使用STM32CUBEMX生成FatFS程式碼,操作SPI FLASH
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-12
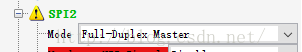
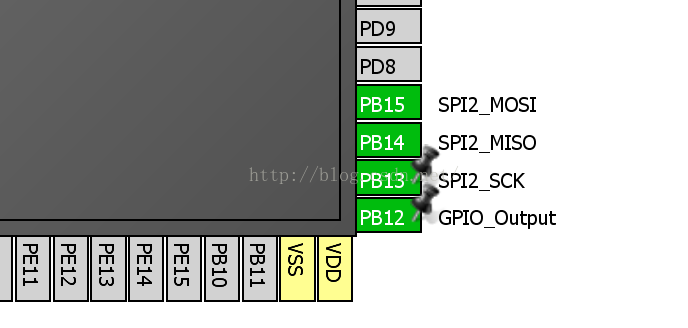
首先配置SPI,我的板子是SPI2連線到SPI FLASH 上,我的flash是W25Q64, PB12用來當CSN。
接下來配置FATFS,這裡選擇使用者定義的。
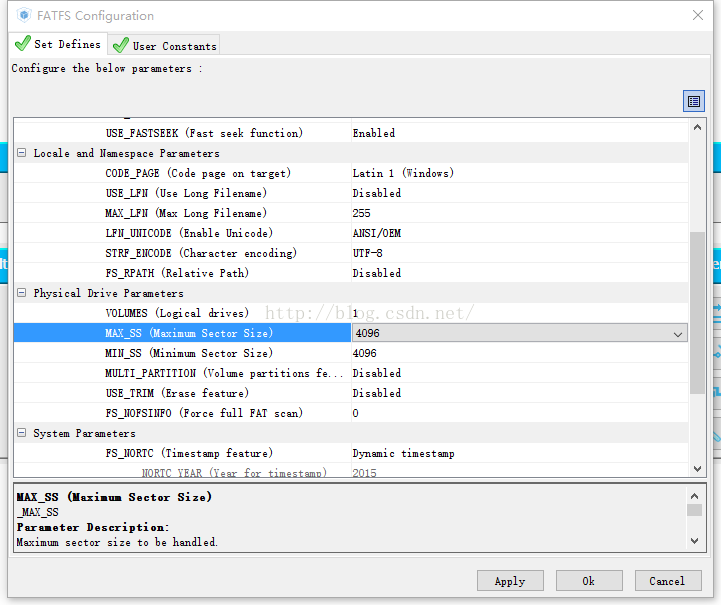
配置FATFS的時候要注意,由於SPI FLASH 的sector是4096位元組的,故需要設定sector的大小為4096,其餘選項根據自己情況配置。
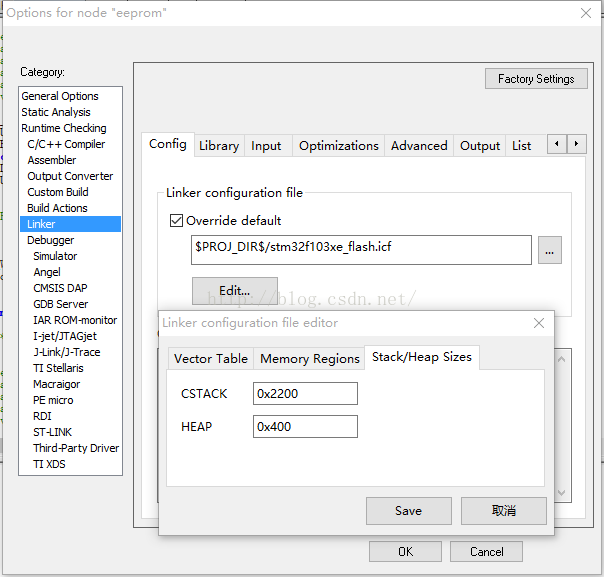
配置好了生成程式碼和工程。記得把堆疊尺寸調大一些。我用IAR這樣配置:
接著把SPI FLASH的讀寫操作實現:讀一個sector和寫一個sector。我寫好的函式叫做W25_WriteSector和W25_ReadSector. 然後定義好常量:
#define PAGE_SIZE 256
#define SECTOR_SIZE 4096
#define SECTOR_COUNT 200
#define BLOCK_SIZE 65536
#define FLASH_PAGES_PER_SECTOR SECTOR_SIZE/PAGE_SIZE下一步開啟user_diskio.c 檔案,填充幾個函式。
/** * @brief Reads Sector(s) * @param pdrv: Physical drive number (0..) * @param *buff: Data buffer to store read data * @param sector: Sector address (LBA) * @param count: Number of sectors to read (1..128) * @retval DRESULT: Operation result */ DRESULT USER_read ( BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */ BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */ DWORD sector, /* Sector address in LBA */ UINT count /* Number of sectors to read */ ) { /* USER CODE HERE */ UINT i = 0; for(i = 0; i < count; i ++) { W25_ReadSector(sector, buff); sector ++; buff += SECTOR_SIZE; } return RES_OK; }
/** * @brief Writes Sector(s) * @param pdrv: Physical drive number (0..) * @param *buff: Data to be written * @param sector: Sector address (LBA) * @param count: Number of sectors to write (1..128) * @retval DRESULT: Operation result */ #if _USE_WRITE == 1 DRESULT USER_write ( BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */ const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */ DWORD sector, /* Sector address in LBA */ UINT count /* Number of sectors to write */ ) { /* USER CODE HERE */ UINT i = 0; for(i = 0; i < count; i ++) { W25_WriteSector(sector, buff); sector ++; buff += SECTOR_SIZE; } return RES_OK; } #endif /* _USE_WRITE == 1 */
/**
* @brief I/O control operation
* @param pdrv: Physical drive number (0..)
* @param cmd: Control code
* @param *buff: Buffer to send/receive control data
* @retval DRESULT: Operation result
*/
#if _USE_IOCTL == 1
DRESULT USER_ioctl (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE cmd, /* Control code */
void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
DRESULT res = RES_OK;
switch(cmd)
{
case CTRL_SYNC :
break;
case CTRL_TRIM:
break;
case GET_BLOCK_SIZE:
*(DWORD*)buff = BLOCK_SIZE;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_SIZE:
*(DWORD*)buff = SECTOR_SIZE;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_COUNT:
*(DWORD*)buff = SECTOR_COUNT;
break;
default:
res = RES_PARERR;
break;
}
return res;
}
#endif /* _USE_IOCTL == 1 */這些函式填充好,就可以用FATFS了。對於一個新的SPI FLASH,先掛載f_mount,再格式化檔案系統f_mkfs,之後就可以做各種新建檔案、讀寫操作了。
補充一個,在fatfs.c 檔案中,定義了這樣一個:
char USER_Path[4]; /* USER logical drive path */之後我們可以在main或者其他檔案裡用extern宣告它,mount和mkfs時的USER_Path都是它。
附上我的測試程式碼
void mount_disk(void)
{
uint8_t res = f_mount(&fs, USER_Path, 0);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("FAILED: %d\n",res);
return;
}
printf("MOUNT OK\n");
}
void format_disk(void)
{
uint8_t res = 0;
printf("PROCESSING...\n");
res = f_mkfs(USER_Path, 1, 4096);
if (res == FR_OK)
{
printf("OK!\n");
}
else
{
printf("failed with: %d\n",res);
}
}
void create_file(void)
{
FIL file;
FIL *pf = &file;
uint8_t res;
res = f_open(pf, "0:/test.txt", FA_OPEN_ALWAYS | FA_WRITE);
if (res == FR_OK)
{
printf("creat ok\n");
}
else
{
printf("creat failed\n");
printf("error code: %d\n",res);
}
f_printf(pf, "hello fatfs!\n");
res = f_close(pf);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("close file error\n");
printf("error code: %d\n",res);
}
}
void get_disk_info(void)
{
FATFS fs;
FATFS *fls = &fs;
FRESULT res;
DWORD fre_clust;
res = f_getfree("/",&fre_clust,&fls); /* Get Number of Free Clusters */
if (res == FR_OK)
{
/* Print free space in unit of MB (assuming 4096 bytes/sector) */
printf("%d KB Total Drive Space.\n"
"%d KB Available Space.\n",
((fls->n_fatent-2)*fls->csize)*4,(fre_clust*fls->csize)*4);
}
else
{
printf("get disk info error\n");
printf("error code: %d\n",res);
}
}
void read_file(void)
{
FIL file;
FRESULT res;
UINT bw;
uint8_t rbuf[100] = {0};
res = f_open(&file, "0:/test.txt", FA_READ);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("open error: %d\n",res);
return;
}
f_read(&file, rbuf, 20, &bw);
printf("%s\n", rbuf);
res = f_close(&file);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
printf("close file error\n");
printf("error code: %d\n",res);
}
}