《學習OpenCV》第七章直方圖(練習7.2)
給定三幅在書中討論的不同光照條件下的手影象,利用cvCalcHist()來獲得室內拍照的手的色膚直方圖
分別給定2維、8維、16維、32維、256維進行運算
#include <iostream> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui.hpp> using namespace std; using namespace cv; #define cvQueryHistValue_1D( hist, idx0 ) cvGetReal1D( (hist)->bins, (idx0) ) #define cvQueryHistValue_2D( hist, idx0 , idx1 ) cvGetReal2D( (hist)->bins, (idx0) , (idx1)) #define binNum 2 // 每一位幅bin的大小 /*畫直方圖*/ void DisplayHistogram(CvHistogram * hist , char * windName) { if(!hist || !windName) { return; } int scale = 100; //縮放比例 int h_bins = hist->mat.dim[0].size; int s_bins = hist->mat.dim[1].size; IplImage * histImg = cvCreateImage(cvSize(h_bins * scale , s_bins * scale), 8, 3); cvSetZero(histImg); //顯示直方圖 float max_value = 0; float bin_value = 0; int intensity = 0; cvGetMinMaxHistValue(hist, 0, &max_value,0,0); for(int i = 0;i<h_bins;i++) { for(int j = 0;j<s_bins;j++) { bin_value = cvQueryHistValue_2D( hist, i, j); intensity = cvRound(bin_value * 255 / max_value); cvRectangle(histImg, cvPoint(i*scale, j*scale), cvPoint((i+1)*scale-1, (j+1)*scale-1), CV_RGB(intensity, intensity, intensity),CV_FILLED); } } cvNamedWindow(windName); cvShowImage(windName, histImg); } int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { /*1、載入圖片*/ const char filename1[] = "/Users/linwang/Downloads/hand1.jpg"; const char filename2[] = "/Users/linwang/Downloads/hand2.jpg"; const char filename3[] = "/Users/linwang/Downloads/hand3.jpg"; IplImage * Img_hand1 = cvLoadImage(filename1); IplImage * Img_hand2 = cvLoadImage(filename2); IplImage * Img_hand3 = cvLoadImage(filename3); /*2、縮放0.3倍*/ float scale = 0.3; IplImage * dst_hand1 = cvCreateImage(cvSize(Img_hand1->width * scale, Img_hand1->height * scale), Img_hand1->depth, Img_hand1->nChannels); IplImage * dst_hand2 = cvCreateImage(cvSize(Img_hand2->width * scale, Img_hand2->height * scale), Img_hand2->depth, Img_hand2->nChannels); IplImage * dst_hand3 = cvCreateImage(cvSize(Img_hand3->width * scale, Img_hand3->height * scale), Img_hand3->depth, Img_hand3->nChannels); cvResize(Img_hand1, dst_hand1); cvResize(Img_hand2, dst_hand2); cvResize(Img_hand3, dst_hand3); /*3、顯示當前的圖片*/ cvNamedWindow("Hand1"); cvNamedWindow("Hand2"); cvNamedWindow("Hand3"); cvShowImage("Hand1", dst_hand1); cvShowImage("Hand2", dst_hand2); cvShowImage("Hand3", dst_hand3); /*4、分別建立三幅手勢影象的HSV空間影象單元*/ IplImage * Hsv_hand1 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand1), 8, 3); IplImage * Hsv_hand2 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand2), 8, 3); IplImage * Hsv_hand3 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand3), 8, 3); cvSetZero(Hsv_hand1); cvSetZero(Hsv_hand2); cvSetZero(Hsv_hand3); /*5、顏色閾轉換,從GRB到HSV*/ cvCvtColor(dst_hand1, Hsv_hand1, CV_RGB2HSV); cvCvtColor(dst_hand2, Hsv_hand2, CV_RGB2HSV); cvCvtColor(dst_hand3, Hsv_hand3, CV_RGB2HSV); /*6、分別建立hsv的三通道*/ IplImage * h_plane1 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand1), 8, 1); IplImage * h_plane2 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand2), 8, 1); IplImage * h_plane3 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand3), 8, 1); IplImage * s_plane1 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand1), 8, 1); IplImage * s_plane2 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand2), 8, 1); IplImage * s_plane3 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand3), 8, 1); IplImage * v_plane1 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand1), 8, 1); IplImage * v_plane2 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand2), 8, 1); IplImage * v_plane3 = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst_hand3), 8, 1); cvSplit(Hsv_hand1, h_plane1, s_plane1, v_plane1, 0); cvSplit(Hsv_hand2, h_plane2, s_plane2, v_plane2, 0); cvSplit(Hsv_hand3, h_plane3, s_plane3, v_plane3, 0); /*7、準備床架吧直方圖hist*/ IplImage * planes1[] = {h_plane1,s_plane1}; IplImage * planes2[] = {h_plane2,s_plane2}; IplImage * planes3[] = {h_plane3,s_plane3}; int h_bins1 = binNum; int h_bins2 = binNum; int h_bins3 = binNum; int s_bins1 = binNum; int s_bins2 = binNum; int s_bins3 = binNum; CvHistogram * hist1; CvHistogram * hist2; CvHistogram * hist3; int hist_size1[] = {h_bins1,s_bins1}; int hist_size2[] = {h_bins2,s_bins2}; int hist_size3[] = {h_bins3,s_bins3}; float h_ranges1[] = {0,180}; float h_ranges2[] = {0,180}; float h_ranges3[] = {0,180}; float s_ranges1[] = {0,255}; float s_ranges2[] = {0,255}; float s_ranges3[] = {0,255}; float * ranges1[] = {h_ranges1,s_ranges1}; float * ranges2[] = {h_ranges2,s_ranges2}; float * ranges3[] = {h_ranges3,s_ranges3}; hist1 = cvCreateHist(2, hist_size1, CV_HIST_ARRAY,ranges1,1); hist2 = cvCreateHist(2, hist_size2, CV_HIST_ARRAY,ranges2,1); hist3 = cvCreateHist(2, hist_size3, CV_HIST_ARRAY,ranges3,1); /*8、計算直方圖並做歸一化*/ cvCalcHist(planes1, hist1 , 0 ,0); cvCalcHist(planes2, hist2 , 0 ,0); cvCalcHist(planes3, hist3 , 0 ,0); cvNormalizeHist(hist1, 1.0); cvNormalizeHist(hist2, 1.0); cvNormalizeHist(hist3, 1.0); /*9、顯示各種直方圖的對比結果*/ cout<<"Bins = "<<binNum<<endl; double dist1_to_2[4] = {0.0}; double dist1_to_3[4] = {0.0}; double dist2_to_3[4] = {0.0}; char *hist_method[4] = {"相關","卡方","直方圖相交","Bhattacharyya距離"}; //依次進行"相關","卡方","直方圖相交","Bhattacharyya距離" 比較操作,並顯示結果 for(int i = 0;i<4;i++) { dist1_to_2[i] = cvCompareHist(hist1, hist2, i); cout<<"Method : "<<hist_method[i]<<"->影象1和影象2的匹配結果-> "<<dist1_to_2[i]<<endl; } for(int i = 0;i<4;i++) { dist1_to_3[i] = cvCompareHist(hist1, hist3, i); cout<<"Method : "<<hist_method[i]<<"->影象1和影象3的匹配結果-> "<<dist1_to_3[i]<<endl; } for(int i = 0;i<4;i++) { dist2_to_3[i] = cvCompareHist(hist2, hist3, i); cout<<"Method : "<<hist_method[i]<<"->影象2和影象3的匹配結果-> "<<dist2_to_3[i]<<endl; } /*10、利用直方圖顯示各種匹配結果*/ cout<<hist1->mat.dim[0].size<<endl; cout<<hist1->mat.dim[1].size<<endl; DisplayHistogram(hist1, "hist1"); DisplayHistogram(hist2, "hist2"); DisplayHistogram(hist3, "hist3"); cvWaitKey(0); cvReleaseHist(&hist1); cvReleaseHist(&hist2); cvReleaseHist(&hist3); cvDestroyWindow("Hand1"); cvDestroyWindow("Hand2"); cvDestroyWindow("Hand3"); cvReleaseImage(&Img_hand1); cvReleaseImage(&Img_hand2); cvReleaseImage(&Img_hand3); cvReleaseImage(&dst_hand1); cvReleaseImage(&dst_hand2); cvReleaseImage(&dst_hand3); cvReleaseImage(&Hsv_hand1); cvReleaseImage(&Hsv_hand2); cvReleaseImage(&Hsv_hand3); cvReleaseImage(&h_plane1); cvReleaseImage(&h_plane2); cvReleaseImage(&h_plane3); cvReleaseImage(&s_plane1); cvReleaseImage(&s_plane2); cvReleaseImage(&s_plane3); cvReleaseImage(&v_plane1); cvReleaseImage(&v_plane2); cvReleaseImage(&v_plane3); return 1; }

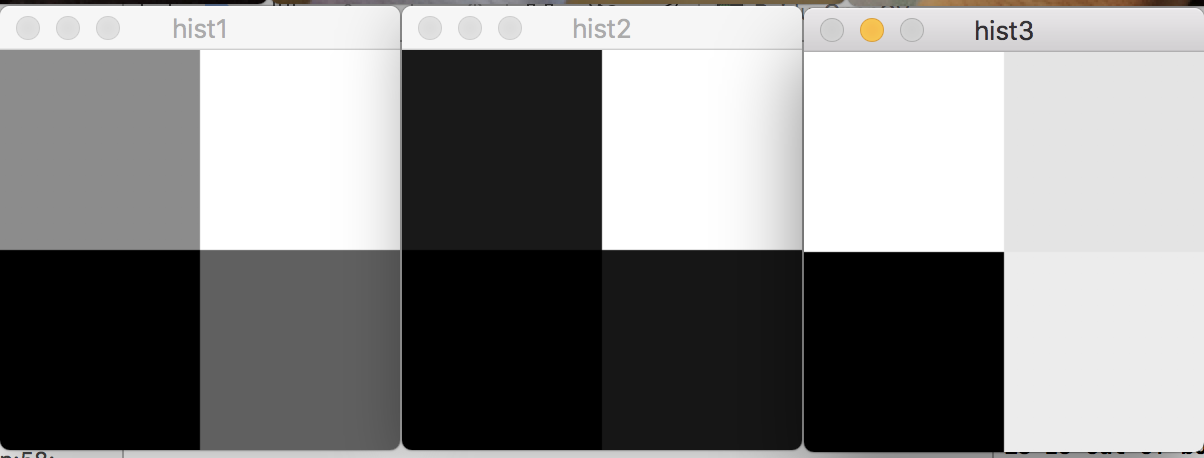
2維
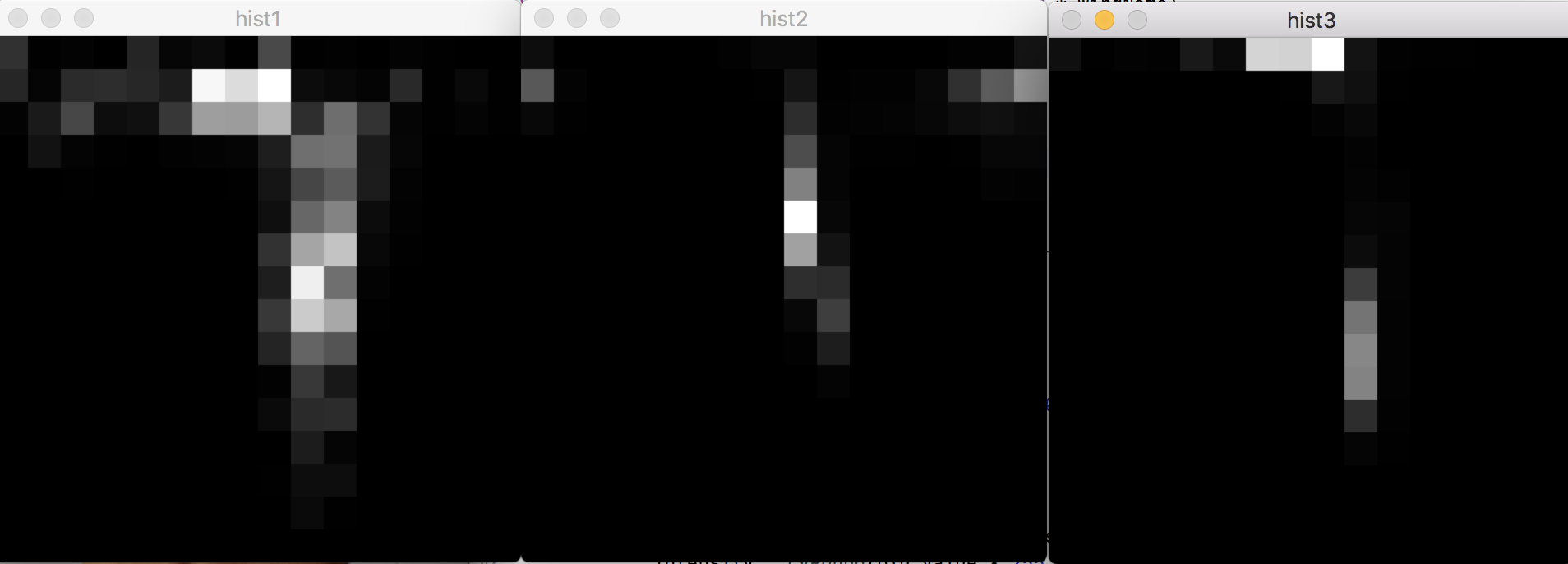
8維
16維
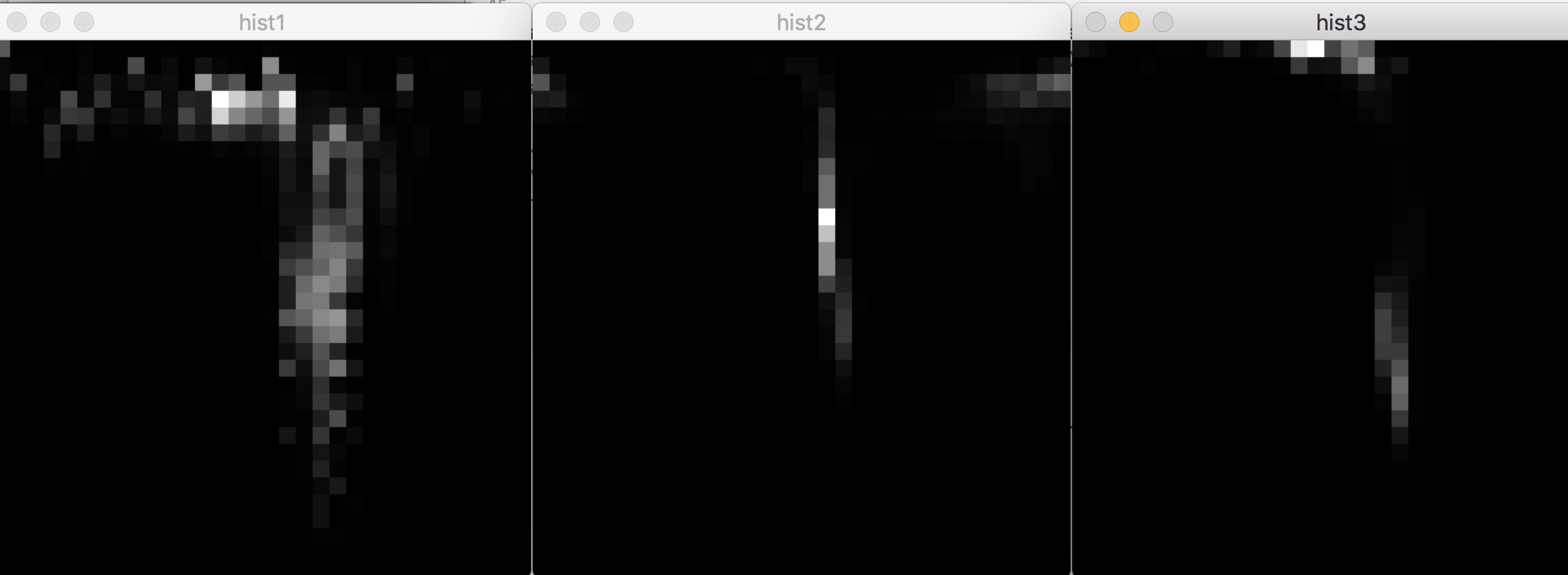
32維:
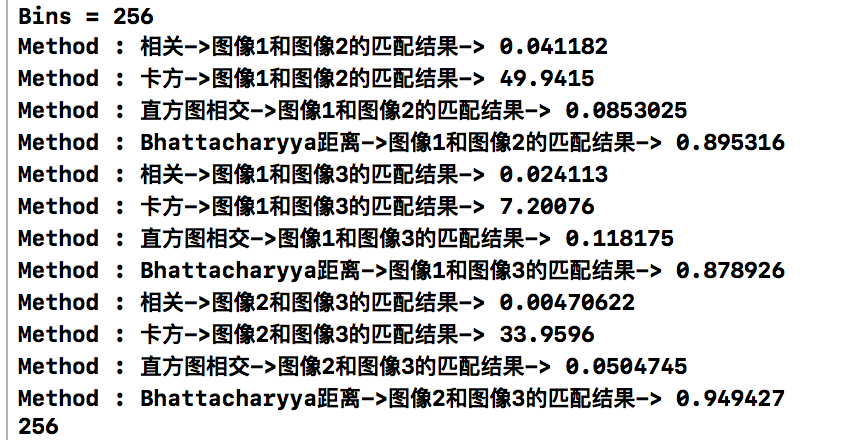
256維
相關推薦
《學習OpenCV》第七章直方圖(練習7.2)
給定三幅在書中討論的不同光照條件下的手影象,利用cvCalcHist()來獲得室內拍照的手的色膚直方圖 分別給定2維、8維、16維、32維、256維進行運算 #include <iostream> #include <opencv2/opencv.hp
吳恩達機器學習(第七章)---邏輯迴歸
一、邏輯迴歸 邏輯迴歸通俗的理解就是,對已知類別的資料進行學習之後,對新得到的資料判斷其是屬於哪一類的。 eg:對垃圾郵件和非垃圾郵件進行分類,腫瘤是惡性還是良性等等。 1.為什麼要用邏輯迴歸: 對於腫瘤的例子: 在外面不考慮最右邊的樣本的時候我們擬合的線性迴歸
《機器學習》 周志華學習筆記第七章 貝葉斯分類器(課後習題)python 實現
課後習題答案 1.試用極大似然法估算西瓜集3.0中前3個屬性的類條件概率。 好瓜有8個,壞瓜有9個 屬性色澤,根蒂,敲聲,因為是離散屬性,根據公式(7.17) P(色澤=青綠|好瓜=是) = 3/8 P(色澤=烏黑|好瓜=是) = 4/8 P(色澤=淺白|好瓜=是) =
《機器學習西瓜書》學習筆記——第七章_貝葉斯分類器_樸素貝葉斯分類器
樸素:特徵條件獨立;貝葉斯:基於貝葉斯定理。 樸素貝葉斯是經典的機器學習演算法之一,也基於概率論的分類演算法,屬於監督學習的生成模型。樸素貝葉斯原理簡單,也很容易實現,多用於文字分類,比如垃圾郵件過濾。 1.演算法思想——基於概率的預測 貝葉斯決策論是概率框架下
C++primer plus 第七章程式設計練習
本人用code::block 編寫,如需參考,善用Ctrl+shift+C 和 Ctrl + shift + X 快捷鍵 如有任何錯誤或疑問,歡迎留言 #include <iostream> using namespace std; double p
C++ Primer Plus第六版 第七章 程式設計練習答案
/******************************************************************************************************************* Author : Yuuji Blo
ACCPHTMLS1第七章上機練習1
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html
《csharp高階程式設計》 學習筆記 第七章 委託和事件
第七章 委託和事件 回撥(callback)函式是windows程式設計的一個重要部分。 回撥函式實際上是方法呼叫的指標,也稱為函式指標,是一個非常強大的程式設計特性。 .NET以委託的形式實現了函式指標的概念。 但特殊在於,與c函式指標不同,.NET委託是型別安全的。 7
c++ primer 第五版學習筆記-第七章 類
本文為轉載,出處:https://blog.csdn.net/libin1105/article/details/48664019 https://blog.csdn.net/sunhero2010/article
HTML第七章上機練習2
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html
HTML第七章上機練習1
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html
《metasploit滲透測試魔鬼訓練營》學習筆記第七章--社會工程學
五.社工工程學 5.1社會工程系框架 5.1.1資訊蒐集 maltego是一個高度自動化的資訊蒐集工具,整合在BT5中,如果國內網路環境使用時無法獲取結果,可能是無法與資訊提供網站建立連線,可以使用VPN
深度學習入門|第七章 卷積神經網絡(三)
soft 有序字典 layer .py 復雜 高效 fin predict cal 前言 本文為學習《深度學習入門》一書的學習筆記,詳情請閱讀原著 五、CNN的實現 搭建進行手寫數字識別的 CNN。這裏要實現如圖 7-23 所示的 CNN。 圖 7-23 簡單
《資料結構與演算法分析》學習筆記-第七章-排序
[toc] *** ## 插入排序 - 插入排序由N-1趟==排序組成==,對於P=1趟到P=N-1趟,插入排序保證從位置0到位置P上的元素為已排序狀態 - 基本有序或者規模較小時十分高效 ``` void InsertSort(int inputArray[], int arrayNum) { int
高等數學:第七章 空間解析幾何(2)數量積 向量積 混合積 曲面及其方程
§7.4 數量積 向量積 混合積 一 兩向量的數量積 1 向量的數量積定義 設物體在常力的作用下沿直線從點移到點,用表示位移向量,力在位移方向上的分力大小為,力所作的功為: 拋開這一問題的物理背景,我們可以給出一般地向量的數量積定義: 設 是兩向量,且它們之間的夾角為
第七章快速排序之“快速插入排序”(練習7.4-5)
O(∩_∩)O~,這個名字乍聽起來比較黃。其實就是先快速排序進行劃分,等劃分小到一定規模比如k時,進行插入排序,因為規模小到一定程度,插入排序的效率更高。我在前面還寫過一個合併插入排序的演算法,思想跟這個相似。 總的時間複雜度為O(nk+nlg(n/k)),這個很好證明:
Python核心程式設計 第七章 練習7–5
7–5. userpw2.py. 下面的問題和例題7.1 中管理名字-密碼的鍵值對資料的程式有關。 (a)修改那個指令碼,使它能記錄使用者上次的登入日期和時間(用time 模組),並與使用者密碼一起 儲存起來。程式的介面有要求使用者輸入使用者名稱和密碼的提示
c primer plus(五版)編程練習-第七章編程練習
兩個感嘆號 nal getchar putc 進制 類型 運算 pre 重做 1.編寫一個程序。該程序讀取輸入直到遇到#字符,然後報告讀取的空格數目、讀取的換行符數目以及讀取的所有其他字符數目。 #include<stdio.h> #include<ct
構建之法第七章學習心得
思想 studio 開發 咨詢服務 生活 int bsp partner har 構建之法第七章學習心得 這周我學習了構建之法第七章MSF的介紹。MSF有9個基本原則,針對信息共享,團隊內部運營,市場,還有客戶。同樣是強調效率,人性,靈活,還有前景。 MSF對信息共享和溝通
算法入門經典-第七章 例題7-1 除法
abcde 輸入 表達式 c++ 技術分享 pan nbsp turn cnblogs 除法輸入正整數n,按從小到大的順序輸出所有形如abcde/fghij=n的表達式,其中a~j恰好為數字0~9的一個排列,2<=n<=79. 樣例輸入: 62 樣例輸出