java併發程式設計條件佇列的喚醒機制探究
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-11
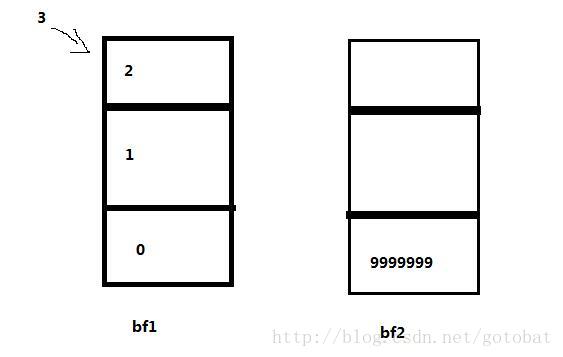
bf1,bf2是兩個大小各為3的條件佇列。3將要put進bf1,此時因為bf1已滿而已呼叫wait()方法掛起執行緒,此時若對bf2()執行take()方法並呼叫notifyall()是否會喚醒wait()中的bf1?(對兩個佇列的操作存在於兩個不同的執行緒中)
先上程式碼
public abstract class BaseBoundedBuffer<V>{
private final V[] buf;
private int tail;
private int head;
private int count;
protected
public class BoundedBuffer<V> extends BaseBoundedBuffer {
private
public class BufferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BoundedBuffer bf =new BoundedBuffer(3,1);
BoundedBuffer bf2=new BoundedBuffer(3,2);
bf2.put(9999999);
new Thread(){
public void run(){
for (int i=0;i<4;i++){
try {
bf.put(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
new Thread(){
public void run(){
try {
System.out.println( bf2.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();
}
}
執行結果如下
2put9999999
1put0
1put1
1put2
1快睡了------put
9999999在執行結果第五行的時候便是上圖所描述的情況(3想要put進bf1,但是因為已經full,bf1進入wait()狀態),第六行輸出了9999999,也就說明bf2執行了take()操作,同時也執行了notifyAll()方法,然而對bf1沒有產生任何影響。
V v= (V) doTake();
notifyAll();
return v;
結果證明: 在使用條件佇列時候,notifyAll()只會喚醒同一物件因執行wait()被掛起的執行緒
