Spring原始碼學習之IOC容器實現原理(一)-DefaultListableBeanFactory
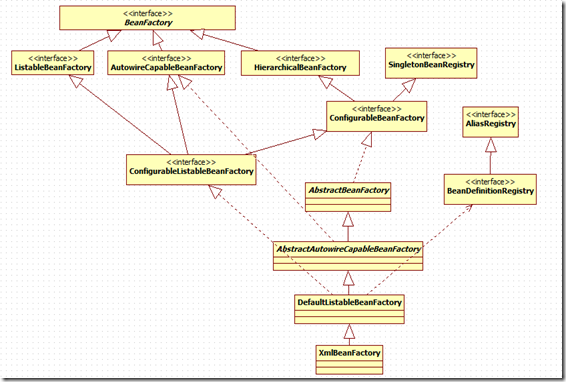
從這個繼承體系結構圖來看,我們可以發現DefaultListableBeanFactory是第一個非抽象類,非介面類。實際IOC容器。所以這篇部落格以DefaultListableBeanFactoryIOC容器為基準進行IOC原理解析。
一.兩個重要介面
前面已經分析了BeanFactor,它的三個直接子類介面,接下來我們繼續分析兩個重要的介面,可以看到這兩個介面也是集大成者。
首先是ConfigurableBeanFactor
1.ConfigurableBeanFactory
從名字可以看到,這是一個可以配置的介面,但是究竟在配置什麼呢?
(1)介面定義
public interface ConfigurableBeanFactory extends HierarchicalBeanFactory, SingletonBeanRegistry
可以看到繼承了HierarchicalBeanFactory和SingletonBeanRegistry兩個介面。
表明實現這個介面的類都是可以分層,支援單例的IOC容器。
(2)java doc
/** * Configuration interface to be implemented by most bean factories. Provides * facilities to configure a bean factory, in addition to the bean factory * client methods in the {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory} * interface. * * <p>This bean factory interface is not meant to be used in normal application * code: Stick to {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory} or * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory} for typical * needs. This extended interface is just meant to allow for framework-internal * plug'n'play and for special access to bean factory configuration methods. */
1.這個介面被大量實現,配置了可以配置容器的方法。
2.這個介面不是常用介面,依賴於BeanFactory和ListableBeanFactory介面,只是屬於框架的一部分。
(3) 原始碼
public interface ConfigurableBeanFactory extends HierarchicalBeanFactory, SingletonBeanRegistry { String SCOPE_SINGLETON = "singleton"; String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = "prototype"; /** * Set the parent of this bean factory. * <p>Note that the parent cannot be changed: It should only be set outside * a constructor if it isn't available at the time of factory instantiation. */ //可以設定父工廠,但是值得注意的是,只能設定一次,不能改變 void setParentBeanFactory(BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws IllegalStateException; /** * Set the class loader to use for loading bean classes. * Default is the thread context class loader. * <p>Note that this class loader will only apply to bean definitions * that do not carry a resolved bean class yet. This is the case as of * Spring 2.0 by default: Bean definitions only carry bean class names, * to be resolved once the factory processes the bean definition. * @param beanClassLoader the class loader to use, * or {@code null} to suggest the default class loader */ //配置ClassLoader,只是應用於Bean definition void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader beanClassLoader); /** * Return this factory's class loader for loading bean classes. */ ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader(); void setTempClassLoader(ClassLoader tempClassLoader); ClassLoader getTempClassLoader(); /** * Set whether to cache bean metadata such as given bean definitions * (in merged fashion) and resolved bean classes. Default is on. * <p>Turn this flag off to enable hot-refreshing of bean definition objects * and in particular bean classes. If this flag is off, any creation of a bean * instance will re-query the bean class loader for newly resolved classes. */ /// 設定、是否快取元資料,如果false,那麼每次請求例項,都會從類載入器重新載入(熱載入),這裡還不太懂 void setCacheBeanMetadata(boolean cacheBeanMetadata); /** * Return whether to cache bean metadata such as given bean definitions * (in merged fashion) and resolved bean classes. */ boolean isCacheBeanMetadata(); //表示式支援,配置表示式支援器 void setBeanExpressionResolver(BeanExpressionResolver resolver); BeanExpressionResolver getBeanExpressionResolver(); //配置conversionService??轉換服務? void setConversionService(ConversionService conversionService); ConversionService getConversionService(); //配置屬性編輯器 void addPropertyEditorRegistrar(PropertyEditorRegistrar registrar); void registerCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType, Class<? extends PropertyEditor> propertyEditorClass); void copyRegisteredEditorsTo(PropertyEditorRegistry registry); //配置型別轉換器?TypeCoverter void setTypeConverter(TypeConverter typeConverter); TypeConverter getTypeConverter(); //字串處理器? void addEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver valueResolver); //處理字串 String resolveEmbeddedValue(String value); /** * Add a new BeanPostProcessor that will get applied to beans created * by this factory. To be invoked during factory configuration. * <p>Note: Post-processors submitted here will be applied in the order of * registration; any ordering semantics expressed through implementing the * {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered} interface will be ignored. Note * that autodetected post-processors (e.g. as beans in an ApplicationContext) * will always be applied after programmatically registered ones. * @param beanPostProcessor the post-processor to register */ //新增後處理器 void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor); /** * Return the current number of registered BeanPostProcessors, if any. */ int getBeanPostProcessorCount(); void registerScope(String scopeName, Scope scope); String[] getRegisteredScopeNames(); Scope getRegisteredScope(String scopeName); AccessControlContext getAccessControlContext(); void copyConfigurationFrom(ConfigurableBeanFactory otherFactory); //註冊別名依賴關係 void registerAlias(String beanName, String alias) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; void resolveAliases(StringValueResolver valueResolver); BeanDefinition getMergedBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /** * Determine whether the bean with the given name is a FactoryBean. boolean isFactoryBean(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; void setCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName, boolean inCreation); boolean isCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName); //註冊依賴Bean void registerDependentBean(String beanName, String dependentBeanName); String[] getDependentBeans(String beanName); String[] getDependenciesForBean(String beanName); void destroyBean(String beanName, Object beanInstance); void destroyScopedBean(String beanName); void destroySingletons(); }
好吧,好一個可配置,嚇尿了有點。總的來說,還是在配置一些IOC容器,沒有超出IOC容器。
總結一下,我現階段能看懂的部分:
1.首先是兩個作用領域物件,判斷是否為singleton,單例還是Prototype,原型。應用於方法registerScope。這兩個有啥區別??
1。 當一個bean的作用域設定為singleton, 那麼Spring IOC容器中只會存在一個共享的bean例項,並且所有對bean的請求,只要id與該bean定義相匹配,則只會返回bean的同一例項。換言之,當把一個bean定義設定為singleton作用域時,Spring IOC容器只會建立該bean定義的唯一例項。這個單一例項會被儲存到單例快取(singleton cache)中,並且所有針對該bean的後續請求和引用都將返回被快取的物件例項,這裡要注意的是singleton作用域和GOF設計模式中的單例是完全不同的,單例設計模式表示一個ClassLoader中只有一個class存在,而這裡的singleton則表示一個容器對應一個bean,也就是說當一個bean被標識為singleton時候,spring的IOC容器中只會存在一個該bean。
2。 prototype作用域部署的bean,每一次請求(將其注入到另一個bean中,或者以程式的方式呼叫容器的getBean()方法)都會產生一個新的bean例項,相當與一個new的操作,對於prototype作用域的bean,有一點非常重要,那就是Spring不能對一個prototype bean的整個生命週期負責,容器在初始化、配置、裝飾或者是裝配完一個prototype例項後,將它交給客戶端,隨後就對該prototype例項不聞不問了。不管何種作用域,容器都會呼叫所有物件的初始化生命週期回撥方法,而對prototype而言,任何配置好的析構生命週期回撥方法都將不會被呼叫。清除prototype作用域的物件並釋放任何prototype bean所持有的昂貴資源,都是客戶端程式碼的職責。(讓Spring容器釋放被singleton作用域bean佔用資源的一種可行方式是,通過使用bean的後置處理器,該處理器持有要被清除的bean的引用。)
2.第二個就是setParentBeanFactory,這個方法後面會被大量使用。對應於getParentBeanFactory。
3.還有一些處理器的配置,重點關注後處理器配置,addBeanPostProcessor以及ClassLoader配置,setBeanClassLoader。
2.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
(1)介面定義
public interface ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
extends ListableBeanFactory, AutowireCapableBeanFactory, ConfigurableBeanFactory
從這裡就可以看出,ConfigurableListableBeanFactory繼承了上面提到的所有介面,所以它是最後的大Boss。真正的集大成者IOC容器介面,而不再是小兒科了。
(2)java doc
/** * Configuration interface to be implemented by most listable bean factories. * In addition to {@link ConfigurableBeanFactory}, it provides facilities to * analyze and modify bean definitions, and to pre-instantiate singletons. * * <p>This subinterface of {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory} * is not meant to be used in normal application code: Stick to * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory} or * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory} for typical * use cases. This interface is just meant to allow for framework-internal * plug'n'play even when needing access to bean factory configuration methods. */
1.對ConfigurableBeanFactory介面的擴充,提供了分析和調整Bean definition的方法。
2.依然不是常用介面?什麼叫常用介面呢。並不是在實際程式設計應用過程中常使用的介面程式碼。這裡的意思可能是我們向上轉型建立BeanFactor時,沒必要指定一個例項為該介面。可以是BeanFactory或者是ListableBeanFactory。
(3)原始碼
public interface ConfigurableListableBeanFactory extends ListableBeanFactory, AutowireCapableBeanFactory, ConfigurableBeanFactory { /** * Ignore the given dependency type for autowiring: * for example, String. Default is none. * @param type the dependency type to ignore */ //忽略自動裝配的依賴型別 void ignoreDependencyType(Class<?> type); /** * Ignore the given dependency interface for autowiring. * <p>This will typically be used by application contexts to register * dependencies that are resolved in other ways, like BeanFactory through * BeanFactoryAware or ApplicationContext through ApplicationContextAware. * <p>By default, only the BeanFactoryAware interface is ignored. * For further types to ignore, invoke this method for each type. * @param ifc the dependency interface to ignore * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware * @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware */ //忽略自動裝配的依賴介面 void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc); /** * Register a special dependency type with corresponding autowired value. * <p>This is intended for factory/context references that are supposed * to be autowirable but are not defined as beans in the factory: * e.g. a dependency of type ApplicationContext resolved to the * ApplicationContext instance that the bean is living in. * <p>Note: There are no such default types registered in a plain BeanFactory, * not even for the BeanFactory interface itself. */ //註冊一個特殊的依賴型別 //用來解決FactorBean引用來註冊在容器中 void registerResolvableDependency(Class<?> dependencyType, Object autowiredValue); /** * Determine whether the specified bean qualifies as an autowire candidate, * to be injected into other beans which declare a dependency of matching type. * <p>This method checks ancestor factories as well. * @param beanName the name of the bean to check * @param descriptor the descriptor of the dependency to resolve * @return whether the bean should be considered as autowire candidate * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name */ //決定這個Bean是否應該被其他Bean自動裝配。 boolean isAutowireCandidate(String beanName, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /** * Return the registered BeanDefinition for the specified bean, allowing access * to its property values and constructor argument value (which can be * modified during bean factory post-processing). * <p>A returned BeanDefinition object should not be a copy but the original * definition object as registered in the factory. This means that it should * be castable to a more specific implementation type, if necessary. * <p><b>NOTE:</b> This method does <i>not</i> consider ancestor factories. * It is only meant for accessing local bean definitions of this factory. * @param beanName the name of the bean * @return the registered BeanDefinition * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name * defined in this factory */ //返回對應Bean的BeanDefinition BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /** * Return a unified view over all bean names managed by this factory. * <p>Includes bean definition names as well as names of manually registered * singleton instances, with bean definition names consistently coming first, * analogous to how type/annotation specific retrieval of bean names works. * @return the composite iterator for the bean names view * @since 4.1.2 * @see #containsBeanDefinition * @see #registerSingleton * @see #getBeanNamesForType * @see #getBeanNamesForAnnotation */ //返回一個Bean名稱的迭代器 Iterator<String> getBeanNamesIterator(); /** * Freeze all bean definitions, signalling that the registered bean definitions * will not be modified or post-processed any further. * <p>This allows the factory to aggressively cache bean definition metadata. */ //鎖定Bean配置,不在改變 void freezeConfiguration(); /** * Return whether this factory's bean definitions are frozen, * i.e. are not supposed to be modified or post-processed any further. * @return {@code true} if the factory's configuration is considered frozen */ boolean isConfigurationFrozen(); /** * Ensure that all non-lazy-init singletons are instantiated, also considering * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean FactoryBeans}. * Typically invoked at the end of factory setup, if desired. * @throws BeansException if one of the singleton beans could not be created. * Note: This may have left the factory with some beans already initialized! * Call {@link #destroySingletons()} for full cleanup in this case. * @see #destroySingletons() */ //初始化所有的單例。 void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException; }
值得注意的方法就是可以根據Bean的名稱返回BeanDefinition,以及可以可以與初始化所有單例。還有就是返回Bean Name的迭代器。
二. DefaultListableBeanFactory
1. 定義
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory implements
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable
只繼承了一個抽象類,同時把集大成的介面ConfigurableListableBeanFactory給實現了,同時還有BeanDefinitionRegistry介面,從名字上看就知道是BeanDefinition的註冊介面。
2.Java doc
/** * Default implementation of the * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory} and * {@link BeanDefinitionRegistry} interfaces: a full-fledged bean factory * based on bean definition objects. *//一個完整的,成熟的IOC容器 * <p>Typical usage is registering all bean definitions first (possibly read * from a bean definition file), before accessing beans. Bean definition lookup * is therefore an inexpensive operation in a local bean definition table, * operating on pre-built bean definition metadata objects. *//主要作為註冊Bean definition * <p>Can be used as a standalone bean factory, or as a superclass for custom * bean factories. Note that readers for specific bean definition formats are * typically implemented separately rather than as bean factory subclasses: * see for example {@link PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader} and * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader}. * * <p>For an alternative implementation of the * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory} interface, * have a look at {@link StaticListableBeanFactory}, which manages existing * bean instances rather than creating new ones based on bean definitions. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller//注意這兩個作者 */
它是真正第一個可以獨立的IOC容器,而且後面的ApplicationContext據說也是依據它來建立。在訪問bean前,先註冊所有的definition(可能從bean definition配置檔案中)。使用預先建立的bean定義元資料物件,從本地的bean definition表中查詢bean definition因而將不會花費太多成本。這個類的直接子類只有XMLBeanFactory,二者的唯一區別就是後者集成了處理XML形式BeanDefinition的方法。
三.IOC容器實現原理
這次先不關注原始碼,先首先看看它的用法,例子參考<Spring 技術內幕>
ClassPathResource res=new ClassPathResource("beans.xml"); DefaultListableBeanFactory factory=new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader=new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory); reader.loadBeanDefinitions(res); Performer performer=(Performer) factory.getBean("dancer"); performer.perform();
簡單解釋一下:
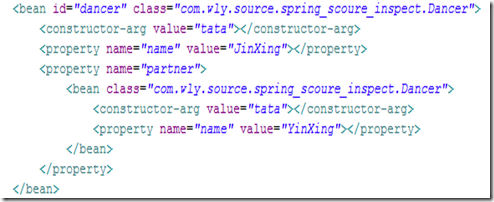
1.我們在beans.xml中定義了一個Bean,id為“dancer”,實現了Performer介面。參考自<Spring in action>例子.
2.利用Resource抽象實現類,來包裝這個包含了BeanDefinition的定義資訊。
3.建立一個BeanFactory,DefaultListableBeanFactory
4.建立一個載入BeanDefinition的讀取器,通過回撥配置給BeanFactory.
5. 從定義好好的Resource中,讀取配置資訊。由XmlBeanDefinitionReader完成解析,完成整個載入和註冊Bean定義的過程。
6. 通過BeanFactory的getBean()方法,獲取對應的Bean。這裡涉及到了Bean的例項化以及依賴注入
其實這也是XmlBeanFactory的實現形式,可以參考其實現原始碼
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory { private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this); /** * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given resource, * which must be parsable using DOM. * @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from * @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException { this(resource, null); } /** * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given input stream, * which must be parsable using DOM. * @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from * @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory * @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException { super(parentBeanFactory); this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); } }
beans.xml的定義如下所示:
簡單解釋一下例子,Dancer類共有三個屬性,一個是danceStyle,一個是name,這兩個都是String型別的,另一個是partner,是Dancer型別,所以這裡採用了內部類的形式。Dancer類繼承了Performer介面,實現了介面的perform方法。
*******************單步除錯分析****************
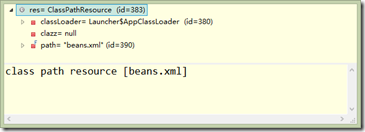
1.ClassPathResource res=new ClassPathResource("beans.xml");
可見Resource 是對Resource檔案的定位過程。提供了兩個屬性,一個是ClassLoader,另一個是path路徑。是對輸入流的一個包裝。
2.DefaultListableBeanFactory factory=new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
接下來單步執行看一下IOC容器建立的過程。
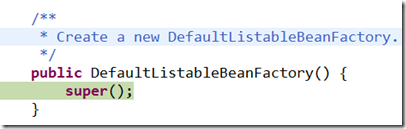
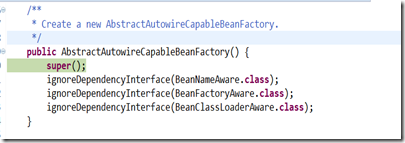
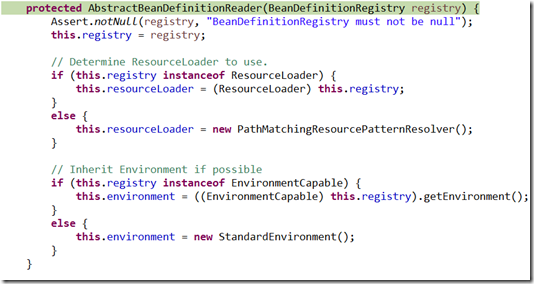
(1) 可見DefaultListableBeanFactory,只是呼叫父類構造器
(2)父類是AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory抽象容器
額,繼續上調預設構造器,同時會呼叫IgnoreDependencyInterface方法,檢視一下這個方法,引數為Class型別。
/** * Ignore the given dependency interface for autowiring. * <p>This will typically be used by application contexts to register * dependencies that are resolved in other ways, like BeanFactory through * BeanFactoryAware or ApplicationContext through ApplicationContextAware. * <p>By default, only the BeanFactoryAware interface is ignored. * For further types to ignore, invoke this method for each type. * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware * @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware */ public void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc) { this.ignoredDependencyInterfaces.add(ifc); }
這個方法主要是需要自動裝配時,忽略的介面型別,ignoredDependencyInterfaces是Set型別的,private final Set<Class<?>> ignoredDependencyInterfaces = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
所以在自動裝配的時候,會自動忽略BeanNameAware.class,BeanFactoryAware.class,BeanClassLoaderAware.class介面型別的類。
(3)父類構造器AbstractBeanFactory,由圖可知這是最頂層的抽象IOC容器
空構造器
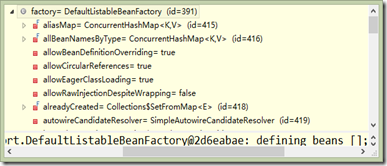
(4)最後看看DefaultListableBeanFactory
其實這裡可以發現採用大量的集合變數來儲存一些涉及到的資料,所以看起來沒有那麼唬人。
3.XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader=new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
接下來看看回調的過程
(1)
可見DefaultListableBeanFactory實現了BeanDefinitionRegistry型別的介面。
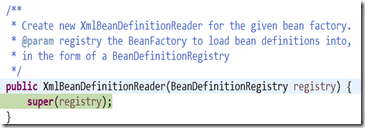
(2)呼叫父類AbstractBeanDefinitionReader,帶有引數的構造器
為什麼registry(也就是上面的factory)可能是ResourceLoader呢?其實這裡是為ApplicationContext埋下了伏筆。
這個構造器主要乾了三件事,一個是將registry繫結到factory,另外兩個就是初始化ResourceLoader和environment(還不瞭解是幹嘛的)。
4.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(res);
好吧,終於到了激動人心的載入BeanDefinition過程。
(1)loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource)方法
應用裝飾器模式,包裝Resource。
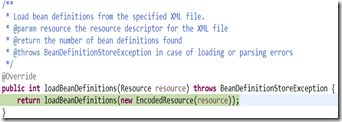
(2)然後是呼叫的過載方法loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource)
/** * Load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file, * allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource()); } //resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded是ThreadLocal型別的,裡面儲存的是Set型別。為了保證執行緒安全。 Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) { currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4); this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); }
//將encodeResource,資源放入存放資源的Set中 if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); } try {
//轉換為輸入流 InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); try {
//包裝成InputSource型別的資源 InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); } //最終呼叫doLoadBeanDefinitions方法。
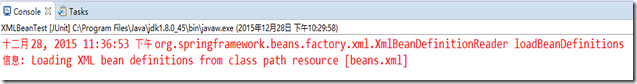
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); } finally { inputStream.close(); } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); } finally { currentResources.remove(encodedResource); if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); } } }所以,每次看到的輸出的載入xml bean definitions的log資訊,就是來自這個方法。所以在loadBeanDefinition過程中,首先輸出的資訊來自這裡。
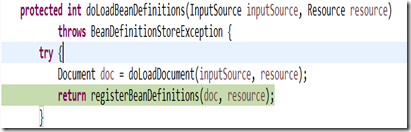
(3) doLoadBeanDefinitions
而這個方法其實會呼叫doLoadDocument()方法獲得Document,即W3C中說的document,即HTML文件或者XML文件等。得到的document物件並沒有按照Spring規則解析。
而通過registerBeanDefinitions,啟動對BeanDefinition的詳細解析過程,這個解析過程涉及到了Spring的配置規則。
(4)registerBeanDefinitions,註冊Bean,通過這個方法Spring會按照Bean語義要求進行解析,並轉化為容器內部的資料結構(BeanDefinition),這個過程是在registerBeanDefinitions中進行的。而這個函式屬於XMLBeanDefinitionReader。
/** * Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document. * Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}. * <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes * {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it. * @param doc the DOM document * @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information) * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors * @see #loadBeanDefinitions * @see #setDocumentReaderClass * @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions */ @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); documentReader.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()); int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; }
最終會呼叫BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的物件documentReader的registerBeanDefinitions方法,按照Spring的Bean定義規則進行解析,同時這裡可以發現這裡返回的是此次註冊的Bean的個數。documentReader是預設設定好的DefaultBeanDefinitionReader。
(5)documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions()
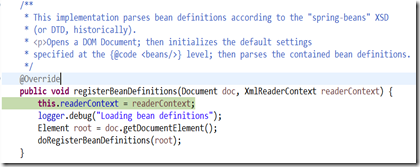
可以看到log資訊,開始”Loading bean definitions”,呼叫doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root)方法
(6)doRegisterBeanDefinitions()方法
/** * Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element. */ protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { // Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In // order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly, // keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create // the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes, // then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference. // this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one. BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { return; } } } preProcessXml(root); parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent; }
好吧,還沒到頭,要注意這裡有一個註釋“
/**
* Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element.
*/
”可以看出是從<beans>作為root節點進行解析。
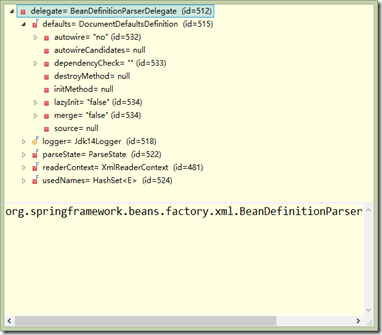
可以看到有一個delegate物件,屬於BeanDefinitionParserDelegate型別,而這個類的定義如下:
/**
* Stateful delegate class used to parse XML bean definitions.
* Intended for use by both the main parser and any extension
* {@link BeanDefinitionParser BeanDefinitionParsers} or
* {@link BeanDefinitionDecorator BeanDefinitionDecorators}.
可以看到這個類的作用主要是有狀態的解析XML BeanDefinition的代理。
同時,由於每個bean可能存在層次關係,而引發遞迴呼叫,為了維護網路層次關係,採用parent屬性保留其parent Bean.接下來看一下預設的delegate屬性長什麼樣子?
可以重點看一下defaults的屬性,如autowire是no,lazyInit=false。
parseBeanDefintions()將是解析BeanDefinition的最終方法?
(7)parseBeanDefinitions
/** * Parse the elements at the root level in the document: * "import", "alias", "bean". * @param root the DOM root element of the document */ protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } }
該方法屬於DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader,即前面得到的documentReader,是處理BeanDefinition的地方,具體的委託處理交給了BeanDefinitionParseDelegate來完成。
當子node是Element型別時,將觸發parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate),繼續解析,-》-》
(8)parseDefaultElement
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {