spring技術內幕筆記:IoC容器初始化過程(2)- BeanDefinition的載入
Spring版本:4.3.8.RELEASE
BeanDefinition載入過程,相當於把定義的BeanDefinition在IoC容器中轉換成一個Spring內部表示的資料結構的過程。IoC容器對Bean的管理和依賴注入功能的實現,就是通過對其持有的BeanDefinition進行的各種相關操作完成的。這些BeanDefinition資料在IoC容器中通過HashMap來儲存和維護。
從DefaultListableBeanFactory的設計入手,看一下IoC容器載入BeanDefinition的過程。
1、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
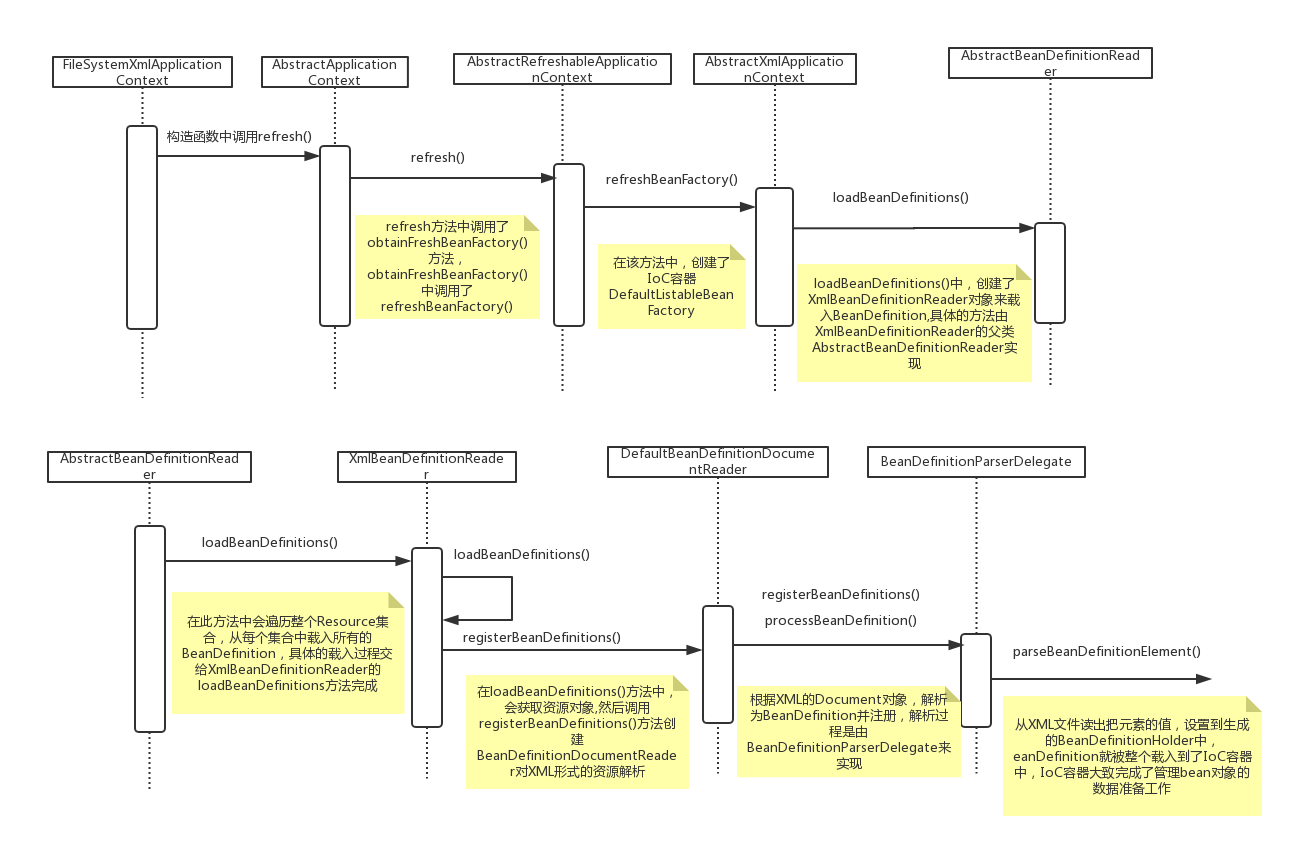
從FileSystemXmlApplicationContext開始,在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的建構函式FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)中呼叫了refresh方法
refresh()方法,啟動了對BeanDefinition資源定位的過程,由AbstractApplicationContext實現public class FileSystemXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractXmlApplicationContext { public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext() { } public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) { super(parent); } /** * 建構函式:需要傳入XML資原始檔的路徑 */ public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException { this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null); } /** * 建構函式:傳入多個資原始檔 */ public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException { this(configLocations, true, null); } /** * 建構函式 * @param configLocations 資原始檔陣列 * @param parent 雙親IoC容器 */ public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { this(configLocations, true, parent); } /** * 建構函式 * @param configLocations 資原始檔路徑 * @param refresh 是否呼叫refresh方法載入BeanDefinition */ public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh) throws BeansException { this(configLocations, refresh, null); } /** * 建構函式 * @param configLocations 資原始檔路徑 * @param refresh 是否呼叫refresh方法載入BeanDefinition * @param parent 雙親IoC容器 * @throws BeansException */ public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { super(parent); setConfigLocations(configLocations); if (refresh) { refresh();//分析容器初始化的一個重要入口 } } /** * 通過資原始檔路徑獲取Resource物件,返回的是一個FileSystemResource物件,通過這個物件可以進行相關I/O操作,完成BeanDefinition定位 * @param path 資原始檔路徑 * @return Resource spring中的資源物件 */ @Override protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) { if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) { path = path.substring(1); } return new FileSystemResource(path); } }
2、AbstractApplicationContext
refresh()方法中,呼叫了obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法,obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法又呼叫了refreshBeanFactory方法,在AbstractApplicationContext中,該方法是一個抽象方法,具體的實現由AbstractApplicationContext的子類AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext來實現。@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // 呼叫obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } } protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { refreshBeanFactory();//呼叫了refreshBeanFactory()方法 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); } return beanFactory; } //由子類AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext實現 protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
3、AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
/**
* AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中實現的refreshBeanFactory()方法
*
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
//如果已經建立了BeanFactory,銷燬並關閉BeanFactory
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//構造了一個BeanFactory,這裡使用DefaultListableBeanFactory實現
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//載入BeanDefinition
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
/**
* 建立DefaultListableBeanFactory的地方
* getInternalParentBeanFactory()的具體實現可以參看AbstractApplicationContext的實現
*
* @return
*/
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() {
return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
}
/**
* 抽象方法,載入BeanDefinition,由子類AbstractXmlApplicationContext實現
*
* @param beanFactory
* @throws BeansException
* @throws IOException
*/
protected abstract void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException, IOException;
}loadBeanDefinitions方法由AbstractXmlApplicationContext類實現
4、AbstractXmlApplicationContextpublic abstract class AbstractXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext {
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
//建立XmlBeanDefinitionReader物件,通過回撥設定到BeanFactory中,beanFactory使用的也是DefaultListableBeanFactory
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
//設定ResourceLoader,因為DefaultResourceLoader是父類,所以this可以直接被呼叫
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
//啟動Bean定義資訊載入的過程,委託給BeanDefinitionReader完成
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
//XmlBeanDefinitionReader物件載入BeanDefinition
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
protected void initBeanDefinitionReader(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) {
reader.setValidating(this.validating);
}
/**
* 載入BeanDefinition
* @param reader
* @throws BeansException
* @throws IOException
*/
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
//以Reource的方式獲取配置檔案的資源位置
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
//呼叫loadBeanDefinitions方法,該方法在XmlBeanDefinitionReader的父類AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中已經實現
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
//以string方式獲取配置檔案的位置
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
} 5、AbstractBeanDefinitionReader
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinitionReader implements EnvironmentCapable, BeanDefinitionReader {
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//如果Resource為空,停止BeanDefinition的載入,否則啟動載入BeanDefinition的過程
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
//對載入Bean的數量進行統計
int counter = 0;
//遍歷整個Resource集合,從每個集合中載入所有的BeanDefinition
for (Resource resource : resources) {
//loadBeanDefinitions方法是一個介面方法,在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中有具體的實現
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
return counter;
}
}在AbstractBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法中,又呼叫了XmlBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法。
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
//(1)入口
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//呼叫載入以XML形式的BeanDefinition的方法,並使用Resource物件建立EncodedResource物件
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
/**
* (2)載入以XML形式的BeanDefinition的方法
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
//獲取資源物件set集合
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
//將當前的資源物件加入set集合
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
//獲取資源物件的輸入流,得到XML檔案
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
//建立InputSource準備進行讀取
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
//設定編碼
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
//具體的讀取過程在doLoadBeanDefinitions方法
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
//移除已經讀取過的資源物件
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
/**
* (3)具體載入BeanDefinition的方法
* 從特定的XML檔案中實際載入BeanDefinition的地方
*/
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//取得XML檔案的Document物件
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
//啟動的是對BeanDefinition解析的詳細過程,會使用到spring的bean配置規則
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
/**
* (4)BeanDefinition解析的詳細過程
* 按照Spring的Bean語義要求進行解析資原始檔並轉換為內部的資料結構BeanDefinition
*/
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//建立BeanDefinitionDocumentReader對XML形式的BeanDefinition進行解析
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
//具體的解析過程在registerBeanDefinitions方法中完成,該方法在DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader中有實現
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
//對載入Bean的數量進行統計
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
/**
* (5)建立BeanDefinitionDocumentReader物件
*
*/
protected BeanDefinitionDocumentReader createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader() {
return BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class.cast(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.documentReaderClass));
}
//使用DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader對XML形式的BeanDefinition進行解析
private Class<?> documentReaderClass = DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class;
}7、DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader
public class DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader implements BeanDefinitionDocumentReader {
/**
* (1)根據XML的Document物件,解析為BeanDefinition
*/
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
//獲取根節點
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
//註冊每一個BeanDefinition
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
/**
* (2)根據根節點註冊每一個BeanDefinition
*/
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
//用於解析BeanDefinition的委託類
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
//在開始處理bean定義之前,允許XML通過處理任何自定義元素型別進行擴充套件
preProcessXml(root);
//從根元素開始解析
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
/**
* (3)從根元素開始解析BeanDefinition
* @param root the DOM root element of the document
*/
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
//獲取根節點的所有子節點
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
//遍歷根節點的子節點集合
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
//如果是預設的元素
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
//解析預設元素
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
//解析自定義元素
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
/**
* (4)解析預設的元素(import、alias、bean、beans)
*/
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
//import
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}//alias
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}//bean
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
//處理元素
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}//beans
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// 遞迴
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
/**
* (5)處理給定的Element元素,解析BeanDefinition並註冊
*/
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
/* BeanDefinition的解析結果由BeanDefinitionHolder來持有,BeanDefinitionHolder是BeanDefinition的封裝類,封裝了
* BeanDefinition的名字和別名,用它來完成向IoC容器的註冊
* 解析過程是由BeanDefinitionParserDelegate來實現,根據XML元素資訊對Spring的bean規則進行解析
*/
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// 向IoC容器註冊解析得到的BeanDefnition
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// 註冊完成後,傳送訊息
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
}8、BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
public class BeanDefinitionParserDelegate {
/**
* (1)解析XML元素
*/
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele) {
return parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, null);
}
/**
* (2)解析元素的詳細過程,並返回BeanDefinitionHolder物件
*/
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
//獲取<bean>元素中定義的id、name和aliase屬性的值
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);//id
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);//name
//aliases
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<String>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
String beanName = id;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
//引發對Bean元素的詳細解析
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
// Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,
// if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix.
// This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility.
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}
/**
* (3)對BeanDefinition定義元素的處理,具體生成BeanDefinition的地方
*/
與<bean>定義相關的。
(1)以解析屬性Property的方法為例,看一下整個BeanDefinition載入過程
/**
* 對指定Bean元素的<property>子元素集合進行解析
*/
public void parsePropertyElements(Element beanEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
//獲取元素下所有的節點
NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, PROPERTY_ELEMENT)) {
//判斷是<property>元素後對<property>元素進行解析
parsePropertyElement((Element) node, bd);
}
}
}
/**
* 解析<property>元素
*/
public void parsePropertyElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) {
//獲取<property>的name屬性
String propertyName = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(propertyName)) {
error("Tag 'property' must have a 'name' attribute", ele);
return;
}
this.parseState.push(new PropertyEntry(propertyName));
try {
//如果同一個Bean中已經有同名的property存在,則不進行解析,也就是同一個Bean中有相同的property,起作用的是第一個
if (bd.getPropertyValues().contains(propertyName)) {
error("Multiple 'property' definitions for property '" + propertyName + "'", ele);
return;
}
//解析<property>值的地方,解析結果會封裝到PropertyValue中,然後設定到BeanDefinitionHolder中
Object val = parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, propertyName);
PropertyValue pv = new PropertyValue(propertyName, val);
parseMetaElements(ele, pv);
pv.setSource(extractSource(ele));
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(pv);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
/**
* 獲取<property>元素的值
*/
public Object parsePropertyValue(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, String propertyName) {
String elementName = (propertyName != null) ?
"<property> element for property '" + propertyName + "'" :
"<constructor-arg> element";
// Should only have one child element: ref, value, list, etc.
NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes();//獲取子節點,應該只有一個子元素,ref、value、list等
Element subElement = null;
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT) &&
!nodeNameEquals(node, META_ELEMENT)) {
// Child element is what we're looking for.
if (subElement != null) {
error(elementName + " must not contain more than one sub-element", ele);
}
else {
subElement = (Element) node;
}
}
}
//是否有ref屬性
boolean hasRefAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
//是否有value屬性
boolean hasValueAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
if ((hasRefAttribute && hasValueAttribute) ||
((hasRefAttribute || hasValueAttribute) && subElement != null)) {
error(elementName +
" is only allowed to contain either 'ref' attribute OR 'value' attribute OR sub-element", ele);
}
//如果是ref屬性
if (hasRefAttribute) {
String refName = ele.getAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error(elementName + " contains empty 'ref' attribute", ele);
}
//建立一個ref的資料物件RuntimeBeanReference,這個物件封裝了ref資訊
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}//如果是value
else if (hasValueAttribute) {
//建立TypedStringValue物件,封裝value資訊
TypedStringValue valueHolder = new TypedStringValue(ele.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE));
valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return valueHolder;
}//如果還有子元素,觸發對子元素的解析
else if (subElement != null) {
return parsePropertySubElement(subElement, bd);
}
else {
// Neither child element nor "ref" or "value" attribute found.
error(elementName + " must specify a ref or value", ele);
return null;
}
}(2)對<property>元素解析的過程
/**
* 解析<property>元素的子元素
*/
public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) {
return parsePropertySubElement(ele, bd, null);
}
/**
* Parse a value, ref or collection sub-element of a property or
* constructor-arg element.
* @param ele subelement of property element; we don't know which yet
* @param defaultValueType the default type (class name) for any
* {@code <value>} tag that might be created
*/
public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, String defaultValueType) {
//如果元素沒有使用spring預設名稱空間,呼叫自定義元素解析方法
if (!isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
return parseNestedCustomElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {//如果是<bean>元素
BeanDefinitionHolder nestedBd = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, bd);
if (nestedBd != null) {
nestedBd = decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, nestedBd, bd);
}
return nestedBd;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, REF_ELEMENT)) {
// A generic reference to any name of any bean.
String refName = ele.getAttribute(BEAN_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean toParent = false;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
// A reference to the id of another bean in the same XML file.
refName = ele.getAttribute(LOCAL_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
// A reference to the id of another bean in a parent context.
refName = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
toParent = true;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
error("'bean', 'local' or 'parent' is required for <ref> element", ele);
return null;
}
}
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error("<ref> element contains empty target attribute", ele);
return null;
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName, toParent);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, IDREF_ELEMENT)) {//<idref>元素
return parseIdRefElement(ele);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, VALUE_ELEMENT)) {//<value>元素
return parseValueElement(ele, defaultValueType);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, NULL_ELEMENT)) {//<null>元素
// It's a distinguished null value. Let's wrap it in a TypedStringValue
// object in order to preserve the source location.
TypedStringValue nullHolder = new TypedStringValue(null);
nullHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return nullHolder;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, ARRAY_ELEMENT)) {//<array>元素
return parseArrayElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, LIST_ELEMENT)) {//<list>元素
return parseListElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, SET_ELEMENT)) {//<set>元素
return parseSetElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, MAP_ELEMENT)) {//<map>元素
return parseMapElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, PROPS_ELEMENT)) {//<props>元素
return parsePropsElement(ele);
}
else {
error("Unknown property sub-element: [" + ele.getNodeName() + "]", ele);
return null;
}
}
parseListElement為例:
/**
* 解析<list>元素
*/
public List<Object> parseListElement(Element collectionEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
String defaultElementType = collectionEle.getAttribute(VALUE_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
NodeList nl = collectionEle.getChildNodes();
ManagedList<Object> target = new ManagedList<Object>(nl.getLength());
target.setSource(extractSource(collectionEle));
target.setElementTypeName(defaultElementType);
target.setMergeEnabled(parseMergeAttribute(collectionEle));
//具體的解析過程
parseCollectionElements(nl, target, bd, defaultElementType);
return target;
}
/**
* 解析集合元素的具體過程
*/
protected void parseCollectionElements(
NodeList elementNodes, Collection<Object> target, BeanDefinition bd, String defaultElementType) {
//遍歷所有的元素節點
for (int i = 0; i < elementNodes.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = elementNodes.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT)) {
//加入到target中,target是一個ManagedList,同時觸發對下一層的呼叫
target.add(parsePropertySubElement((Element) node, bd, defaultElementType));
}
}
}
經過逐層解析,在XML檔案中定義的BeanDefinition就被整個載入到了IoC容器中,並在容器中建立的資料對映。在IoC容器中建立的對應的資料結構以AbstractBeanDefinition
為入口,讓IoC容器執行索引、查詢和操作。
經過以上的載入過程,IoC容器大致完成了管理bean物件的資料準備工作,但是,現在在IoC容器中存在的還只是靜態配置資訊,要完全發揮容器的作用,還需要完成資料向容器的註冊。
整體的流程:
相關推薦
spring技術內幕筆記:IoC容器初始化過程(2)- BeanDefinition的載入
Spring版本:4.3.8.RELEASEBeanDefinition載入過程,相當於把定義的BeanDefinition在IoC容器中轉換成一個Spring內部表示的資料結構的過程。IoC容器對Bean的管理和依賴注入功能的實現,就是通過對其持有的BeanDefiniti
spring技術內幕筆記:IoC容器的初始化過程(3)- BeanDefinition的註冊
Spring版本:4.3.8.RELEASE DefaultListableBeanFactory中,通過一個HashMap來持有和載入BeanDefinition,解析得到的BeanDefinition向IoC容器的beanDefinitionMap註冊過程 是在載入B
spring原始碼學習之路---深度分析IOC容器初始化過程(三)
分析FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的建構函式,到底都做了什麼,導致IOC容器初始化成功。 public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean ref
Spring原始碼解析--《SPRING技術內幕:深入解析Spring架構與設計原理》讀書筆記(一):IOC容器初始化過程
通過閱讀相關章節內容,Spring中IOC容器的載入中,我們需要了解下列幾個概念: Resource:是一個定位、訪問資源的抽象介面,包含了多種資源操作的基礎方法定義,如getInputStream()、exists()、isOpen()、getD
Spring技術內幕之IOC容器的實現(01)-IOC容器初始化過程
Spring IOC容器的初始化過程 Spring IOC容器的初始化過程主要包括BeanDefinition的Resouce定位/載入/註冊三個基本過程。Spring把這三個過程的實現分別放在不同的模組下,通過這樣的設計方式可以使使用者更加靈活地對這個三個過程進行裁剪和自
spring原始碼學習之路---IOC容器初始化要義之bean定義載入(四)
上章說到要帶各位去看看bean定義載入的要義,其實就是loadBeanDefinitions這個方法的具體實現步驟,下面我們跟隨這個方法去看下它到底是如何載入bean定義的。 上面是我擷取的實現了loadBeanDefinitions的類級別截圖,loadBeanDefinit
Spring原始碼解析-4、IOC容器初始化
IOC容器初始化的幾個步驟 IOC容器的初始化由以下三個步驟構成: 1、BeanDefinition的Resource定位 由ResourceLoader通過統一的Resource介面來完成,Resource對不同形式的BeanDefinition有統一的介面。 比如檔案系統中的Bean
【Spring】- IOC容器初始化過程
浪費了“黃金五年”的Java程式設計師,還有救嗎? >>>
OCR技術淺探 : 文字定位和文字切割(2)
文字定位 經過前面的特徵提取,我們已經較好地提取了影象的文字特徵,下面進行文字定位。 主要過程分兩步: 1、鄰近搜尋,目的是圈出單行文字; 2、文字切割,目的是將單行文字切割為單字。 鄰近搜尋 我們可以對提取的特徵圖進行連通區域搜尋,得到的每個連通區域視為一個漢字。 這對於大多數漢字來說是適用,但是對於一
手把手,嘴對嘴,講解UCOSII嵌入式操作系統的初始化過程(二)
同學 save sam 嵌入式操作系統 相關信息 trie allow 狀態 cos 本章重點講解空閑任務的建立過程。 任務建立函數定義如下: 1 INT8U OSTaskCreate (void (*task)(void *p_arg), 2
beanfactory中單例bean的初始化過程(一)
Date 10.06 pm Point 完成beanfactory中單例bean的初始化 beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons() 拿到所有的bean定義資訊(在 beanDefinitionNames中,遍歷list 獲取到bean的定義資訊 如果這個bean不是抽
spring學習筆記:ioc容器高階特性
Spring容器的高階特性涉及到屬性編輯器,使用外部屬性檔案,國際化,容器事件等等; 今天講解一下屬性編輯器,使用外部資源,國際化。 屬性編輯器 如果你沒有了解過屬性編輯器,建議你先google一下,我簡單的解釋一下什麼是屬性編輯器,看一個新寫的有代表性的bean:pack
spring技術內幕筆記1
springspring的設計目標(為什麽要用spring) 如果我們要簡要地描述Spring的設計目標,可以這麽說,Spring為開發者提供的是一個一站式的輕量級應用開發框架(平臺)。作為平臺,Spring抽象了我們在許多應用開發中遇到的共性問題;同時,作為一個輕量級的應用開發框架,Spring和傳統的J2
Spring源碼分析總結(一)-IOC容器初始化
Spring源碼分析總結一、IOC容器的初始化過程 IOC容器的初始化是由refresh()方法啟動。經常使用的ApplicationContext 有:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext、XmlWebApp
03.Spring IoC 容器 - 初始化
itl ret num servlet fontsize eat 圖片 number sources 基本概念 Spring IoC 容器的初始化過程在監聽器 ContextLoaderListener 類中定義。 具體由該類的的 configureAndRefreshWe
【spring原始碼分析】IOC容器初始化(二)
前言:在【spring原始碼分析】IOC容器初始化(一)中已經分析了匯入bean階段,本篇接著分析bean解析階段。 1.解析bean程式呼叫鏈 同樣,先給出解析bean的程式呼叫鏈: 根據程式呼叫鏈,整理出在解析bean過程中主要涉及的類和相關方法。 2.解析bean原始碼分
SPRING原理解析-Ioc容器初始化
IoC容器的初始化就是含有BeanDefinition資訊的Resource的定位、載入、解析、註冊四個過程,最終我們配置的bean,以beanDefinition的資料結構存在於IoC容器即記憶體中。這裡並不涉及bean的依賴注入,只是bean定義的載入。但
【Spring Framework 深入】—— IoC容器初始化 -> Bean定義資源的Resource定位
基本概念 ApplicationContext 繼承體系 本文主要關注ApplicationContext的繼承體系,至於BeanFactory的分支,以後再研究。 BeanFactory or ApplicationContext? Bea
Spring原始碼解讀-Spring IoC容器初始化之資源定位
**IoC初始化過程 首先spring IoC容器的初始化,要分成三大部分,BeanDefinition的 Resource定位、載入和註冊三個基本過程。 今天我要說的就是資原始檔的定位,IoC容
spring 原始碼分析--IOC容器初始化六
上一節將xml文件解析為DOM ,並且建立了一個 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate 型別的物件,在這一節,將使用這個物件來完成對bean的裝載工作。 2.1.1.1 parseBeanDefinitions (root, delegate): 該方法體完成註冊過程。