Spring(五)依賴注入原理及多種資料型別的裝配
基本型別物件注入
package test.spring.dao;
public interface PersonDao {
public abstract void add();
}package test.spring.dao.impl; import test.spring.dao.PersonDao; public class PersonDaoBean implements PersonDao { @Override public void add(){ System.out.println("執行PersonDaoBean裡的test1()方法"); } }
package test.spring.service; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; public interface PersonService { public abstract void save(); public Set<String> getSet(); public List<String> getList(); public Properties getProperties(); public Map<String, String> getMap(); }
package test.spring.service.impl; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; import test.spring.dao.PersonDao; import test.spring.entity.Property; import test.spring.service.PersonService; public class PersonServiceBean2 implements PersonService { private PersonDao personDao; private String name; private Integer num; private Set<String> set = new HashSet<String>(); private List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); private Properties properties = new Properties(); private Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); public Map<String, String> getMap() { return map; } public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) { this.map = map; } public Properties getProperties() { return properties; } public void setProperties(Properties properties) { this.properties = properties; } public List<String> getList() { return list; } public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } public Set<String> getSet() { return set; } public void setSet(Set<String> set) { this.set = set; } public Integer getNum() { return num; } public void setNum(Integer num) { this.num = num; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public PersonDao getPersonDao() { return personDao; } public void setPersonDao(PersonDao personDao) { this.personDao = personDao; } @Override public void save() { personDao.add(); System.out.println(name); System.out.println(num); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<!-- 這時候這個bean就可以由spring幫我們建立和維護,用到時只需從spring容器中獲取 -->
<!--
<bean id="personService" class="test.spring.service.impl.PersonServiceBean"
lazy-init="false" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
</bean>
-->
<!--
<bean id="personService2" class="test.spring.service.impl.PersonServiceBeanFactory"
factory-method="createPersonServiceBean"></bean> <bean id="personServiceFactory"
class="test.spring.service.impl.PersonServiceBeanFactory">
</bean>
<bean id="personService3"
factory-bean="personServiceFactory" factory-method="createPersonServiceBean2">
</bean>
-->
<!-- 基本型別物件注入 -->
<!--
<bean id="personDao" class="test.spring.dao.impl.PersonDaoBean"></bean>
<bean id="personService" class="test.spring.service.impl.PersonServiceBean2">
-->
<!-- name是service中對於的屬性名,ref是對於的bean -->
<!--
<property name="personDao" ref="personDao"></property> </bean>
-->
<!-- 使用內部bean,但該bean不能被其他bean使用 -->
<bean id="personDao" class="test.spring.dao.impl.PersonDaoBean" />
<bean id="personService" class="test.spring.service.impl.PersonServiceBean2">
<!-- name是service中對於的屬性名,ref是對於的bean -->
<property name="personDao" ref="personDao" />
<!-- 為基本資料型別注入值 -->
<property name="name" value="LinDL" />
<property name="num" value="2015" />
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>ONE</value>
<value>TWO</value>
<value>THREE</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>第一個list元素</value>
<value>第二個list元素</value>
<value>第三個list元素</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="key1">value1</prop>
<prop key="key2">value2</prop>
<prop key="key3">value3</prop>
</props>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="map-key1" value="map-value-1" />
<entry key="map-key2" value="map-value-2" />
<entry key="map-key3" value="map-value-3" />
</map>
</property>
</bean>
</beans> package test.spring.jnit;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import test.spring.service.PersonService;
public class SpringTest2 {
@Test
public void test() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"beans.xml");
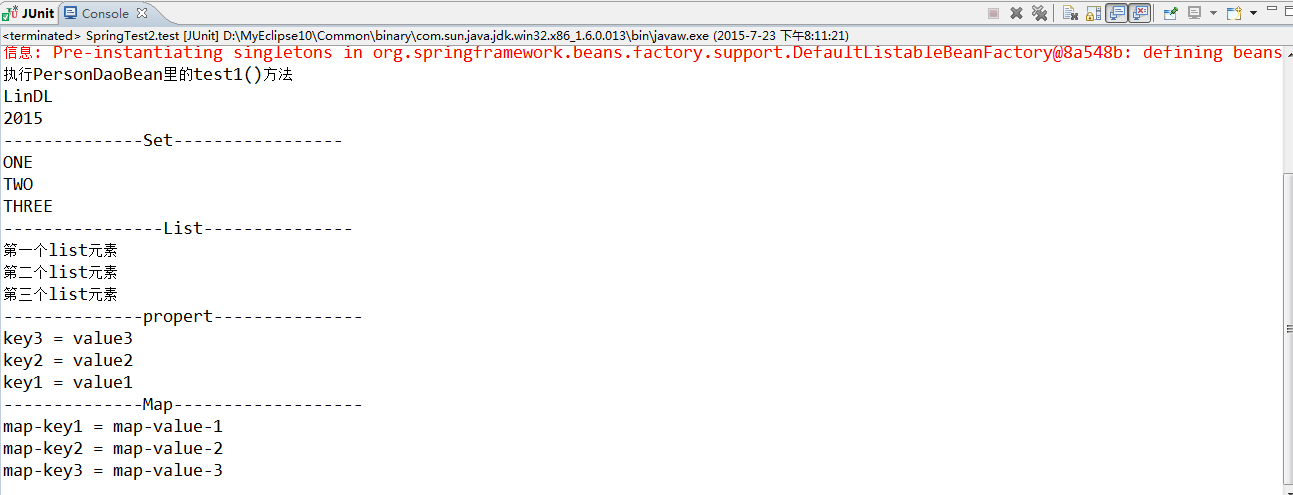
PersonService personService=(PersonService) applicationContext.getBean("personService");
personService.save();
System.out.println("--------------Set-----------------");
for(String str:personService.getSet()){
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("----------------List---------------");
for(String str:personService.getList()){
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("--------------propert---------------");
for(Object key:personService.getProperties().keySet()){
System.out.println(key+" = "+personService.getProperties().getProperty((String) key));
}
System.out.println("--------------Map-------------------");
for(String key:personService.getMap().keySet()){
System.out.println(key+" = "+personService.getMap().get(key));
}
// InjectTest injectTest=new InjectTest("beans.xml");
// PersonService personService=(PersonService) injectTest.getBean("personService");
// personService.save();
}
}
編碼剖析依賴注入原理
package test.spring.entity;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Bean2 {
private String id;
private String classPath;
private List<Property> properties=new ArrayList<Property>();
public Bean2(String id, String classPath) {
this.id = id;
this.classPath = classPath;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getClassPath() {
return classPath;
}
public void setClassPath(String classPath) {
this.classPath = classPath;
}
public List<Property> getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(List<Property> properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
}
package test.spring.entity;
public class Property {
private String name;
private String ref;
private String value;
public Property(String name, String ref, String value) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.ref = ref;
this.value = value;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getRef() {
return ref;
}
public void setRef(String ref) {
this.ref = ref;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
<pre name="code" class="java">package test.spring.jnit;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.ConvertUtils;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.XPath;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import org.springframework.asm.commons.Method;
import test.spring.entity.Bean;
import test.spring.entity.Bean2;
import test.spring.entity.Property;
public class InjectTest {
private List<Bean2> beanDefines = new ArrayList<Bean2>();
private Map<String, Object> singletons = new HashMap<String, Object>();
public InjectTest(String filename){
this.readXML(filename);
this.instanceBeans();
this.injectObject();
}
/**
* 為bean物件的屬性注入值
*/
private void injectObject() {
for(Bean2 beanDefinition : beanDefines){
Object bean = singletons.get(beanDefinition.getId());
if(bean!=null){
try {
PropertyDescriptor[] ps = Introspector.getBeanInfo(bean.getClass()).getPropertyDescriptors();
for(Property propertyDefinition : beanDefinition.getProperties()){
for(PropertyDescriptor properdesc : ps){
if(propertyDefinition.getName().equals(properdesc.getName())){
java.lang.reflect.Method setter = properdesc.getWriteMethod();//獲取屬性的setter方法 ,private
if(setter!=null){
Object value = null;
if(propertyDefinition.getRef()!=null && !"".equals(propertyDefinition.getRef().trim())){
value = singletons.get(propertyDefinition.getRef());
}else{
value = ConvertUtils.convert(propertyDefinition.getValue(), properdesc.getPropertyType());
}
setter.setAccessible(true);
setter.invoke(bean, value);//把引用物件注入到屬性
}
break;
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* 完成bean的例項化
*/
private void instanceBeans() {
for(Bean2 beanDefinition : beanDefines){
try {
if(beanDefinition.getClassPath()!=null && !"".equals(beanDefinition.getClassPath().trim()))
singletons.put(beanDefinition.getId(), Class.forName(beanDefinition.getClassPath()).newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 讀取xml配置檔案
* @param filename
*/
private void readXML(String filename) {
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
Document document=null;
try{
URL xmlpath = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(filename);
document = saxReader.read(xmlpath);
Map<String,String> nsMap = new HashMap<String,String>();
nsMap.put("ns","http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans");//加入名稱空間
XPath xsub = document.createXPath("//ns:beans/ns:bean");//建立beans/bean查詢路徑
xsub.setNamespaceURIs(nsMap);//設定名稱空間
List<Element> beans = xsub.selectNodes(document);//獲取文件下所有bean節點
for(Element element: beans){
String id = element.attributeValue("id");//獲取id屬性值
String clazz = element.attributeValue("class"); //獲取class屬性值
Bean2 beanDefine = new Bean2(id, clazz);
XPath propertysub = element.createXPath("ns:property");
propertysub.setNamespaceURIs(nsMap);//設定名稱空間
List<Element> propertys = propertysub.selectNodes(element);
for(Element property : propertys){
String propertyName = property.attributeValue("name");
String propertyref = property.attributeValue("ref");
String propertyValue = property.attributeValue("value");
Property propertyDefinition = new Property(propertyName, propertyref, propertyValue);
beanDefine.getProperties().add(propertyDefinition);
}
beanDefines.add(beanDefine);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 獲取bean例項
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
public Object getBean(String beanName){
return this.singletons.get(beanName);
}
}相關推薦
Spring(五)依賴注入原理及多種資料型別的裝配
基本型別物件注入 package test.spring.dao; public interface PersonDao { public abstract void add(); }package test.spring.dao.impl; import te
依賴注入原理,作用,注入方式——Spring IOC/DI(二)
依賴注入原理,作用,注入方式 前言 上一章我們講到了IOC和DI概述: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34598667/article/details/83275560 這一章接上一章繼續講 依賴注入(Dependency Injection)是用於實現控制反
spring通過註解方式依賴注入原理 (私有成員屬性如何注入)
一、spring如何建立依賴的物件 用過spring的都知道我們在dao、service層加上@repository、@Service就能將這兩個物件交給spring管理,在下次使用的時候使用@resource 或者@Autowired 就可以拿到而不需要自己再去new了
Spring依賴注入,帶來的資料初始化問題
applicationContext.xml配置檔案1.舉個例子:<bean id="AService" class="com.backgroud.restful.AService"> </bean><context:component-scan
spring中依賴注入的方式及實現(2)
依賴注入的方式1、屬性注入2、構造器注入3、工廠方法注入(很少使用,不推薦)1、屬性注入(1)屬性注入即通過 setter 方法注入Bean 的屬性值或依賴的物件(2)屬性注入使用 <proper
在Spring中依賴注入的幾種方式實現鬆耦合
一、普通注入方式: (1)在IDEA工作空間內先建立lib包然後匯入Spring的架包(複製進去的架包要按住滑鼠右鍵出現Add as Library)。 (2)在已經建立好架包的基礎上在src目錄下建立XML檔案,檔案命為applicationContext.xml,需要注意的是我們建
Spring IOC 依賴注入( 二 )
目錄 1、什麼是IOC 2、什麼是DI 3、第一個IOC示例程式 -- 通過id獲取物件(重點) 1、建立一個Java工程:
sql注入原理及預防措施
SQL注入就是通過把SQL命令插入到Web表單提交或輸入域名或頁面請求的查詢字串,最終達到欺騙伺服器執行惡意的SQL命令。對於很多網站都有使用者提交表單的埠,提交的資料插入MySQL資料庫中,就有可能發生SQL注入安全問題,那麼,如何防止SQL注入呢? 針對SQL注入安全問題的預防,需時刻認定使
spring的依賴注入 -------基於註解方式
前言: 做了2年的軟體,剛開始入行的時候,沒有個目標基本上都是在摸索,技術看的我眼花繚亂,這個想學,那個也想學結果是對很多技術一知半解的,工作中才發現,我們要掌握的一門可以搞定快速開發搞定所有業務需求的技術, 所以現在我要對spring的東西達到一個深層次的掌握,儘量避免百度,在開發
spring 04-Spring框架依賴注入基本使用
Spring的依賴注入形式實際上所有物件產生控制都要通過applicationContext.xml檔案實現 依賴注入必須啟動容器後才可以進行該配置檔案的內部的載入操作 依賴注入之有參構造 定義一個Dept類 package cn.liang.vo; import
Spring IoC容器設計原理及高階特性
文章目錄 Spring IoC容器概述 IoC容器系列的設計與實現:BeanFactory和ApplicationContext BeanFactory BeanFactory容器的設計原理 Applicatio
spring中依賴注入方式總結
文章來源於今日頭條使用者:分散式系統架構 一、註解注入 註解注入在Spring中是用的最多的一種方式,就是在java程式碼中使用註解的方式進行裝配,在程式碼中加入@Resource或者@Autowired、 1、Autowired是自動注入,自動從spring的上下文找到合適的bean來
SSM(一):spring-ioc依賴注入筆記
一、java代理模式 java代理模式是ioc的前置知識。代理模式非常簡單,看程式碼就一目瞭然了。 public interface role { public void makeMoney(); } role public cla
Spring IOC 依賴注入( 二 )
目錄 圖解: 流程圖解: 圖解流程: 1、什麼是IOC IOC 全稱指的是 Inverse Of Control 控制反轉。 原
也談Spring之依賴注入DI/控制反轉IOC
首先提問, 什麼是 Spring IOC 容器? Spring 框架的核心是 Spring 容器。容器建立物件,將它們裝配在一起,配置它們並管理它們的完整生命週期。Spring 容器使用依賴注入來管理組成應用程式的元件。容器通過讀取提供的配置元資料來接收物件
Spring監聽器之ApplicationListener原理及原始碼解析及例項
一、原理及原始碼解析 事件:ContextRefreshedEvent、IOCTest_Ext$1[source=我釋出的事件]、ContextClosedEvent; * 1)、ContextRefreshedEvent事件: * 1)、容器建立物件:re
通俗易懂的spring的依賴注入(和控制反轉)的講解。
Spring 能有效地組織J2EE應用各層的物件。不管是控制層的Action物件,還是業務層的Service物件,還是持久層的DAO物件,都可在Spring的管理下有機地協調、執行。Spring將各層的物件以鬆耦合的方式組織在一起,Action物件無須關心Service物件的具體實現,Service
php laravel實現依賴注入原理(反射機制)
在使用laravel的時候,可以看到大量地使用了依賴注入。比如控制器中的HttpRequest物件,各種Model的實現類等等。這種實現方式的好處在於不需要再方法中頻繁地new某些例項,實現模組的解耦。 依賴注入使用PHP反射API實現 反射機制被多種語言使用,用來獲取類、例項物件、方法
【架構師之路】依賴注入原理---IoC框架
github上一篇比較貼切的舉例: https://github.com/android-cn/blog/tree/master/java/dependency-injection 1 IoC理論的背景 我們都知道,在採用面向物件方法設
Spring 的依賴注入應用代替工廠模式
介面 package FactoryExample; public interface Human { void eat(); void walk(); void show(); } 實現 實現一 package FactoryExample; public clas