteAddress();
throw NetUtils.wrapException(address.getHostName(),
address.getPort(),
NetUtils.getHostname(),
0,
call.error);
}
} else {
return call.getRpcResponse();
}
}
}Hadoop Server
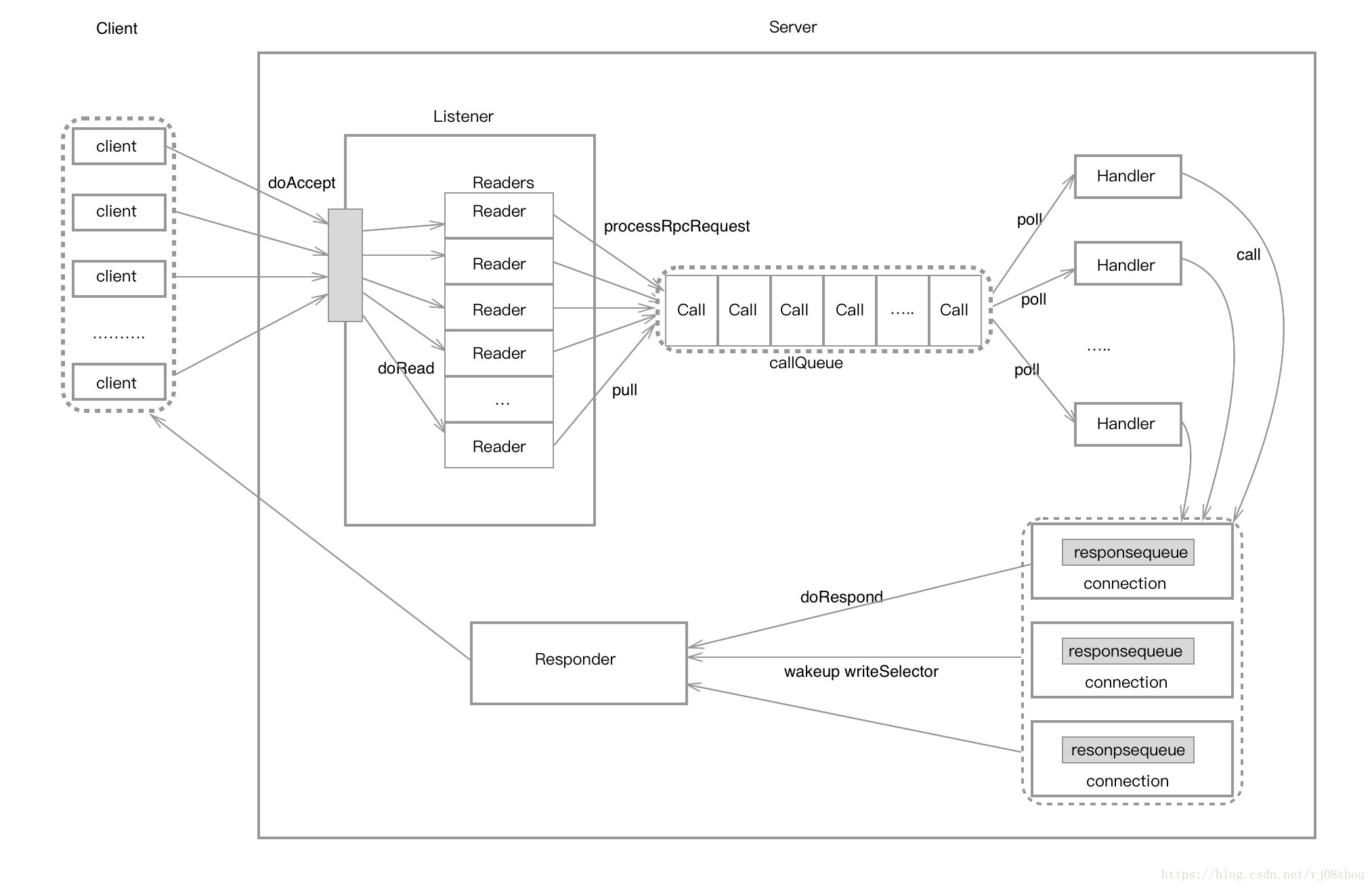
Server即服務端。Hadoop Server為了保證高效能採用了很多提高併發處理能力的技術,其中有執行緒池、事件驅動以及使用了Reactor模式。
這裡不對Reactor進行介紹了。只是貼一張Reactor模式的圖:
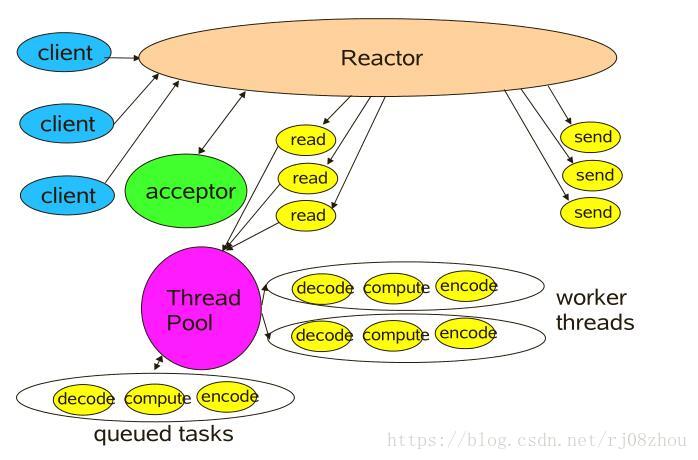
ipc.Server的整體架構和上面的一致。由於篇幅關係,不再貼出Server的outline圖。直接分析其中的實現吧。
Call 和客戶端類似,將rpcRequest和rpcResponse以及連線資訊封裝起來,由Reader讀取來自客戶端的連線請求解析後組裝而成,應該該是由於Reactor模式中將一次連線的操作分割為連線,讀取,處理和寫入等單元操作後,為了控制是同一個連線的操作而建立的類。
Listener 相當於Acceptor角色,整個Server只有一個Listener執行緒,負責用於監聽來自客戶端的請求。看看原始碼:
private class Listener extends Thread {
private ServerSocketChannel acceptChannel = null; //the accept channel
private Selector selector = null; //the selector that we use for the server
private Reader[] readers = null; //Reader
...省略中間程式碼...
public Listener() throws IOException {
address = new InetSocketAddress(bindAddress, port);
// Create a new server socket and set to non blocking mode
acceptChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
acceptChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// Bind the server socket to the local host and port
bind(acceptChannel.socket(), address, backlogLength, conf, portRangeConfig);
port = acceptChannel.socket().getLocalPort(); //Could be an ephemeral port
// create a selector;
selector= Selector.open();
readers = new Reader[readThreads];
for (int i = 0; i < readThreads; i++) {
Reader reader = new Reader(
"Socket Reader #" + (i + 1) + " for port " + port);
readers[i] = reader;
reader.start();
}
// Register accepts on the server socket with the selector.
acceptChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
this.setName("IPC Server listener on " + port);
this.setDaemon(true);
}
...
}首先Listener類初始化時,會建立起socket連線,繫結相關的地址後,建立內部的Reader陣列,同時開啟Selector,在通道上建立對SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT的監聽。當Server建立Listener完畢並呼叫start方法時,Listener執行緒的run方法開始執行,其中主要是一個doAccept()方法
void doAccept(SelectionKey key) throws InterruptedException, IOException, OutOfMemoryError {
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel channel;
while ((channel = server.accept()) != null) {
channel.configureBlocking(false);
channel.socket().setTcpNoDelay(tcpNoDelay);
channel.socket().setKeepAlive(true);
Reader reader = getReader();
Connection c = connectionManager.register(channel);
key.attach(c); // so closeCurrentConnection can get the object
reader.addConnection(c);
}
}這個方法主要是採用Round Robin輪詢排程的方式獲取一個Reader,並建立起一個Connection物件。Connection是指一個連線物件,Server將rpc連線的資訊和操作封裝成Connection。 Connection中的操作有處理讀取的請求資料readAndProcess(),以及封裝返回的應答資料等。通過ConnectionManager來管理這些Connection。同時Connection建立時會生成一個responsequeue物件,用於處理完請求後對應答的緩衝。
- Reader Reader是Listener中的一個內部類,當穿件Listener時,會建立一個Reader的陣列,這些Reader分別負責接收來自客戶端連線的Rpc請求。Reader執行緒中主要是執行doRunLoop()方法,首先會建立一個pendingConnections的Connection佇列作為緩衝,防止當單個connection佔用過多時間時對readingSelector產生的飢餓現象。然後建立對SelectionKey.OP_READ事件的監聽,同時呼叫doRead()->readAndProcess()->processOneRpc()->processRpcRequest()方法,處理完connectionhead和connectionContext後,將客戶端傳來的rpcRequest資訊封裝成一個Call物件,然後將Call物件放置到callqueue中。callqueue作為Reader和Handler之間的快取佇列,防止當Reader產生過多Call時Handler執行緒處理不過來的情形。
private void processRpcRequest(RpcRequestHeaderProto header,
DataInputStream dis) throws WrappedRpcServerException,
InterruptedException {
...省略...
Writable rpcRequest;
try { //Read the rpc request 讀取Rpc請求
rpcRequest = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(rpcRequestClass, conf);
rpcRequest.readFields(dis);
} catch (Throwable t) { // includes runtime exception from newInstance
LOG.warn("Unable to read call parameters for client " +
getHostAddress() + "on connection protocol " +
this.protocolName + " for rpcKind " + header.getRpcKind(), t);
String err = "IPC server unable to read call parameters: "+ t.getMessage();
throw new WrappedRpcServerException(
RpcErrorCodeProto.FATAL_DESERIALIZING_REQUEST, err);
}
...省略...
//封裝為一個Call物件
Call call = new Call(header.getCallId(), header.getRetryCount(),
rpcRequest, this, ProtoUtil.convert(header.getRpcKind()),
header.getClientId().toByteArray(), traceSpan);
callQueue.put(call); // queue the call; maybe blocked here
incRpcCount(); // Increment the rpc count
}- Handler 這個是處理請求的執行緒類,Server可以同時存在多個Handler執行緒,它們並行的從共享佇列callqueue中讀取Call物件,然後執行對應的呼叫函式之後,即將應答結果通過reponse.doRespond()返回給客戶端。 下面是Handler執行緒執行時的部分程式碼:
@Override
public void run() {
...
while (running) {
TraceScope traceScope = null;
try {
final Call call = callQueue.take(); // 從callqueue中取用於處理的Call物件
...
try {//執行對應的呼叫函式,涉及到了使用者許可權
if (call.connection.user == null) {
value = call(call.rpcKind, call.connection.protocolName, call.rpcRequest,
call.timestamp);
} else {
value =
call.connection.user.doAs
(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Writable>() {
@Override
public Writable run() throws Exception {
// make the call
return call(call.rpcKind, call.connection.protocolName,
call.rpcRequest, call.timestamp);
}
}
);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
...
}
CurCall.set(null);
synchronized (call.connection.responseQueue) {
//封裝好應答資訊
setupResponse(buf, call, returnStatus, detailedErr,
value, errorClass, error);
...
//向responsequeue中增加資料,同時檢視responsequeue長度是否為1,如果為1的話則直接向客戶端傳送應答。
responder.doRespond(call);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
...
}
LOG.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": exiting");
}- Responder 負責將應答返回給客戶端。Responder建立時會開啟一個writeSeletor用於監聽channel中的SelectionKey.OP_WRITE事件。當Responder執行緒執行時,會相應的執行doRunLoop()->doAsyncWrite()->processResponse()方法來執行寫的操作。
private void doAsyncWrite(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
Call call = (Call)key.attachment();
if (call == null) {
return;
}
if (key.channel() != call.connection.channel) {
throw new IOException("doAsyncWrite: bad channel");
}
synchronized(call.connection.responseQueue) {
if (processResponse(call.connection.responseQueue, false)) {
try {
key.interestOps(0);
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
LOG.warn("Exception while changing ops : " + e);
}
}
}
}
private boolean processResponse(LinkedList<Call> responseQueue,
boolean inHandler) throws IOException {
boolean error = true;
boolean done = false; // there is more data for this channel.
int numElements = 0;
Call call = null;
try {
synchronized (responseQueue) {
//如果responsequeue已經處理完
numElements = responseQueue.size();
if (numElements == 0) {
error = false;
return true; // no more data for this channel.
}
call = responseQueue.removeFirst();
SocketChannel channel = call.connection.channel;
//儘量向通道寫入資料
int numBytes = channelWrite(channel, call.rpcResponse);
if (numBytes < 0) {
return true;
}
if (!call.rpcResponse.hasRemaining()) {
call.rpcResponse = null;
call.connection.decRpcCount();
if (numElements == 1) { // last call fully processes.
done = true; // no more data for this channel.
} else {
done = false; // more calls pending to be sent.
}
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": responding to " + call
+ " Wrote " + numBytes + " bytes.");
}
} else {
//如果由於特殊原因(資料量過大或者網路波動),那麼重新將Call放入responsequeue中,由Responder處理
// If we were unable to write the entire response out, then
// insert in Selector queue.
//
call.connection.responseQueue.addFirst(call);
if (inHandler) {
// set the serve time when the response has to be sent later
call.timestamp = Time.now();
incPending();
try {
writeSelector.wakeup();
channel.register(writeSelector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE, call);
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
done = true;
} finally {
decPending();
}
}
}
error = false; // everything went off well
}
} finally {
if (error && call != null) {
LOG.warn(Thread.currentThread().getName()+", call " + call + ": output error");
done = true; // error. no more data for this channel.
closeConnection(call.connection);
}
}
return done;
} 從原始碼可以看到,當Handler沒能將結果一次性返回給客戶端時,會想writeSelector註冊SelectionKey.OP_WRITE事件,進而有Responder採用非同步方式處理髮送這個結果。這樣的好處是在處理一些大的請求任務時也相容處理一些小的任務。下面展示了Server各個元件的處理流程:
Hadoop RPC的使用
這裡介紹一下Hadoop RPC的使用。
- 首先定義一個RPC協議,這個自定義的協議必須繼承VersionedProtocol。
/**
* 自定義的protocol協議
*/
public interface MyProtocol extends VersionedProtocol{
public static final long versionID = 1L ;
public String echo() throws IOException;
}- 實現自定義的協議 。
public class MyProtocolImpl implements MyProtocol {
@Override
public long getProtocolVersion(String protocol, long clientVersion) throws IOException {
return MyProtocol.versionID;
}
@Override
public ProtocolSignature getProtocolSignature(String protocol, long clientVersion,
int clientMethodsHash)
throws IOException {
return new ProtocolSignature(MyProtocol.versionID, null);
}
@Override
public String echo() throws IOException {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance() ;
Date date = cal.getTime() ;
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd-hh-mm-ss") ;
return sdf.format(date) ;
}
}- 使用RPC中的Builder構建一個Server 。
public class Server {
public Server() throws HadoopIllegalArgumentException, IOException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration() ;
org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RPC.Server server = new RPC.Builder(conf).
setProtocol(MyProtocol.class).setInstance(new MyProtocolImpl()).
setBindAddress("localhost").setPort(9000).setNumHandlers(5).build() ;
server.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws HadoopIllegalArgumentException, IOException {
new Server() ;
}
}- 構建Client 。
public class Client {
public Client() throws IOException {
InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9000) ;
MyProtocol proxy = RPC.getProxy(MyProtocol.class, MyProtocol.versionID, addr,
new Configuration()) ;
proxy.echo() ;
}
public static void main(String args...){
new Client() ;
}
}在不同的程序中分別啟動Server和Client,即可看到輸出.
Yarn RPC
Yarn RPC是Hadoop Yarn將原有的序列化部分分隔開,將具體的RPC實現交給RpcEngine介面。如WritableRpcEngine和ProtobufRpcEngine分別採用的是hadoop自帶的序列化框架和protobuf序列化框架實現的RPC。
Yarn提供一個對外的抽象類YarnRPC,具體由YarnRPC中的create(conf)方法實現,由引數yarn.ipc.rpc.class決定,預設值是HadoopYarnProtoRPC。
public static final String IPC_RPC_IMPL =
IPC_PREFIX + "rpc.class";
public static final String DEFAULT_IPC_RPC_IMPL =
"org.apache.hadoop.yarn.ipc.HadoopYarnProtoRPC";
...省略...
String clazzName = conf.get(YarnConfiguration.IPC_RPC_IMPL);
if (clazzName == null) {
clazzName = YarnConfiguration.DEFAULT_IPC_RPC_IMPL;
}
try {
return (YarnRPC) Class.forName(clazzName).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new YarnRuntimeException(e);
}HadoopYarnProtoRPC提供了getProxy()和getServer()方法來生成客戶端和服務端。其中都是通過RPC工廠提供器RpcFactoryProvider來生成RpcClientFactory和RpcServerFactory。當然預設的客戶端和服務端都是採用protobuf來序列化的,如RpcClientFactoryPBImpl和RpcServerFactoryPBImpl。
public Object getProxy(Class protocol, InetSocketAddress addr,
Configuration conf) {
return RpcFactoryProvider.getClientFactory(conf).getClient(protocol, 1,
addr, conf);
}
public Server getServer(Class protocol, Object instance,
InetSocketAddress addr, Configuration conf,
SecretManager<? extends TokenIdentifier> secretManager,
int numHandlers, String portRangeConfig) {
return RpcFactoryProvider.getServerFactory(conf).getServer(protocol,
instance, addr, conf, secretManager, numHandlers, portRangeConfig);
}其中RpcClientFactoryPBImpl這個客戶端的工廠類會掃描包中路徑impl.pb.client.*PBClientImpl的類,然後通過java的反射來生成類的例項。如client和ResourceManager之間通訊的客戶端協議ApplicationClientProtocolPBClientImpl類。其中生成客戶端的程式碼為:
public ApplicationClientProtocolPBClientImpl(long clientVersion,
InetSocketAddress addr, Configuration conf) throws IOException {
RPC.setProtocolEngine(conf, ApplicationClientProtocolPB.class,
ProtobufRpcEngine.class);
proxy = RPC.getProxy(ApplicationClientProtocolPB.class, clientVersion, addr, conf);
}還是採用了RPC.getProxy方法建立客戶端。
同理,RpcServerFactoryPBImpl這個服務端的工廠類會掃描包路徑下的impl.pb.service.*PBServiceImpl類,通過反射生成類的例項。如ResourceTrackerPBServiceImpl。然後獲取該例項對應的協議類,呼叫createServer方法生成Server。
private Server createServer(Class<?> pbProtocol, InetSocketAddress addr, Configuration conf,
SecretManager<? extends TokenIdentifier> secretManager, int numHandlers,
BlockingService blockingService, String portRangeConfig) throws IOException {
RPC.setProtocolEngine(conf, pbProtocol, ProtobufRpcEngine.class);
RPC.Server server = new RPC.Builder(conf).setProtocol(pbProtocol)
.setInstance(blockingService).setBindAddress(addr.getHostName())
.setPort(addr.getPort()).setNumHandlers(numHandlers).setVerbose(false)
.setSecretManager(secretManager).setPortRangeConfig(portRangeConfig)
.build();
LOG.info("Adding protocol "+pbProtocol.getCanonicalName()+" to the server");
server.addProtocol(RPC.RpcKind.RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER, pbProtocol, blockingService);
return server;
}也是採用了RPC.Builder.build()方法建立server。