人群中多看了一眼
資料結構設計
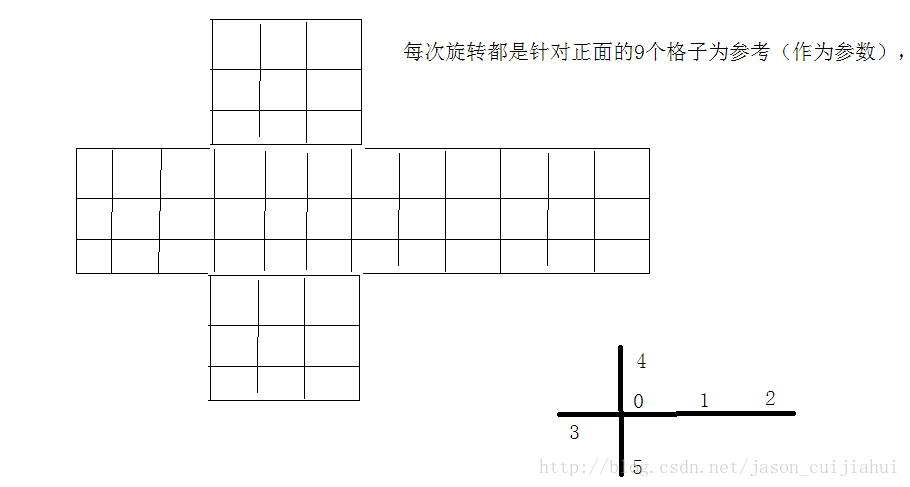
1.設計一個魔方(六面)的程式
思路:
把魔方從正面看展開成一個平面,如圖1所示。設計一個類,其中Spacexy[SPACE][LEN][LEN];中的SPACE為0~5表示六個面,每個數字代表哪一面見圖1.LEN為0~2,[LEN][LEN]表示某個面的3*3的9個格子。
類中的方法是根據展開的平面設計的,具體的某個面的某個格子由Spacexy[SPACE][LEN][LEN];定位。
注: [LEN][LEN] = [i][j] ;i, j按照矩陣的方式取
實現:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class 2.Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
題目:
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
For example, you may serialize the following tree
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5as “[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]”, just the same as how LeetCode OJ serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
實現:
// 我的版本比較蠢
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
};
string toString(const int& t) {
ostringstream oss;
oss<<t;
return oss.str();
}
int toInt(const string& str) {
istringstream iss(str);
int num;
iss >> num;
return num;
}
string serialize(Node *root) {
string result = "";
if(root==NULL) return "";
queue<Node*> record;
record.push(root);
while(!record.empty()) {
Node* e = record.front();
if(e==NULL)
result += "null,";
else {
result += toString(e->data)+",";
record.push(e->left);
record.push(e->right);
}
record.pop();
}
return result;
}
Node* CreateBinaryTree(vector<string> &a, int i, int n) {
if(i>n-1 || a[i]=="null") return NULL;
Node *p = new Node;
p->data = toInt(a[i]);
p->left = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+1, n);
p->right = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+2, n);
return p;
}
void SplitString(const string& s, vector<string>& v, const string& c)
{
string::size_type pos1, pos2;
pos2 = s.find(c);
pos1 = 0;
while(string::npos != pos2)
{
v.push_back(s.substr(pos1, pos2-pos1));
pos1 = pos2 + c.size();
pos2 = s.find(c, pos1);
}
if(pos1 != s.length())
v.push_back(s.substr(pos1));
}
Node* deserialize(string data) {
vector<string> sArr;
SplitString(data, sArr, ",");
Node* root = CreateBinaryTree(sArr, 0, sArr.size());
return root;
}
int main() {
Node *p1 = new Node;
p1->data = 1;
p1->left = NULL;
p1->right = NULL;
Node *p2 = new Node;
p2->data = 2;
p2->left = NULL;
p2->right = NULL;
p1->left = p2;
string sResult = serialize(p1);
cout<<serialize(p1)<<endl;
deserialize(sResult);
cout<<serialize(deserialize(serialize(p1)))<<endl;
return 0;
}// 別人的版本
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return "#";
return to_string(root->val)+","+serialize(root->left)+","+serialize(root->right);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
return mydeserialize(data);
}
TreeNode* mydeserialize(string& data) {
if (data[0]=='#') {
if(data.size() > 1) data = data.substr(2);
return nullptr;
} else {
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(helper(data));
node->left = mydeserialize(data);
node->right = mydeserialize(data);
return node;
}
}
private:
int helper(string& data) {
int pos = data.find(',');
int val = stoi(data.substr(0,pos));
data = data.substr(pos+1);
return val;
}
};大資料處理
1.多檔案頻率排序
題目:
有10個檔案,每個檔案1G,每個檔案的每一行存放的都是使用者的query,每個檔案的query都可能重複。要求按照query的頻度排序。
思路:
a) 方案1
1. 順序讀取10個檔案,按照hash(query)的結果將query寫入到另外10個檔案中。這樣新生成的檔案每個的大小大約也1G(假設hash函式是隨機的)。
2. 找一臺記憶體在2G左右的機器,依次對 用hash_map(query, query_count)來統計每個query出現的次數。利用快速/堆/歸併排序按照出現次數進行排序。將排序好的query和對應的query_cout輸出到檔案中。這樣得到了10個排好序的檔案。
3. 對 這10個檔案進行歸併排序(內排序與外排序相結合)。
b) 方案2:
一般query的總量是有限的,只是重複的次數比較多而已,可能對於所有的query,一次性就可以加入到記憶體了。這樣,我們就可以採用trie樹/hash_map等直接來統計每個query出現的次數,然後按出現次數做快速/堆/歸併排序就可以了。
c) 方案3:
與方案1類似,但在做完hash,分成多個檔案後,可以交給多個檔案來處理,採用分散式的架構來處理(比如MapReduce),最後再進行合併。
演算法
樹結構
二叉樹
1.二叉樹層次遍歷
題目:
輸入一顆二元樹,從上往下按層列印樹的每個結點,同一層中按照從左往右的順序列印。
8
/ \
6 10
/ \ / \
5 79 11輸出:
8 6 10 5 7 9 11
思路:
用佇列,出隊列印,並壓入左右兒子。
實現:
struct Node{
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
}
void levelPrint(Node* root){
if(root==NULL) return;
queue<Node*> record;
record.push(root);
while(!record.empty()){
cout<<record.front()->data<<' ';
if(record.front()->left!=NULL)
record.push(record.front()->left);
if(record.front()->right!=NULL)
record.push(record.front()->right);
record.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}2.映象二叉樹
題目:
請完成一個函式,輸入一個二叉樹,該函式輸出它的映象。
// 原二叉樹
8
/ \
6 10
/ \ / \
5 79 11
// 映象二叉樹
8
/ \
10 6
/ \ / \
11 97 5二叉樹結點的定義如下:
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
int data;
BinaryTreeNode *Left;
BinaryTreeNode *Right;
}; 思路:
遞迴思路:
把左子樹和右子樹變成映象子樹後,在把左右子樹的root相互交換。
迭代思路:
類似層次遍歷那種思路,不過用的是棧
實現:
// 遞迴實現
void Mirror(BinaryTreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL) return;
Mirror(root->Left);
Mirror(root->Right);
BinaryTreeNode *tmp = root->Left;
root->Left = root->Right;
root->Right = tmp;
}// 迭代實現
// 這種相當於先序遍歷映象樹
void Mirror(BinaryTreeNode *root){
stack<Node*> record;
if(root!=NULL)
record.push(root);
while(!record.empty()){
Node* tmproot = record.top();
record.pop();
if (tmproot->Left!=NULL)
record.push(tmproot->Left);
if (tmproot->Right!=NULL)
record.push(tmproot->Right);
Node* tmp = tmproot->Left;
tmproot->Left = tmproot->Right;
tmproot->Right = tmp;
}
}補充:
這個要寫個測試樣例。
3.求二叉樹中結點的最大距離
題目:
如果我們把二叉樹堪稱一個圖,父子結點之間的連線看成是雙向的。我們姑且定義“距離”為兩個結點之間的邊的個樹。求一棵二叉樹中相距最遠的兩個結點之間的邊的個樹。
思路:
可以用遞迴的思路去做,設父結點為F,左子樹為L,右子樹為R,則樹F相距最遠無非有這三種可能:
- 樹L相距最遠
- 樹R相距最遠
- 樹L到結點F的最長距離+1+樹R到結點F的最長距離
實現:
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
int data;
BinaryTreeNode *Left;
BinaryTreeNode *Right;
};
int TreeMaxLength(BinaryTreeNode *root, int &depth){
int ld, rd;
if(root==NULL){
depth = 0;
return 0;
}
lm = TreeMaxLength(root->Left, ld);
rm = TreeMaxLength(root->Right, rd);
depth = (ld>rd?ld:rd)+1;
// bridge是邊的條數而不是結點的個數
int bridge = ld+rd;
int tmp = lm>rm?lm:rm;
return (tmp>bridge?tmp:bridge);
}4.從陣列生成一棵二叉樹
實現:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
int val;
TreeNode(int x=0)
: val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
};
TreeNode* CreateBinaryTree(int a[], int i, int n){
// 陣列中的值-1代表結點null
if(i>n-1 || a[i]==-1) return NULL;
TreeNode *p = new TreeNode(a[i]);
p->left = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+1, n);
p->right = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+2, n);
return p;
}
void Destory(TreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL) return ;
Destory(root->left);
Destory(root->right);
delete root;
}
5.列印一棵二叉樹
實現:
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//using std::vector;
//using std::cout;
//using std::endl;
//using std::max;
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root);
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
int val;
TreeNode(int x=0)
: val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
};
static int MaxLevel(TreeNode *root)
{
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return max(MaxLevel(root->left), MaxLevel(root->right)) + 1;
}
// test whether all elements in vector are NULL
static bool IsAllElementsNULL(const vector<TreeNode*> &nodes)
{
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
while(it != nodes.end()){
if(*it) return false;
++it;
}
return true;
}
static void PrintWhiteSpaces(int num)
{
for(int i=0; i<num; ++i)
cout << " ";
}
void PrintNode(vector<TreeNode*> &nodes, int level, int max_level)
{
if(nodes.empty() || IsAllElementsNULL(nodes)) return; // exit
int floor = max_level - level;
int endge_lines = 1 << (max(floor-1, 0));
int first_spaces = (1 << floor) - 1;
int between_spaces = (1 << (floor+1)) - 1;
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces);
// print the 'level' level
vector<TreeNode*> new_nodes;
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
for(; it != nodes.end(); ++it){
if(*it != NULL){
cout << (*it)->val;
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->left);
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->right);
}
else{
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
cout << " ";
}
PrintWhiteSpaces(between_spaces);
}
cout << endl;
// print the following /s and \s
for(int i=1; i<= endge_lines; ++i){
for(int j=0; j<nodes.size(); ++j){
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces - i);
if(nodes[j] == NULL){
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines + i + 1);
continue;
}
if(nodes[j]->left != NULL)
cout << "/";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(i+i-1);
if(nodes[j]->right != NULL)
cout << "\\";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines - i);
}
cout << endl;
}
PrintNode(new_nodes, level+1, max_level);
}
// wrapper function
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root)
{
int max_level = MaxLevel(root);
vector<TreeNode*> nodes;
nodes.push_back(root);
PrintNode(nodes, 1, max_level);
}
int main()
{
TreeNode *root(NULL);
root = new TreeNode(1);
root->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->right = new TreeNode(3);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(4);
root->right->right = new TreeNode(7);
root->left->left->left = new TreeNode(8);
root->left->left->right = new TreeNode(9);
PrintBinaryTree(root);
// root = Destroy(root);
return 0;
} 6.非遞迴實現二叉樹的前序中序後序遍歷
實現:
遞迴前序遍歷
void preorderRecursive(TreeNode *node){
if(node == NULL) return;
visit(node);
preorderRecursive(node->left);
preorderRecursive(node->right);
}非遞迴前序遍歷,用棧
void preorderRecursive(TreeNode *node){
stack<TreeNode*> s;
if(node!=NULL) s.push(node);
while(!s.empty()){
TreeNode *tmp = s.top();
s.pop();
visit(tmp);
if(tmp->right!=NULL) s.push(tmp->right);
if(tmp->left!=NULL) s.push(tmp->left);
}
}非遞迴中序遍歷,沒有左結點,則對結點進行訪問
void inorderRecursive(TreeNode *node){
stack<TreeNode*> s;
TreeNode *tmp = node;
while(!s.empty() || tmp!=NULL){
if(tmp!=NULL){
s.push(tmp);
tmp = tmp->left;
}
else{
tmp = s.top();
s.pop();
visit(tmp);
tmp = tmp->right;
}
}
}非遞迴後序遍歷,利用非遞迴前序遍歷進行轉化
void postorderRecursive(TreeNode *node){
stack<TreeNode *> sTraverse, sVisit;
if(node!=NULL) sTraverse.push(node);
while(!sTraverse.empty()){
Node *tmp = sTraverse.top();
sTraverse.pop();
sVisit.push(tmp);
// 先右結點
if(tmp->right != NULL) tmp = tmp->right;
// 後左結點
if(tmp->left != NULL) tmp = tmp->left;
}
while(!sVisit.empty()){
visit(sVisit.top());
sVisit.pop();
}
}7.二叉樹的深度
題目:輸入一棵二叉樹的根結點,求該樹的深度。
實現:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
int val;
TreeNode(int x=0)
: val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
};
// 核心程式碼
void searchDepth(TreeNode *root, int depth, int &maxDepth){
if(root==NULL){
if(depth>maxDepth)
maxDepth = depth;
return;
}
searchDepth(root->left, depth+1, maxDepth);
searchDepth(root->right, depth+1, maxDepth);
}
// 測試程式碼
TreeNode* CreateBinaryTree(int a[], int i, int n){
// 陣列中的值-1代表結點null
if(i>n-1 || a[i]==-1) return NULL;
TreeNode *p = new TreeNode(a[i]);
p->left = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+1, n);
p->right = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+2, n);
return p;
}
void Destory(TreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL) return ;
Destory(root->left);
Destory(root->right);
delete root;
}
int main(){
int tree[] = {10, 6, 14, 4, -1, -1, 16, -1, 3};
TreeNode* root = CreateBinaryTree(tree, 0, 9);
int max = 0;
searchDepth(root, 0, max);
cout<<max<<endl;
Destory(root);
return 0;
}
8.二叉樹兩個結點的最低共同父結點(LCP)
題目:
輸入二叉樹中的兩個結點,輸出這兩個結點在數中最低的共同父結點。
思路(遞迴):
1. 在左子樹查詢目標物件
2. 在右子樹查詢目標物件
a) 如果在左子樹中什麼都沒找到,則表明都在右子樹上,然後LCP是最早查詢的目標物件
b) 如果在左子樹中什麼都沒找到,則表明都在右子樹上,然後LCP是最早查詢的目標物件
c) 如果在左右子樹各找到一個,則表明LCP是根結點
實現:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
int val;
TreeNode(int x=0)
: val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
};
TreeNode* CreateBinaryTree(int a[], int i, int n){
// 陣列中的值-1代表結點null
if(i>n-1 || a[i]==-1) return NULL;
TreeNode *p = new TreeNode(a[i]);
p->left = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+1, n);
p->right = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+2, n);
return p;
}
void Destory(TreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL) return ;
Destory(root->left);
Destory(root->right);
delete root;
}
TreeNode* GetLCP(TreeNode *root, TreeNode *n1, TreeNode *n2){
if(root==NULL || n1==NULL || n2==NULL) return NULL;
if(n1==root || n2==root) return root;
// 在左子樹上找n1或n2
TreeNode* leftSub = GetLCP(root->left, n1, n2);
// 在右子樹上找n1或n2
TreeNode* rightSub = GetLCP(root->right, n1, n2);
if(leftSub==NULL){// n1和n2都不能在左子樹找到,則返回右子樹中率先遇到n1或n2的結點
return rightSub;
}
else if(rightSub==NULL){
return leftSub;
}
else{// n1和n2分別在左右子樹上,所以返回根結點
return root;
}
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8};
TreeNode *root = CreateBinaryTree(arr, 0, 8);
/*
1
2 3
4 5 6 7
8
*/
TreeNode *n1 = root->left->left->left;
TreeNode *n2 = root->left->right;
TreeNode *result = GetLCP(root, n1, n2);
cout<<result->val<<endl;
Destory(root);
} 9.Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
題目:
Given a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (ie, from left to right, then right to left for the next level and alternate between).
For example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7return its zigzag level order traversal as:
[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]實現:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
void zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> r1;
stack<TreeNode*> r2;
r1.push(root);
while(r1.empty()==false || r2.empty()==false) {
while(!r1.empty()) {
TreeNode* e = r1.front();
cout<<e->val<<" ";
if(e->left!=NULL) r2.push(e->left);
if(e->right!=NULL) r2.push(e->right);
r1.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
while(!r2.empty()) {
TreeNode* e = r2.top();
cout<<e->val<<" ";
if(e->left!=NULL) r1.push(e->left);
if(e->right!=NULL) r1.push(e->right);
r2.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
int main() {
TreeNode *n1 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode *n2 = new TreeNode(9);
TreeNode *n3 = new TreeNode(20);
TreeNode *n4 = new TreeNode(15);
TreeNode *n5 = new TreeNode(7);
n1->left = n2;
n1->right = n3;
n3->left = n4;
n3->right = n5;
zigzagLevelOrder(n1);
}10.Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
題目:
Given preorder and inorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree.
Note:
You may assume that duplicates do not exist in the tree.
For example, given
preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Return the following binary tree:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7思路
實現:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(-1), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
TreeNode* helper(vector<int>& preorder, int preI, int preJ, vector<int>& inorder, int inI, int inJ) {
if(preI > preJ || inI > inJ) return NULL;
int rootVal = preorder[preI];
int rootIndex = 0;
for(int i=inI;i<=inJ;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == rootVal) {
rootIndex = i;
break;
}
}
TreeNode* newNode = new TreeNode(rootVal);
int lLen = rootIndex - inI;
int rLen = inJ - rootIndex;
newNode->left = helper(preorder, preI+1, preI+lLen, inorder, inI, rootIndex-1);
newNode->right = helper(preorder, preI+lLen+1, preJ, inorder, rootIndex+1, inJ);
return newNode;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
return helper(preorder, 0, preorder.size()-1, inorder, 0, inorder.size()-1);
}
// 列印二叉樹
TreeNode* Array2BinaryTree(int arr[], int i, int j){
if(i>j) return NULL;
int mid = (i+j)/2;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode;
root->val = arr[mid];
root->left = Array2BinaryTree(arr, i, mid-1);
root->right = Array2BinaryTree(arr, mid+1, j);
return root;
}
// 列印二叉樹
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root);
static int MaxLevel(TreeNode *root)
{
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return max(MaxLevel(root->left), MaxLevel(root->right)) + 1;
}
// test whether all elements in vector are NULL
static bool IsAllElementsNULL(const vector<TreeNode*> &nodes)
{
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
while(it != nodes.end()){
if(*it) return false;
++it;
}
return true;
}
static void PrintWhiteSpaces(int num)
{
for(int i=0; i<num; ++i)
cout << " ";
}
void PrintNode(vector<TreeNode*> &nodes, int level, int max_level)
{
if(nodes.empty() || IsAllElementsNULL(nodes)) return; // exit
int floor = max_level - level;
int endge_lines = 1 << (max(floor-1, 0));
int first_spaces = (1 << floor) - 1;
int between_spaces = (1 << (floor+1)) - 1;
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces);
// print the 'level' level
vector<TreeNode*> new_nodes;
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
for(; it != nodes.end(); ++it){
if(*it != NULL){
cout << (*it)->val;
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->left);
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->right);
}
else{
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
cout << " ";
}
PrintWhiteSpaces(between_spaces);
}
cout << endl;
// print the following /s and \s
for(int i=1; i<= endge_lines; ++i){
for(int j=0; j<nodes.size(); ++j){
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces - i);
if(nodes[j] == NULL){
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines + i + 1);
continue;
}
if(nodes[j]->left != NULL)
cout << "/";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(i+i-1);
if(nodes[j]->right != NULL)
cout << "\\";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines - i);
}
cout << endl;
}
PrintNode(new_nodes, level+1, max_level);
}
// wrapper function
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root)
{
int max_level = MaxLevel(root);
vector<TreeNode*> nodes;
nodes.push_back(root);
PrintNode(nodes, 1, max_level);
}
int main() {
int preArr[] = {3, 9, 20, 15, 7};
int inArr[] = {9, 3, 15, 20, 7};
vector<int> preorder(preArr, preArr+5);
vector<int> inorder(inArr, inArr+5);
TreeNode* root = buildTree(preorder, inorder);
PrintBinaryTree(root);
return 0;
}
二叉查詢樹
1.把一個有序整數陣列轉化為二叉查詢樹
思路:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
int val;
TreeNode(int x=0)
: val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
};
TreeNode* Array2BinaryTree(int arr[], int i, int j){
if(i>j) return NULL;
int mid = (i+j)/2;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode;
root->val = arr[mid];
root->left = Array2BinaryTree(arr, i, mid-1);
root->right = Array2BinaryTree(arr, mid+1, j);
return root;
}
// 列印二叉樹
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root);
static int MaxLevel(TreeNode *root)
{
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return max(MaxLevel(root->left), MaxLevel(root->right)) + 1;
}
// test whether all elements in vector are NULL
static bool IsAllElementsNULL(const vector<TreeNode*> &nodes)
{
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
while(it != nodes.end()){
if(*it) return false;
++it;
}
return true;
}
static void PrintWhiteSpaces(int num)
{
for(int i=0; i<num; ++i)
cout << " ";
}
void PrintNode(vector<TreeNode*> &nodes, int level, int max_level)
{
if(nodes.empty() || IsAllElementsNULL(nodes)) return; // exit
int floor = max_level - level;
int endge_lines = 1 << (max(floor-1, 0));
int first_spaces = (1 << floor) - 1;
int between_spaces = (1 << (floor+1)) - 1;
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces);
// print the 'level' level
vector<TreeNode*> new_nodes;
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
for(; it != nodes.end(); ++it){
if(*it != NULL){
cout << (*it)->val;
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->left);
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->right);
}
else{
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
cout << " ";
}
PrintWhiteSpaces(between_spaces);
}
cout << endl;
// print the following /s and \s
for(int i=1; i<= endge_lines; ++i){
for(int j=0; j<nodes.size(); ++j){
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces - i);
if(nodes[j] == NULL){
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines + i + 1);
continue;
}
if(nodes[j]->left != NULL)
cout << "/";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(i+i-1);
if(nodes[j]->right != NULL)
cout << "\\";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines - i);
}
cout << endl;
}
PrintNode(new_nodes, level+1, max_level);
}
// wrapper function
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root)
{
int max_level = MaxLevel(root);
vector<TreeNode*> nodes;
nodes.push_back(root);
PrintNode(nodes, 1, max_level);
}
int main(){
int test1[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int test2[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
TreeNode *root1 = Array2BinaryTree(test1, 0, 4);
PrintBinaryTree(root1);
TreeNode *root2 = Array2BinaryTree(test2, 0, 5);
PrintBinaryTree(root2);
return 0;
} 其他:
非遞迴實現。
堆
1.隊伍晉級
題目:
n 支隊伍比賽,分別編號為 0, 1, 2, …, n-1,已知它們之間的實力對比關係,
儲存在一個二維陣列 w[n][n]中,w[i][j] 的值代表編號為 i,j 的隊伍中更強的一支。
所以 w[i][j]=i 或者 j,現在給出它們的出場順序,並存儲在陣列 order[n]中,
比如 order[n] = {4, 3, 5, 8, 1……},那麼第一輪比賽就是 4 對 3, 5 對 8,…….
勝者晉級,敗者淘汰,同一輪淘汰的所有隊伍排名不再細分,即可以隨便排,
下一輪由上一輪的勝者按照順序,再依次兩兩比,比如可能是 4 對 5,直至出現第一名
程式設計實現,給出二